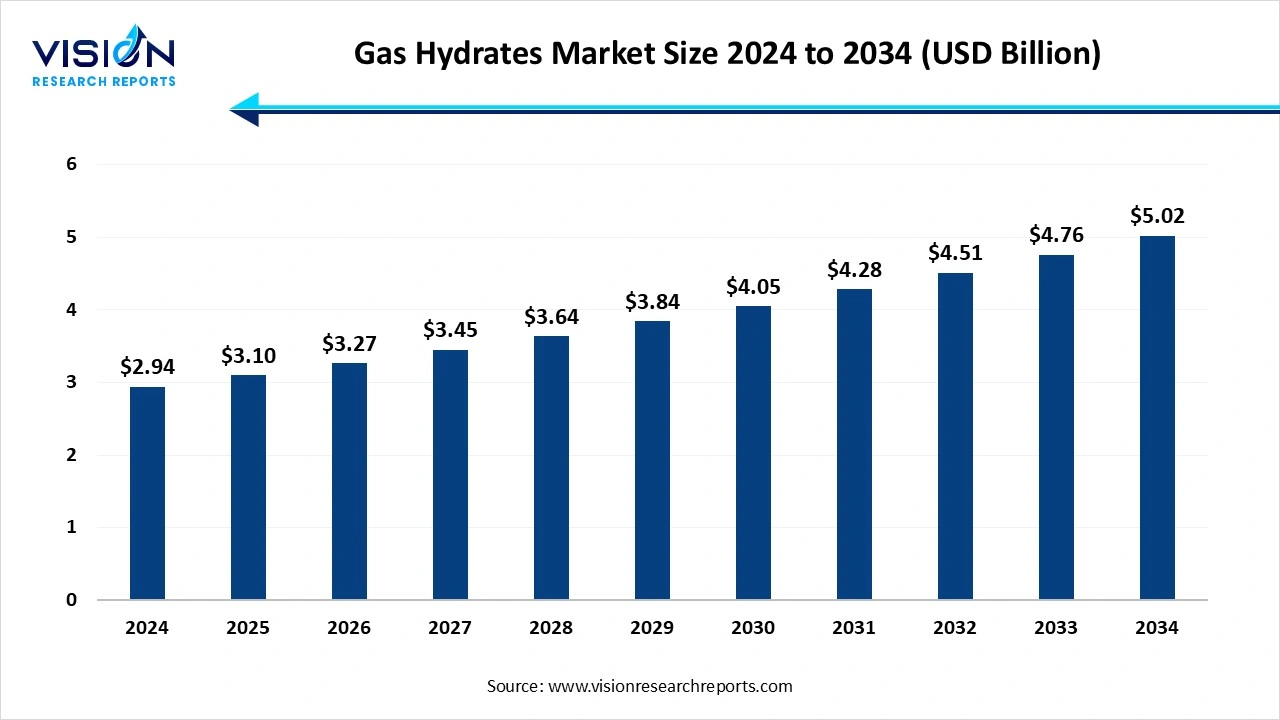
The global gas hydrates market size was valued at USD 2.94 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 5.02 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 5.50% from 2025 to 2034.
The global gas hydrates market is gaining significant momentum, driven by the growing interest in unconventional energy resources and the increasing demand for cleaner energy alternatives. Gas hydrates, crystalline ice-like compounds composed of water and natural gas, primarily methane, are found in deep-sea sediments and permafrost regions. As an abundant source of natural gas, gas hydrates hold immense potential for meeting future energy demands. Technological advancements in exploration and extraction methods, coupled with increasing government investments in research, are expected to propel market growth.
he gas hydrates market is primarily driven by the rising global demand for clean and sustainable energy sources. As countries strive to reduce carbon emissions and transition towards greener energy, gas hydrates—composed mainly of methane are gaining attention as a potential alternative to conventional fossil fuels. The abundance of gas hydrate reserves in offshore and permafrost regions offers a vast, untapped energy source.
Another critical growth factor is the increasing investment in research and development by governments and energy companies worldwide. Countries like Japan, India, and the United States have launched extensive research programs to explore and develop gas hydrate reserves, with successful pilot projects demonstrating the resource’s potential.
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the gas hydrates market driven by vast natural gas hydrate reserves, especially in countries like China, India, and Japan. These nations are actively exploring and investing in gas hydrate extraction technologies, with strong government support—Japan’s "Methane Hydrate Research and Development Project," China’s successful extraction in the South China Sea, and India’s National Gas Hydrate Program (NGHP) are prime examples. The region’s rapidly growing energy demand, coupled with technological advancements in exploration and extraction, further strengthens its leadership.The strategic location of numerous offshore basins enhances economic viability, making Asia-Pacific the clear leader in the global gas hydrates market.
The North American gas hydrates market is witnessing a significant shift driven by technological innovation and a strong emphasis on environmental sustainability. Industry players and research organizations are actively developing advanced extraction techniques, including depressurization and thermal stimulation, to enhance the efficiency and eco-friendliness of gas hydrate production.
The global gas hydrates market can be categorized based on the type of deposits, primarily divided into onshore gas hydrates and offshore/marine gas hydrates. Onshore gas hydrates are predominantly found in permafrost regions, such as the Arctic regions of Canada, Russia, and Alaska. These onshore deposits are relatively easier to access compared to their offshore counterparts due to the stability of permafrost environments. The ongoing shift toward more sustainable energy practices and reduced carbon emissions is further driving the potential for residential use, as natural gas from hydrates offers a cleaner alternative to coal and other fossil fuels.
In contrast, offshore or marine gas hydrates are primarily found in deep-sea sediments along continental margins. These reserves are significantly larger than onshore deposits, making them an attractive target for energy companies and governments. However, extracting gas hydrates from offshore locations presents several technical and environmental challenges. Deep-sea drilling, high-pressure conditions, and the risk of seabed destabilization are some of the critical issues that need to be addressed. Despite these challenges, offshore gas hydrates are gaining considerable attention due to their vast potential. Major countries like Japan, India, and the United States have launched extensive research programs to explore and develop these offshore reserves.
The global gas hydrates market is increasingly being recognized for its potential applications in various sectors, particularly in residential energy use. Gas hydrates, which consist of methane gas trapped in ice-like structures, hold great promise as a sustainable and abundant source of energy. In residential applications, gas hydrates could serve as an alternative source of natural gas for heating, cooking, and other household energy needs. This is especially relevant in regions where traditional natural gas reserves are scarce or hard to access.
In the commercial sector, gas hydrates are garnering attention as a viable fuel source for various industrial applications. Methane, extracted from gas hydrates, can be utilized for power generation, industrial heating, and other commercial energy needs. This application has the potential to reduce reliance on traditional energy sources like coal and oil, which are not only environmentally harmful but also increasingly expensive. As global demand for cleaner fuels rises, methane extracted from gas hydrates could serve as an alternative fuel for transportation. Methane-powered vehicles, particularly in commercial fleets, are being explored for their reduced emissions and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional gasoline and diesel-powered vehicles. As research into gas hydrate extraction and storage technologies advances, the commercial and vehicle fuel applications of gas hydrates are expected to play a significant role in the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
By Grade
By ApplicationÂ
By RegionalÂ
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Gas Hydrates Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Gas Hydrates Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Gas Hydrates Market, By Grade
8.1. Gas Hydrates Market, by Grade
8.1.1. Onshore Gas Hydrates
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Offshore/Marine Gas Hydrates
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Gas Hydrates Market, By Application
9.1. Gas Hydrates Market, by Application
9.1.1. Residential
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Commercial
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Industrials
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.4. Vehicle Fuel
9.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.5. Energy
9.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Gas Hydrates Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
10.1. U.S.
10.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Grade
10.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1. Schlumberger Limited
11.1.1. Company Overview
11.1.2. Product Offerings
11.1.3. Financial Performance
11.1.4. Recent Initiatives
11.2. Halliburton Company
11.2.1. Company Overview
11.2.2. Product Offerings
11.2.3. Financial Performance
11.2.4. Recent Initiatives
11.3. ExxonMobil Corporation
11.3.1. Company Overview
11.3.2. Product Offerings
11.3.3. Financial Performance
11.3.4. Recent Initiatives
11.4. Japan Oil, Gas and Metals National Corporation (JOGMEC)
11.4.1. Company Overview
11.4.2. Product Offerings
11.4.3. Financial Performance
11.4.4. LTE Scientific
11.5. ConocoPhillips
11.5.1. Company Overview
11.5.2. Product Offerings
11.5.3. Financial Performance
11.5.4. Recent Initiatives
11.6. Mitsui Engineering & Shipbuilding Co., Ltd.
11.6.1. Company Overview
11.6.2. Product Offerings
11.6.3. Financial Performance
11.6.4. Recent Initiatives
11.7. Chevron Corporation
11.7.1. Company Overview
11.7.2. Product Offerings
11.7.3. Financial Performance
11.7.4. Recent Initiatives
11.8. Royal Dutch Shell plc
11.8.1. Company Overview
11.8.2. Product Offerings
11.8.3. Financial Performance
11.8.4. Recent Initiatives
11.9. PetroChina Company Limited
11.9.1. Company Overview
11.9.2. Product Offerings
11.9.3. Financial Performance
11.9.4. Recent Initiatives
11.10. TotalEnergies SE
11.10.1. Company Overview
11.10.2. Product Offerings
11.10.3. Financial Performance
11.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 12. Research Methodology
12.1. Primary Research
12.2. Secondary Research
12.3. Assumptions
Chapter 13. Appendix
13.1. About Us
13.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others