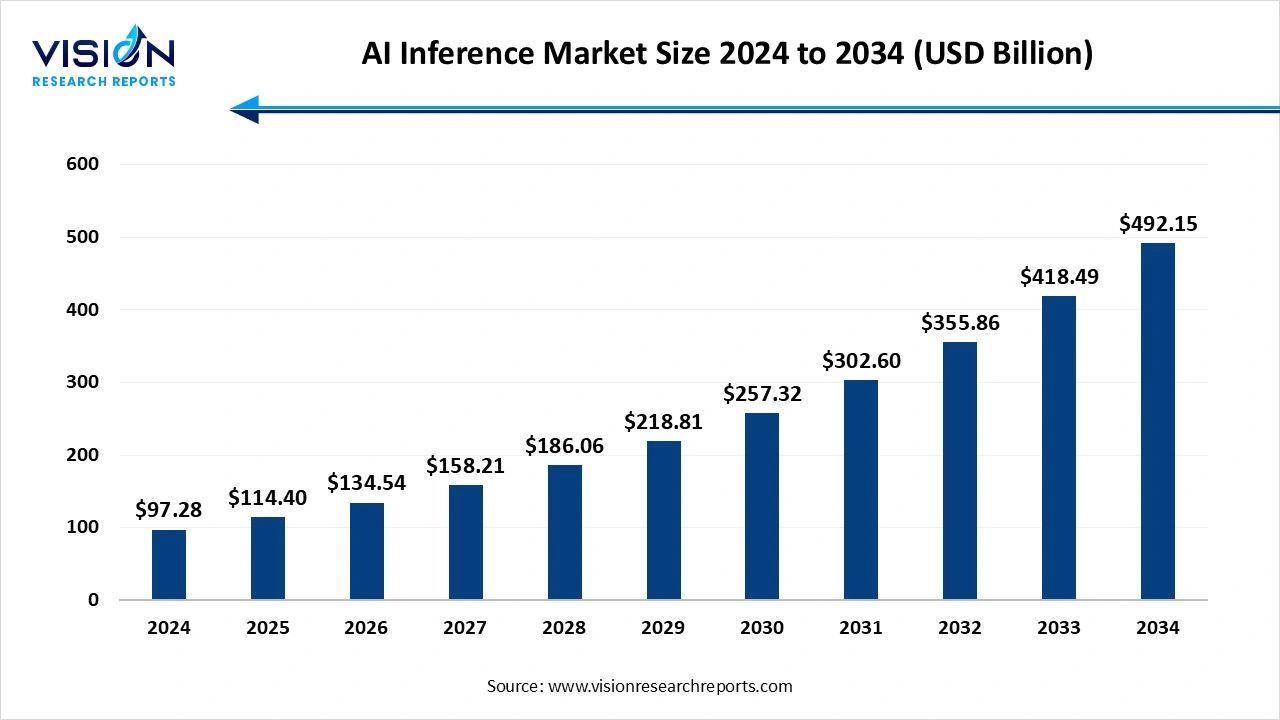
The global AI inference market size was surpassed at USD 97.28 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 492.15 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 17.60% from 2025 to 2034.
The AI inference market is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing deployment of AI models in real-world applications such as autonomous vehicles, healthcare diagnostics, fraud detection, and personalized recommendations. Inference the process of running trained machine learning models to make predictions is becoming more efficient due to advances in specialized hardware like GPUs, TPUs, and AI accelerators, edge computing, and model optimization techniques. As organizations prioritize low-latency, real-time decision-making, demand for scalable, cost-effective inference solutions is surging. Major tech players and emerging startups alike are innovating across hardware, software, and cloud platforms to capture market share, making the AI inference landscape highly competitive and dynamic.
One of the primary growth drivers of the AI inference market is the increasing adoption of AI-powered applications across industries such as healthcare, automotive, finance, retail, and manufacturing. Businesses are leveraging AI for tasks like real-time image and speech recognition, predictive analytics, and automation, all of which rely heavily on fast and accurate inference capabilities. As enterprises move AI workloads from centralized data centers to the edge closer to where data is generated there is growing demand for low-latency, energy-efficient inference solutions. This shift is fueling investments in edge AI chips and devices that can perform inference tasks locally with minimal reliance on cloud infrastructure.
Another significant factor is the rapid development of optimized hardware and software designed to accelerate inference performance. Leading semiconductor companies are creating specialized AI accelerators and processors tailored for high-throughput, low-power inference operations. At the same time, advancements in neural network compression, quantization, and pruning techniques are enabling more efficient model deployment without sacrificing accuracy. These innovations are reducing the computational cost of inference, making it more accessible to a broader range of applications and industries.
North America led the global AI inference market, accounting for a 39% share in 2024. The region's significant investments in research and development have accelerated advancements in AI inference technologies, enabling the development of highly efficient and scalable solutions. Key sectors such as healthcare, automotive, finance, and information technology have been early adopters, leveraging AI inference to improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and unlock new revenue streams. Additionally, North America benefits from a mature and expansive cloud infrastructure, complemented by a well-established ecosystem of semiconductor manufacturers, software developers, and service providers
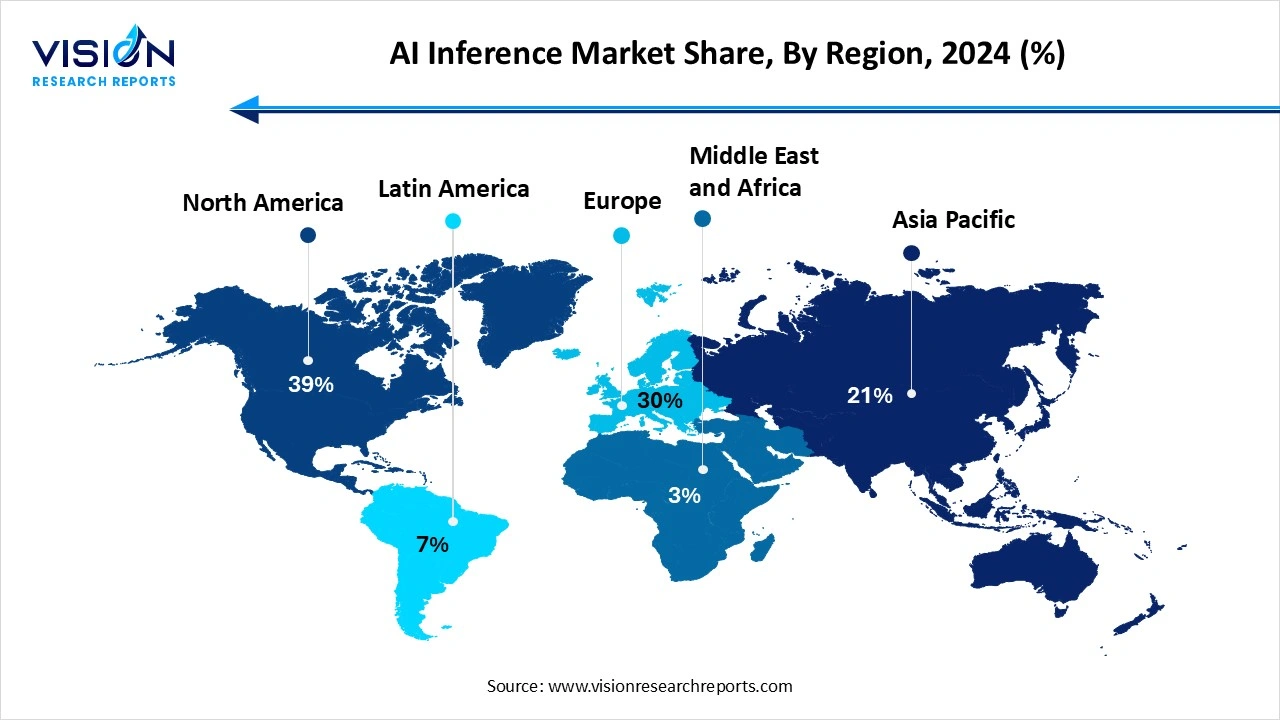 In the Asia-Pacific region, rapid economic growth, expanding digital infrastructure, and strong government initiatives in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are propelling the AI inference market forward. The region is witnessing a surge in AI applications across smart cities, telecommunications, retail, and autonomous systems. The availability of affordable hardware components and a large talent pool are enabling faster adoption of both cloud-based and edge inference solutions. Additionally, emerging markets within Asia-Pacific are beginning to embrace AI technologies, promising sustained growth in the coming years.
In the Asia-Pacific region, rapid economic growth, expanding digital infrastructure, and strong government initiatives in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are propelling the AI inference market forward. The region is witnessing a surge in AI applications across smart cities, telecommunications, retail, and autonomous systems. The availability of affordable hardware components and a large talent pool are enabling faster adoption of both cloud-based and edge inference solutions. Additionally, emerging markets within Asia-Pacific are beginning to embrace AI technologies, promising sustained growth in the coming years.
The High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) segment holds a commanding position in the AI inference market, accounting for 66% of total revenue. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) has gained prominence as a powerful solution for high-performance AI inference workloads. Designed to deliver exceptionally fast data transfer rates, HBM is particularly suited for scenarios where large datasets must be processed rapidly and efficiently. Its 3D-stacked architecture allows for close proximity to the processing unit, significantly reducing latency and energy consumption while increasing bandwidth. As AI models become increasingly complex requiring faster access to data and greater memory throughput HBM is becoming essential in high-end applications such as autonomous vehicles, large-scale natural language processing, and data center inference operations.
On the other hand, Double Data Rate (DDR) memory remains a widely adopted and cost-effective choice for a broad range of AI inference applications. DDR memory, including the latest DDR5 generation, offers substantial improvements in bandwidth and power efficiency compared to its predecessors, making it suitable for mid-tier AI workloads where performance needs are balanced against cost constraints. DDR technology is especially prevalent in enterprise servers, cloud infrastructures, and edge devices where scalability and affordability are crucial. While it may not match HBM in terms of speed and throughput, DDR provides sufficient performance for many AI inference tasks, particularly those with lower latency and bandwidth requirements.
The GPU segment generated the highest revenue among all segments in 2024. In the global AI inference market, compute units form the backbone of efficient and rapid processing of AI models, with Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) and Neural Processing Units (NPUs) emerging as key technologies. GPUs have long been the preferred choice for AI workloads due to their highly parallel architecture, which enables them to handle large volumes of matrix operations essential for neural network inference. Their versatility and mature ecosystem have made GPUs dominant in data centers and cloud-based AI services, where they deliver scalable and powerful inference performance.
Neural Processing Units (NPUs), on the other hand, represent a newer class of specialized accelerators designed specifically for AI inference tasks. Unlike general-purpose GPUs, NPUs are architected to optimize deep learning workloads with greater energy efficiency and lower latency, making them especially suitable for edge devices and mobile platforms. By tailoring their design to accelerate operations such as convolution and matrix multiplication, NPUs can deliver high performance within power and thermal constraints that GPUs may struggle to meet outside data centers. The rise of NPUs reflects the growing demand for on-device AI inference, where real-time processing, privacy, and reduced cloud dependency are critical.
The machine learning (ML) models segment dominated the market 2024. Machine learning inference involves applying trained models to make predictions or classify data in real time, and it remains foundational across numerous industries. From fraud detection in finance to predictive maintenance in manufacturing and personalized recommendations in retail, machine learning enables organizations to derive actionable insights efficiently. The widespread adoption of machine learning is supported by advances in hardware and software that optimize inference speed and accuracy, allowing businesses to automate decision-making processes and enhance operational efficiency.
Generative AI, a more recent and transformative application area, is reshaping the AI inference landscape by enabling systems to create content such as text, images, audio, and even code. Unlike traditional machine learning, generative AI models require complex inference computations to generate novel outputs based on learned patterns. This capability is unlocking new possibilities in creative industries, customer service automation, drug discovery, and virtual assistants. The surge in generative AI adoption is propelling demand for powerful inference solutions that can handle large model sizes and deliver real-time responses.
The IT and telecommunications sector segment dominated the market 2024. IT and telecommunications sector is a major contributor to the growth of the global AI inference market, driven by the increasing demand for intelligent network management, fraud detection, and customer experience enhancement. AI inference enables real-time data processing to optimize network traffic, predict maintenance needs, and automate service delivery, which is critical for handling the massive volumes of data generated by modern digital infrastructure. Telecommunications companies are leveraging AI-powered inference to improve the quality of service, enhance security protocols, and support emerging technologies like 5G and edge computing.
In the healthcare industry, AI inference is transforming patient care and operational efficiency by enabling rapid diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and predictive analytics. AI models deployed for medical imaging analysis, disease detection, and drug discovery require real-time inference capabilities to assist healthcare professionals in making timely, accurate decisions. The rise of wearable health devices and remote monitoring systems is further increasing the demand for edge inference solutions that can process sensitive patient data locally, ensuring privacy while delivering immediate insights.
By Memory
By Compute
By Application
By End Use
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on AI Inference Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: AI Inference Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global AI Inference Market, By Memory
8.1. AI Inference Market, by Memory
8.1.1. HBM (High Bandwidth Memory)
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. DDR (Double Data Rate)
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global AI Inference Market, By Compute
9.1. AI Inference Market, by Compute
9.1.1. GPU
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. CPU
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. FPGA
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.4. NPU
9.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.5. Others
9.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Global AI Inference Market, By Application
10.1. AI Inference Market, by Application
10.1.1. Generative AI
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.2. Machine Learning
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
10.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.4. Computer Vision
10.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.5. Others
10.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 11. Global AI Inference Market, By End Use
11.1. AI Inference Market, by End Use
11.1.1. BFSI
11.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.2. Healthcare
11.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.3. Retail and E-commerce
11.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.4. Automotive
11.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.5. IT and Telecommunications
11.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.5. Manufacturing
11.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.5. Security
11.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.5. Others
11.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 12. Global AI Inference Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
12.1. North America
12.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.1.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.1.5. U.S.
12.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.1.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.1.6. Rest of North America
12.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.1.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.1.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.1.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.2. Europe
12.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.2.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.2.5. UK
12.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.2.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.2.6. Germany
12.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.2.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.2.7. France
12.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.2.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.2.8. Rest of Europe
12.2.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.2.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.2.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.2.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.3. APAC
12.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.3.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.3.5. India
12.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.3.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.3.6. China
12.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.3.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.3.7. Japan
12.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.3.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.3.8. Rest of APAC
12.3.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.3.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.3.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.3.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.4. MEA
12.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.4.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.4.5. GCC
12.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.4.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.4.6. North Africa
12.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.4.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.4.7. South Africa
12.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.4.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.4.8. Rest of MEA
12.4.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.4.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.4.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.4.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.5. Latin America
12.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.5.5. Brazil
12.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.5.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.5.6. Rest of LATAM
12.5.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Memory
12.5.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Compute
12.5.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
12.5.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
Chapter 13. Company Profiles
13.1. NVIDIA Corporation
13.1.1. Company Overview
13.1.2. Product Offerings
13.1.3. Financial Performance
13.1.4. Recent Initiatives
13.2. Intel Corporation
13.2.1. Company Overview
13.2.2. Product Offerings
13.2.3. Financial Performance
13.2.4. Recent Initiatives
13.3. Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD)
13.3.1. Company Overview
13.3.2. Product Offerings
13.3.3. Financial Performance
13.3.4. Recent Initiatives
13.4. Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
13.4.1. Company Overview
13.4.2. Product Offerings
13.4.3. Financial Performance
13.4.4. Recent Initiatives
13.5. Google LLC
13.5.1. Company Overview
13.5.2. Product Offerings
13.5.3. Financial Performance
13.5.4. Recent Initiatives
13.6. Xilinx, Inc. (now part of AMD)
13.6.1. Company Overview
13.6.2. Product Offerings
13.6.3. Financial Performance
13.6.4. Recent Initiatives
13.7. Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
13.7.1. Company Overview
13.7.2. Product Offerings
13.7.3. Financial Performance
13.7.4. Recent Initiatives
13.8. Graphcore Ltd.
13.8.1. Company Overview
13.8.2. Product Offerings
13.8.3. Financial Performance
13.8.4. Recent Initiatives
13.9. MediaTek Inc.
13.9.1. Company Overview
13.9.2. Product Offerings
13.9.3. Financial Performance
13.9.4. Recent Initiatives
13.10. Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
13.10.1. Company Overview
13.10.2. Product Offerings
13.10.3. Financial Performance
13.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 14. Research Methodology
14.1. Primary Research
14.2. Secondary Research
14.3. Assumptions
Chapter 15. Appendix
15.1. About Us
15.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others