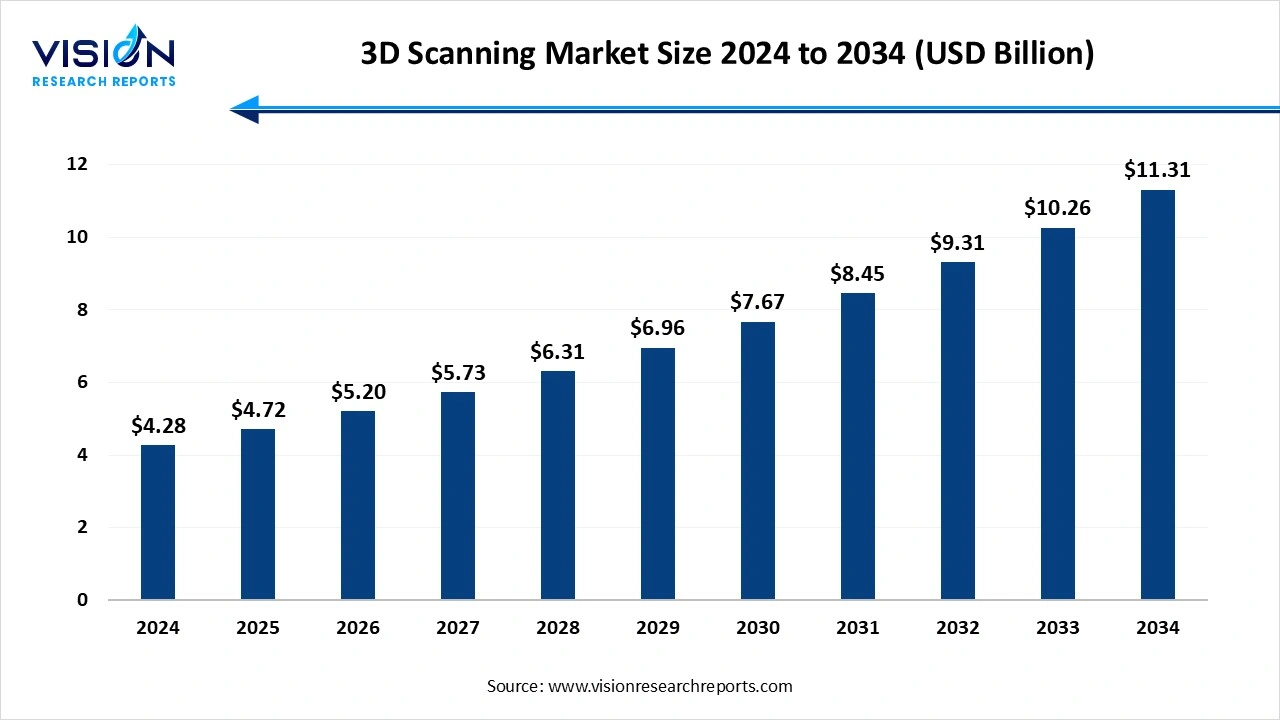
The global 3d scanning market size was surpassed at USD 4.28 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 11.31 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.20% from 2025 to 2034.
The global 3D scanning market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and increasing adoption across various industries such as automotive, healthcare, aerospace, and manufacturing. The ability to capture precise digital representations of physical objects has revolutionized product design, quality control, and reverse engineering processes. Innovations in laser scanning, structured light, and photogrammetry have enhanced the accuracy and speed of 3D scanning solutions, making them more accessible and cost-effective. Additionally, the rising demand for augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications further fuels market expansion.
The growth of the 3D scanning market is primarily driven by rapid technological advancements that have significantly improved the accuracy, speed, and affordability of scanning devices. Innovations such as laser triangulation, structured light scanning, and photogrammetry have made 3D scanning more accessible across diverse sectors. Industries like automotive, aerospace, and healthcare are increasingly leveraging these technologies for applications including quality inspection, reverse engineering, and custom prosthetics. Moreover, the integration of 3D scanning with complementary technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) is enhancing data processing capabilities and enabling real-time analytics, thereby boosting demand further.
Another key factor fueling market growth is the rising adoption of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing practices worldwide. Organizations are focusing on digital transformation to improve operational efficiency, reduce production costs, and accelerate product development cycles. 3D scanning plays a critical role in this ecosystem by enabling precise measurements and rapid prototyping.
North America dominates the global 3D scanning market, holding the largest share at 41% in 2024. The region benefits from strong infrastructure, advanced research and development activities, and a robust ecosystem of technology providers, contributing to rapid market adoption. Additionally, government initiatives supporting digital transformation and smart manufacturing further bolster the demand for 3D scanning solutions.
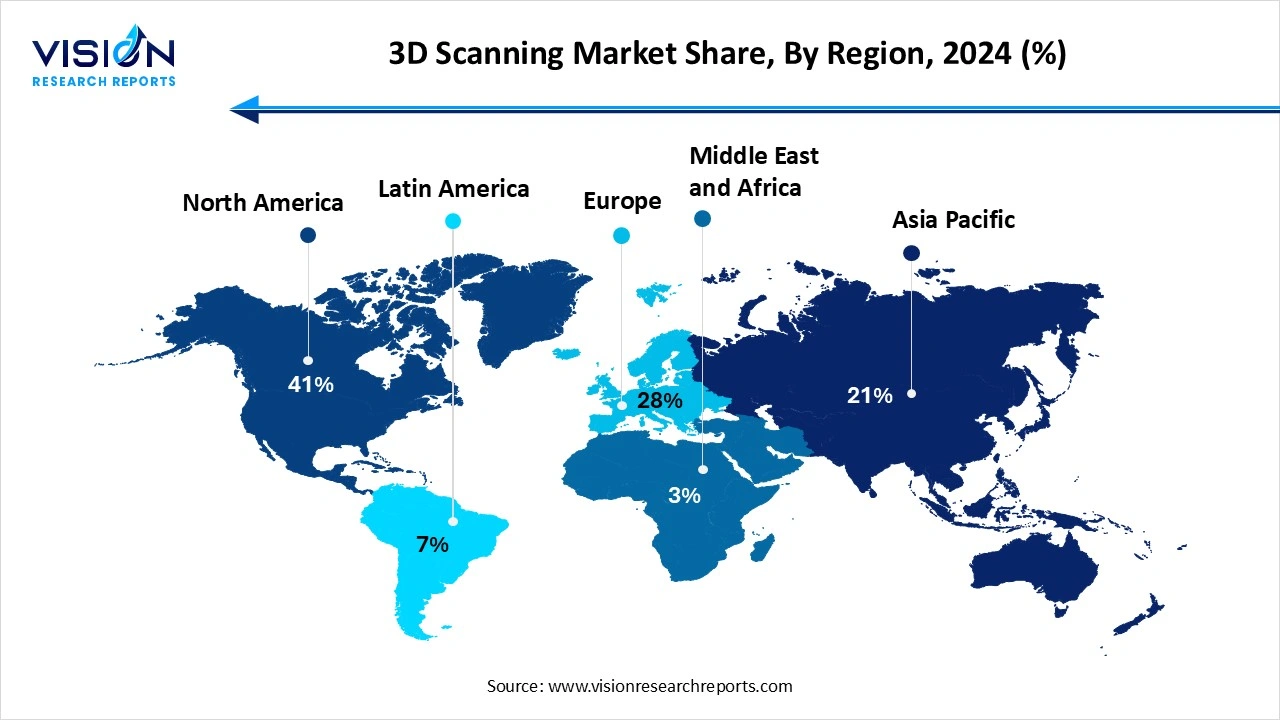 Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by rapid industrialization, expanding automotive and electronics manufacturing hubs, and increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure. Nations like China, Japan, and South Korea are at the forefront of adopting advanced 3D scanning technologies, supported by government initiatives promoting smart factories and digital innovation.
Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by rapid industrialization, expanding automotive and electronics manufacturing hubs, and increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure. Nations like China, Japan, and South Korea are at the forefront of adopting advanced 3D scanning technologies, supported by government initiatives promoting smart factories and digital innovation.
Laser scanners held the largest market share, accounting for 46% of the total segment in 2024. These scanners use laser beams to measure the exact shape and dimensions of an object, making them particularly useful in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction where accuracy is paramount. The capability of laser scanners to operate in various environmental conditions and capture complex geometries has driven their demand in quality control, reverse engineering, and large-scale infrastructure projects. Despite their relatively higher cost, the reliability and accuracy of laser scanners continue to make them a preferred choice for professional-grade applications.
optical scanners utilize structured light or photogrammetry techniques to create 3D representations by capturing multiple images or projecting patterns onto an object’s surface. Optical scanners are often favored for their speed, ease of use, and ability to capture color and texture details, making them ideal for applications in healthcare, entertainment, and cultural heritage preservation. These scanners tend to be more cost-effective and portable compared to laser-based systems, which has led to their growing adoption in fields requiring rapid and detailed surface scanning, such as dental modeling and animation. As technology advances, optical scanners are increasingly integrated with software enhancements that improve resolution and reduce scanning time, broadening their applicability across both industrial and consumer markets.
The short-range scanning segment held the largest market in 2024. Short-range 3D scanners are designed to capture highly detailed and precise data at close proximity, typically within a few centimeters to a few meters. These scanners are widely used in fields such as healthcare, manufacturing, and cultural heritage preservation, where fine detail and accuracy are critical. Short-range scanners are particularly effective for scanning small objects, intricate designs, and surfaces that require high-resolution outputs, such as dental molds, jewelry, and components in quality inspection processes.
long-range 3D scanners are engineered to measure objects and environments over much greater distances, often extending from several meters up to hundreds of meters. These scanners find extensive use in industries like construction, mining, aerospace, and infrastructure development, where capturing large-scale structures or terrains is essential. Long-range scanning technologies, often employing laser-based systems, enable detailed mapping and surveying of expansive areas, including buildings, bridges, and geological formations. The ability to quickly capture large volumes of data with precision makes long-range scanners invaluable for applications such as topographic surveys, site monitoring, and structural analysis.
The hardware segment has continued to lead the 3D scanning market, driven by strong demand for high-precision scanning equipment. Continuous advancements in sensor technology, miniaturization, and portability have led to more efficient and user-friendly hardware solutions, broadening their applications across industries like automotive, healthcare, aerospace, and manufacturing. The growing demand for high-precision scanning and the need to capture complex geometries are driving innovation and investment in hardware development, making it a key revenue generator within the 3D scanning market.
The software segment plays an equally vital role by providing the tools necessary to process, analyze, and visualize the raw data collected by hardware devices. Advanced software solutions enable the conversion of scanned data into usable 3D models, facilitate error correction, and support integration with other digital design and manufacturing systems. Software innovations focus on improving usability, enhancing data accuracy, and enabling real-time processing, which is essential for applications such as quality inspection, reverse engineering, and digital twin creation.
The global 3D scanning market includes a significant segment of tripod-mounted 3D scanners, which are widely recognized for their stability, precision, and suitability for capturing detailed data over larger objects or environments. These scanners are typically fixed on tripods to ensure minimal movement during the scanning process, which enhances accuracy, especially in applications such as architectural surveying, industrial inspection, and large-scale reverse engineering. Tripod-mounted scanners are favored in scenarios where high-resolution scans of static objects or environments are required, as their setup allows for comprehensive coverage and extended scanning sessions without operator-induced errors.
portable coordinate measuring machine (CMM)-based 3D scanners offer flexibility and mobility, making them ideal for on-site inspections, quality control, and maintenance tasks across various industries. These scanners combine the accuracy of traditional CMM technology with the convenience of portability, allowing users to measure objects in hard-to-reach or constrained spaces without relocating them to a dedicated measurement facility. Portable CMM-based scanners are especially valuable in manufacturing environments where speed and adaptability are critical, supporting processes such as assembly verification and dimensional analysis.
The laser triangulation technology segment in the global 3D scanning market is renowned for its precision and efficiency in capturing detailed surface geometries. This technology operates by projecting a laser beam onto the object and measuring the angle of the reflected light to calculate exact distances and create a 3D model. Laser triangulation is widely used in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and electronics for applications that require high accuracy, including quality inspection, reverse engineering, and dimensional analysis. Its capability to deliver rapid scanning with fine detail makes it suitable for scanning small to medium-sized objects.
laser pulse-based technology, also known as time-of-flight (ToF) scanning, measures the time it takes for a laser pulse to travel to the target and back to the sensor, enabling the capture of large-scale environments and distant objects. This method is particularly effective for long-range scanning applications such as topographic mapping, construction site monitoring, and infrastructure inspection. The ability of laser pulse-based scanners to cover extensive areas quickly while maintaining accuracy has made them indispensable in industries that require detailed spatial data over broad geographic regions.
The reverse engineering segment led the 3D scanning market in 2024. Reverse engineering stands out as a key application driving the growth of the global 3D scanning market. This process involves capturing the precise dimensions and geometry of an existing physical object to create accurate digital models. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing extensively use reverse engineering to replicate parts, improve product designs, and facilitate repairs or modifications without relying on original design documents. The precision offered by 3D scanning technology allows engineers to reconstruct complex components quickly and with high fidelity, significantly reducing time-to-market and development costs.
Virtual simulation is another transformative application that leverages 3D scanning technology to create realistic digital environments for testing and training purposes. By integrating scanned data into virtual models, industries like healthcare, automotive, and entertainment can simulate real-world scenarios without physical prototypes. This capability enhances decision-making by allowing users to visualize and analyze system behaviors under various conditions, reducing the need for costly physical trials. In healthcare, for instance, virtual simulation aids in pre-surgical planning and medical training, improving patient outcomes.
The 3D scanning market was primarily driven by the automotive industry in 2024. The automotive industry is one of the foremost end users driving the expansion of the global 3D scanning market. Automotive manufacturers utilize 3D scanning technology extensively throughout the vehicle design, development, and production processes. From capturing precise measurements for quality control to reverse engineering parts for prototyping and customization, 3D scanning enhances efficiency and accuracy. It enables rapid inspection of complex components, ensuring adherence to strict safety and performance standards.
In the healthcare sector, 3D scanning technology has revolutionized patient care, medical research, and device manufacturing. It is widely used for creating detailed anatomical models, aiding in diagnostics, surgical planning, and the production of customized implants and prosthetics. The ability to capture accurate, non-invasive 3D representations of the human body improves treatment outcomes and reduces procedural risks. Healthcare providers employ 3D scanning for applications such as dental modeling, orthopedics, and reconstructive surgery, where precision is critical.
By Product
By Range
By Component
By Type
By Technology
By Application
By End Use
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
5.1. Market Dynamics
5.1.1. Market Drivers
5.1.2. Market Restraints
5.1.3. Market Opportunities
5.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
5.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
5.2.3. Threat of substitute
5.2.4. Threat of new entrants
5.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 6. Competitive Landscape
6.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
6.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
6.1.3. Vendor Landscape
6.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
6.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 7. Global 3D Scanning Market, By Product
7.1. 3D Scanning Market, by Product
7.1.1. Laser Scanner
7.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
7.1.2. Structured Light Scanner
7.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
7.1.3. Optical Scanner
7.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
7.1.4. Others
7.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 8. Global 3D Scanning Market, By Range
8.1. 3D Scanning Market, by Range
8.1.1. Short-Range
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Medium Range
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Long-Range
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global 3D Scanning Market, By Component
9.1. 3D Scanning Market, by March
9.1.1. Hardware
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Software
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Services
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Global 3D Scanning Market, By Type
10.1. 3D Scanning Market, by Type
10.1.1. Tripod Mounted
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.2. Fixed CMM Based
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.3. Portable CMM Based
10.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.4. Desktop
10.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 11. Global 3D Scanning Market, By Technology
11.1. 3D Scanning Market, by Technology
11.1.1. Laser Triangulation
11.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.2. Pattern Fringe Triangulation
11.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.3. Laser Pulse Based
11.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.4. Laser Phase-shift Based
11.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 12. Global 3D Scanning Market, By Application
12.1. 3D Scanning Market, by Application
12.1.1. Reverse Engineering
12.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
12.1.2. Quality Control & Inspection
12.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
12.1.3. Virtual Simulation
12.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
12.1.4. Others
12.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 13. Global 3D Scanning Market, By End Use
13.1. 3D Scanning Market, by End Use
13.1.1. Automotive
13.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
13.1.2. Aerospace & Defense
13.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
13.1.3. Healthcare
13.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
13.1.4. Architecture & Construction
13.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
13.1.5. Education & Research
13.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
13.1.6. Media & Entertainment
13.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
13.1.7. Robotics & Automation
13.1.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
13.1.8. Others
13.1.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 14. Global 3D Scanning Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
14.1. North America
14.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.1.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.1.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.1.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.1.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.1.8. U.S.
14.1.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.1.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.1.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.1.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.1.8.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.1.8.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.1.8.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.1.9. Rest of North America
14.1.9.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.1.9.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.1.9.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.1.9.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.1.9.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.1.9.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.1.9.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.2. Europe
14.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.2.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.2.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.2.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.2.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.2.8. UK
14.2.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.2.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.2.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.2.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.2.8.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.2.8.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.2.8.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.2.9. Germany
14.2.9.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.2.9.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.2.9.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.2.9.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.2.9.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.2.9.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.2.9.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.2.10. France
14.2.10.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.2.10.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.2.10.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.2.10.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.2.10.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.2.10.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.2.10.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.2.11. Rest of Europe
14.2.11.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.2.11.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.2.11.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.2.11.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.2.11.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.2.11.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.2.11.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.3. APAC
14.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.3.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.3.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.3.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.3.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.3.8. India
14.3.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.3.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.3.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.3.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.3.8.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.3.8.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.3.8.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.3.9. China
14.3.9.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.3.9.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.3.9.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.3.9.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.3.9.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.3.9.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.3.9.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.3.10. Japan
14.3.10.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.3.10.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.3.10.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.3.10.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.3.10.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.3.10.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.3.10.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.3.11. Rest of APAC
14.3.11.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.3.11.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.3.11.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.3.11.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.3.11.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.3.11.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.3.11.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.4. MEA
14.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.4.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.4.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.4.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.4.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.4.8. GCC
14.4.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.4.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.4.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.4.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.4.8.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.4.8.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.4.8.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.4.9. North Africa
14.4.9.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.4.9.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.4.9.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.4.9.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.4.9.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.4.9.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.4.9.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.4.10. South Africa
14.4.10.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.4.10.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.4.10.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.4.10.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.4.10.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.4.10.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.4.10.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.4.11. Rest of MEA
14.4.11.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.4.11.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.4.11.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.4.11.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.4.11.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.4.11.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.4.11.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.5. Latin America
14.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.5.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.5.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.5.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.5.8. Brazil
14.5.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.5.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.5.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.5.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.5.8.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.5.8.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.5.8.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
14.5.9. Rest of LATAM
14.5.9.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
14.5.9.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Range
14.5.9.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by March
14.5.9.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
14.5.9.5. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
14.5.9.6. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
14.5.9.7. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
Chapter 15. Company Profiles
15.1. FARO Technologies, Inc.
15.1.1. Company Overview
15.1.2. Product Offerings
15.1.3. Financial Performance
15.1.4. Recent Initiatives
15.2. Hexagon AB
15.2.1. Company Overview
15.2.2. Product Offerings
15.2.3. Financial Performance
15.2.4. Recent Initiatives
15.3. Nikon Corporation
15.3.1. Company Overview
15.3.2. Product Offerings
15.3.3. Financial Performance
15.3.4. Recent Initiatives
15.4. Creaform (a subsidiary of AMETEK, Inc.)
15.4.1. Company Overview
15.4.2. Product Offerings
15.4.3. Financial Performance
15.4.4. Recent Initiatives
15.5. Trimble Inc.
15.5.1. Company Overview
15.5.2. Product Offerings
15.5.3. Financial Performance
15.5.4. Recent Initiatives
15.6. Carl Zeiss AG
15.6.1. Company Overview
15.6.2. Product Offerings
15.6.3. Financial Performance
15.6.4. Recent Initiatives
15.7. Artec 3D
15.7.1. Company Overview
15.7.2. Product Offerings
15.7.3. Financial Performance
15.7.4. Recent Initiatives
15.8. Shining 3D
15.8.1. Company Overview
15.8.2. Product Offerings
15.8.3. Financial Performance
15.8.4. Recent Initiatives
15.9. 3D Systems, Inc.
15.9.1. Company Overview
15.9.2. Product Offerings
15.9.3. Financial Performance
15.9.4. Recent Initiatives
15.10. Leica Geosystems (part of Hexagon AB)
15.10.1. Company Overview
15.10.2. Product Offerings
15.10.3. Financial Performance
15.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 16. Research Methodology
16.1. Primary Research
16.2. Secondary Research
16.3. Assumptions
Chapter 17. Appendix
17.1. About Us
17.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others