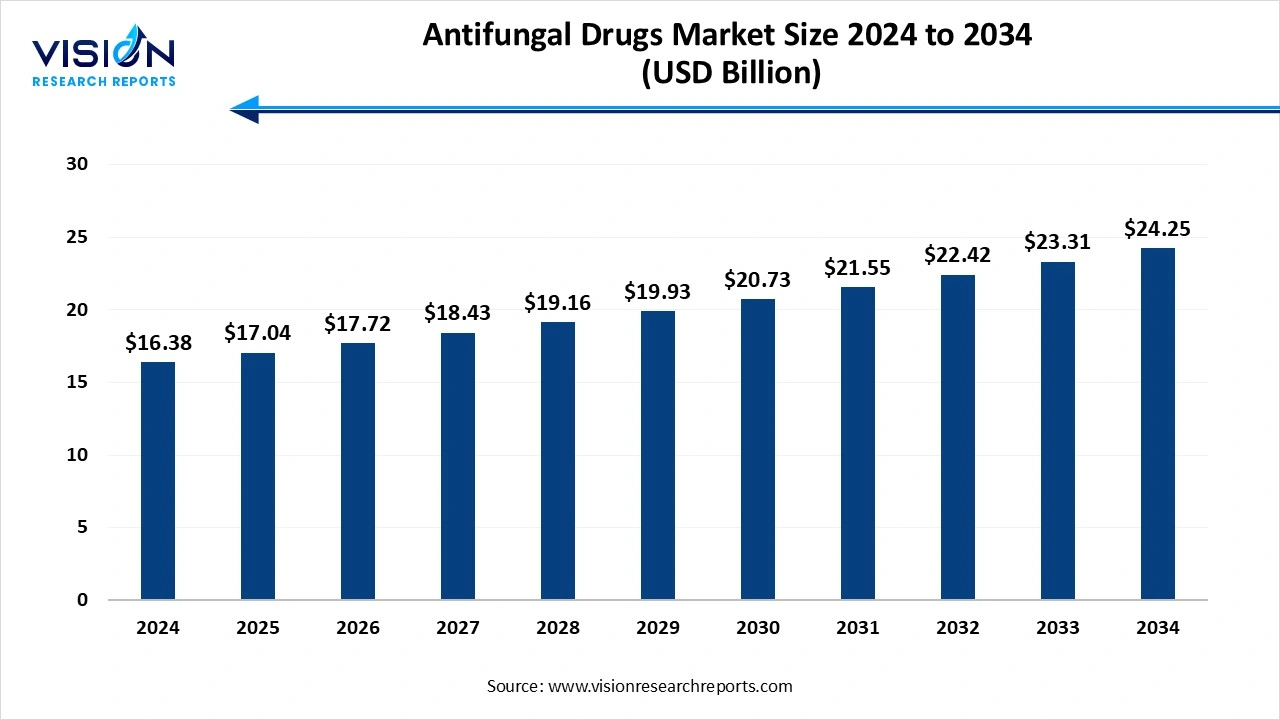
The global antifungal drugs market size was worth USD 16.38 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth approximately USD 17.04 billion in 2025, reaching USD 24.25 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4% over the forecast period. The rising prevalence of fungal infection, innovation in drug delivery systems, and growing immunocompromised populations fuel the market growth.
An antifungal drug is a medicine which are used to treat fungal infection, kill the fungal cells, or stop their growth. The global antifungal drug market growth is driven by the rising prevalence of fungal infections. People with weakened immune systems are highly susceptible to fungal infection. The rising chronic conditions, such as diabetes, contribute to a larger patient population vulnerable to fungal infections. Widespread or improper use of current antifungal drugs, including those used in agriculture, has accelerated the development of resistance. This creates an urgent demand for novel therapies with new mechanisms of action.
Innovation in drug development and diagnostic tools is helping to expand treatment options and improve patient outcomes. Advancements in drug delivery systems, such as extended-release tablets, liposomal formulations, and nanoparticle carriers, enhance the efficacy and safety of antifungal agents while improving patient adherence. Pharmaceutical companies are focused on developing new antifungal agents with novel mechanisms of action to combat drug-resistant strains and expand the range of therapeutic options.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 16.38 Billion |
| Revenue Forecast by 2034 | USD 24.25 Billion |
| Growth rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 4% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Regions | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Companies Covered | Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, Astellas Pharma Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Bayer AG, Merck & Co., Inc., Sanofi S.A., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd., and Abbott Laboratories. |
Drug-resistant infections are harder to treat, often requiring longer hospital stays, extensive monitoring, and the use of more expensive, less-effective, or more toxic second-line therapies. This increases the overall financial burden on patients and healthcare systems. Expansion in the immunocompromised population, reduced efficacy, a shift in drug classes, and the threat of resistance have spurred increased investment in research and development (R&D) for new antifungal drugs. Companies are working on agents with novel mechanisms of action to overcome the limitations of existing therapies.
The increasing emergence and spread of drug-resistant fungal strains, such as Candida auris, reduce the effectiveness of existing treatments and necessitate the continuous development of new antifungal agents.
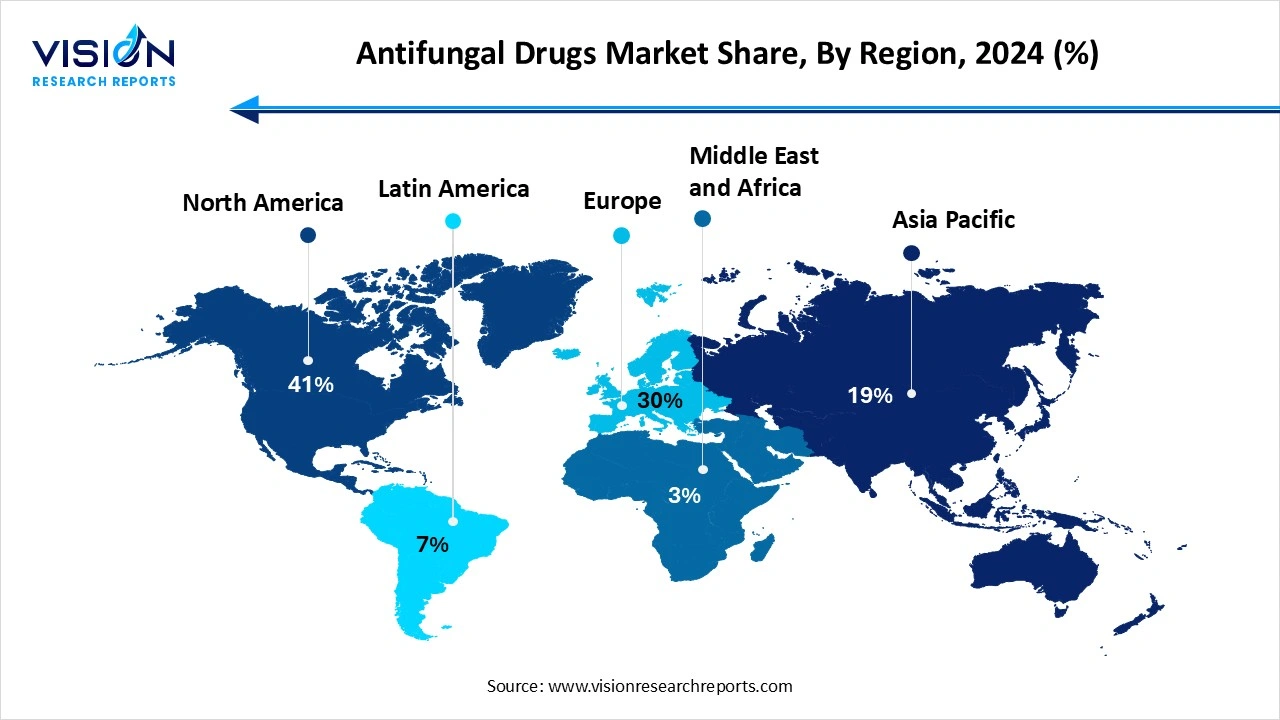
North America holds the largest share of the antifungal drugs market at 41% in 2024. The high incidence of fungal infections, particularly in immunocompromised populations, coupled with advanced healthcare infrastructure and significant investment in R&D, the region also benefits from supportive regulatory frameworks, including expedited FDA approval processes, which contribute to market growth.
United States Antifungal Drugs Market Trends
The increasing fungal infection, growing population undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplantation, and other immunosuppressant treatments, is increasing the demand for effective therapies. The development of resistance to existing drugs, especially azoles, is a major concern, as is the growing demand for novel and more potent antifungal agents. Rising awareness about fungal disease and improvements in diagnostic capabilities contribute to earlier detection and treatment.
Asia Pacific expects significant growth in the antifungal drugs market during the forecast period. There is a higher incidence of fungal infection, and advancement in economies in the region are expanding their healthcare infrastructure and improving patient access to medical services and medication, driving the demand. Increase healthcare awareness among professionals and the public about fungal infections, and local pharmaceutical manufacturers are increasing their production of generic antifungal drugs, which improves availability and affordability. Strategic partnerships with multinational companies are also facilitating the market entry of new drugs.
Why did the Azoles Drug Class Segment Dominate the Antifungal Drugs Market?
The azoles drug class segment led the market, capturing a revenue share of 48% in 2024. It has broad-spectrum efficacy against various fungal pathogens and a superior safety profile compared to older treatments like polyenes. The availability of diverse formulations and improved pharmacokinetics further bolsters their clinical utility and widespread adoption. While facing challenges like increasing drug resistance, Azoles remain the preferred and most commonly prescribed option for treating a wide range of fungal infections. Their established market history and use in both treatment and prophylactic care solidify their leading position within the antifungal drugs market.
The echinocandins segment is the fastest-growing in the Antifungal Drugs market during the forecast period. Their unique mechanism of action targets the fungal cell wall, which provides targeted and potent efficacy. This makes them a preferred first-line treatment for invasive fungal infections, especially in critically ill and immunocompromised patients. Their favorable safety profile, with fewer side effects and drug interactions compared to older antifungals, further boosts their market adoption.
How the Candidiasis Segment hold the Largest Share in the Antifungal Drugs Market?
The candidiasis segment held the largest revenue share in the Antifungal Drugs market in 2024. It has high prevalence across diverse patient populations, including both immunocompromised and healthy individuals. The market is driven by the need for treatments ranging from common superficial infections to severe, expensive-to-treat invasive forms. A growing incidence of antifungal resistance and high treatment costs further fuel demand for both new and existing therapies.
The aspergillosis segment is experiencing the fastest growth in the market during the forecast period. The growing incidence of invasive aspergillosis and improving fungal diagnostic technologies are enabling earlier and more accurate detection of invasive aspergillosis. Innovation of pharmaceutical firms in research and development of novel antifungal drugs and greater awareness of invasive healthcare providers and the public is leading to more proactive identification and treatment of the infections. Expansion in market access and awareness fuels the market growth.
How the Oral Drug Segment hold the Largest Share in the Antifungal Drugs Market?
The oral drug segment held the largest revenue share in the Antifungal Drugs market in 2024. The oral antifungal drugs are more effective against skin and nail infections, oral drugs are crucial for life-threatening fungal infections that have spread throughout the body. The oral dosage form is easy to administer and apply. Oral drugs, specifically tablets and capsules, are widely used in outpatient care and are a preferred option for healthcare providers due to their long shelf-life and stability. The convenience of at-home therapy continues to support strong market demand.
The ointment segment is experiencing the fastest growth in the market during the forecast period. The major infection occurred in the nails, skin, and hair. The ointment is directly applied to the infected area and is easy to apply. Many antifungal ointments are available over-the-counter (OTC) without a prescription. This accessibility, especially through retail and online pharmacies, allows consumers to self-treat common infections promptly and conveniently. Consumers are becoming more proactive about self-care and hygiene. The availability of effective and easy-to-use OTC ointments meets this demand, further boosting sales.
How the Hospital Pharmacies Segment hold the Largest Share in the Antifungal Drugs Market?
The hospital pharmacies segment held the largest revenue share in the antifungal drugs market in 2024. The hospitals are treating serious, life-threatening fungal infections. Hospitals provide immediate access to advanced, specialized antifungal treatments, including intravenous formulations. Hospitals often have formularies and centralized procurement systems that ensure consistent access to a wide range of antifungal drugs, including those that may be restricted to hospital use. The widespread use of chemotherapy, organ transplantation, and intensive care support in hospitals increases the risk of hospital-acquired fungal infections, further driving demand for antifungal drugs within these settings.
The retail pharmacies segment is experiencing the fastest growth in the market during the forecast period. The increased consumer access and convenience. Factors such as the rise of over-the-counter and topical treatments for common infections, growing self-medication trends, and the integration of online pharmacies contribute to this expansion. This shift in purchasing behavior for less severe cases away from hospitals further accelerates the growth of the retail segment.
By Drug Class
By Indication
By Dosage Form
By Distribution Channel
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Antifungal Drugs Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Antifungal Drugs Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Antifungal Drugs Market, By Drug Class
8.1. Antifungal Drugs Market, by Drug Class
8.1.1. Azoles
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Echinocandins
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Polyenes
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.4. Allylamines
8.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.5. Others
8.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global Antifungal Drugs Market, By Indication
9.1. Antifungal Drugs Market, by Indication
9.1.1. Dermatophytosis
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Aspergillosis
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Candidiasis
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.4. Others
9.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Global Antifungal Drugs Market, By Dosage Form
10.1. Antifungal Drugs Market, by Dosage Form
10.1.1. Oral Drugs
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.2. Ointments
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.3. Powders
10.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.4. Others
10.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 11. Global Antifungal Drugs Market, By Distribution Channel
11.1. Antifungal Drugs Market, by Distribution Channel
11.1.1. Hospital Pharmacies
11.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.2. Retail Pharmacies
11.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.3. Others
11.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 12. Global Antifungal Drugs Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
12.1. North America
12.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.1.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.1.5. U.S.
12.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.1.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.1.6. Rest of North America
12.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.1.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.1.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.1.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.2. Europe
12.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.2.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.2.5. UK
12.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.2.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.2.6. Germany
12.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.2.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.2.7. France
12.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.2.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.2.8. Rest of Europe
12.2.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.2.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.2.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.2.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.3. APAC
12.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.3.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.3.5. India
12.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.3.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.3.6. China
12.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.3.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.3.7. Japan
12.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.3.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.3.8. Rest of APAC
12.3.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.3.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.3.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.3.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.4. MEA
12.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.4.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.4.5. GCC
12.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.4.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.4.6. North Africa
12.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.4.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.4.7. South Africa
12.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.4.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.4.8. Rest of MEA
12.4.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.4.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.4.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.4.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.5. Latin America
12.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.5.5. Brazil
12.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.5.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
12.5.6. Rest of LATAM
12.5.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Drug Class
12.5.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Indication
12.5.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Dosage Form
12.5.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
Chapter 13. Company Profiles
13.1. Pfizer Inc.
13.1.1. Company Overview
13.1.2. Product Offerings
13.1.3. Financial Performance
13.1.4. Recent Initiatives
13.2. Novartis AG
13.2.1. Company Overview
13.2.2. Product Offerings
13.2.3. Financial Performance
13.2.4. Recent Initiatives
13.3. Astellas Pharma Inc.
13.3.1. Company Overview
13.3.2. Product Offerings
13.3.3. Financial Performance
13.3.4. Recent Initiatives
13.4. GlaxoSmithKline plc
13.4.1. Company Overview
13.4.2. Product Offerings
13.4.3. Financial Performance
13.4.4. Recent Initiatives
13.5. Bayer AG
13.5.1. Company Overview
13.5.2. Product Offerings
13.5.3. Financial Performance
13.5.4. Recent Initiatives
13.6. Merck & Co., Inc.
13.6.1. Company Overview
13.6.2. Product Offerings
13.6.3. Financial Performance
13.6.4. Recent Initiatives
13.7. Sanofi S.A.
13.7.1. Company Overview
13.7.2. Product Offerings
13.7.3. Financial Performance
13.7.4. Recent Initiatives
13.8. Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
13.8.1. Company Overview
13.8.2. Product Offerings
13.8.3. Financial Performance
13.8.4. Recent Initiatives
13.9. Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
13.9.1. Company Overview
13.9.2. Product Offerings
13.9.3. Financial Performance
13.9.4. Recent Initiatives
13.10. Abbott Laboratories
13.10.1. Company Overview
13.10.2. Product Offerings
13.10.3. Financial Performance
13.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 14. Research Methodology
14.1. Primary Research
14.2. Secondary Research
14.3. Assumptions
Chapter 15. Appendix
15.1. About Us
15.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others