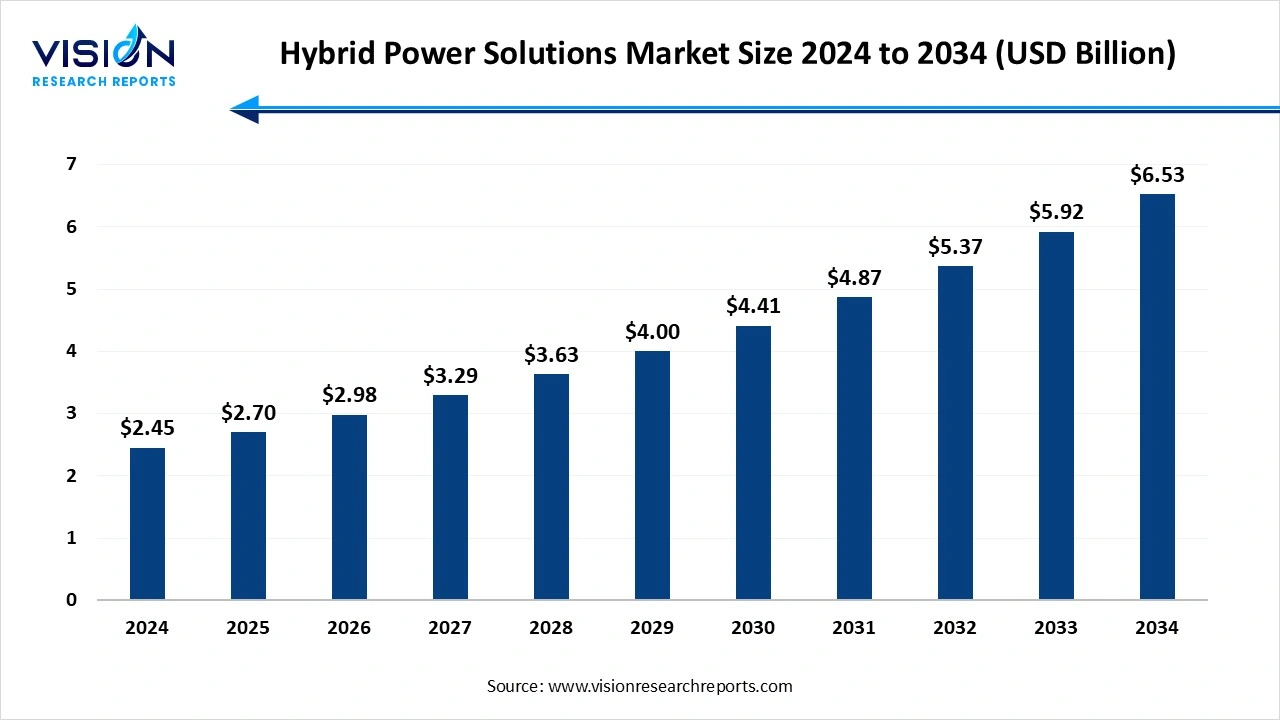
The global hybrid power solutions market size was estimated at USD 2.45 billion in 2024 and it is expected to surpass around USD 6.53 billion by 2034, poised to grow at a CAGR of 10.30% from 2025 to 2034.
The hybrid power solutions market is witnessing robust growth as industries and governments increasingly seek reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy alternatives. These systems, which combine two or more power sources such as solar, wind, diesel generators, and batteries, offer enhanced energy security and reduced carbon emissions. Their flexibility and scalability make them ideal for remote locations, telecom towers, off-grid applications, and temporary power needs in construction and mining sectors.
The growth of the hybrid power solutions market is primarily driven by the rising demand for reliable and uninterrupted power supply in off-grid and remote areas. These regions often lack stable grid infrastructure, making hybrid systems a cost-effective and efficient alternative. The growing deployment of telecom towers, particularly in developing regions, further contributes to demand, as hybrid systems ensure continuous operation with minimal fuel usage and maintenance. 
Government policies and incentives promoting clean energy also play a pivotal role in market expansion. Many countries are offering subsidies, tax benefits, and regulatory support to encourage the use of solar, wind, and other renewable sources within hybrid systems. Technological advancements, such as improved battery storage, advanced energy management systems, and smart grid integration, have enhanced the performance and reliability of hybrid power solutions. 
One of the key trends shaping the hybrid power solutions market is the growing integration of renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind, with advanced battery storage systems. This trend is being fueled by declining costs of solar panels and lithium-ion batteries, making hybrid systems more affordable and efficient. Moreover, the use of intelligent energy management systems that can optimize power generation, storage, and consumption is enhancing system performance and reducing operational costs.
Another significant trend is the increasing adoption of hybrid power solutions in mobile and temporary applications such as construction sites, disaster relief zones, and events. Portable and containerized hybrid systems are gaining popularity due to their ease of deployment, scalability, and ability to operate independently of grid power. Additionally, there is a rising focus on hybrid microgrids for community electrification and industrial usage, especially in regions prone to power outages.
Despite the promising growth, the hybrid power solutions market faces several key challenges that can hinder its expansion. One of the primary obstacles is the high initial capital investment required for setting up hybrid systems. Although operational costs are relatively low in the long run, the upfront expenses related to advanced components like batteries, inverters, and control systems can be a barrier for small- and medium-scale users, especially in developing countries.
Another challenge is the lack of standardized regulatory frameworks and policy support in many regions. Inconsistent government incentives and unclear grid interconnection policies can create uncertainty for investors and project developers. Moreover, in some areas, continued reliance on conventional energy subsidies can distort market competition, making it harder for hybrid systems to gain traction. Technical challenges such as maintaining system reliability, managing fluctuating renewable inputs, and ensuring seamless switching between sources further complicate adoption.
The Asia Pacific region led the global hybrid power solutions market, accounting for the largest revenue share of 43% in 2024. Countries like India, China, and Indonesia are investing heavily in hybrid systems to meet growing energy demands in off-grid and semi-urban areas. Government initiatives promoting rural electrification and subsidies for renewable energy integration have further accelerated market growth in this region.
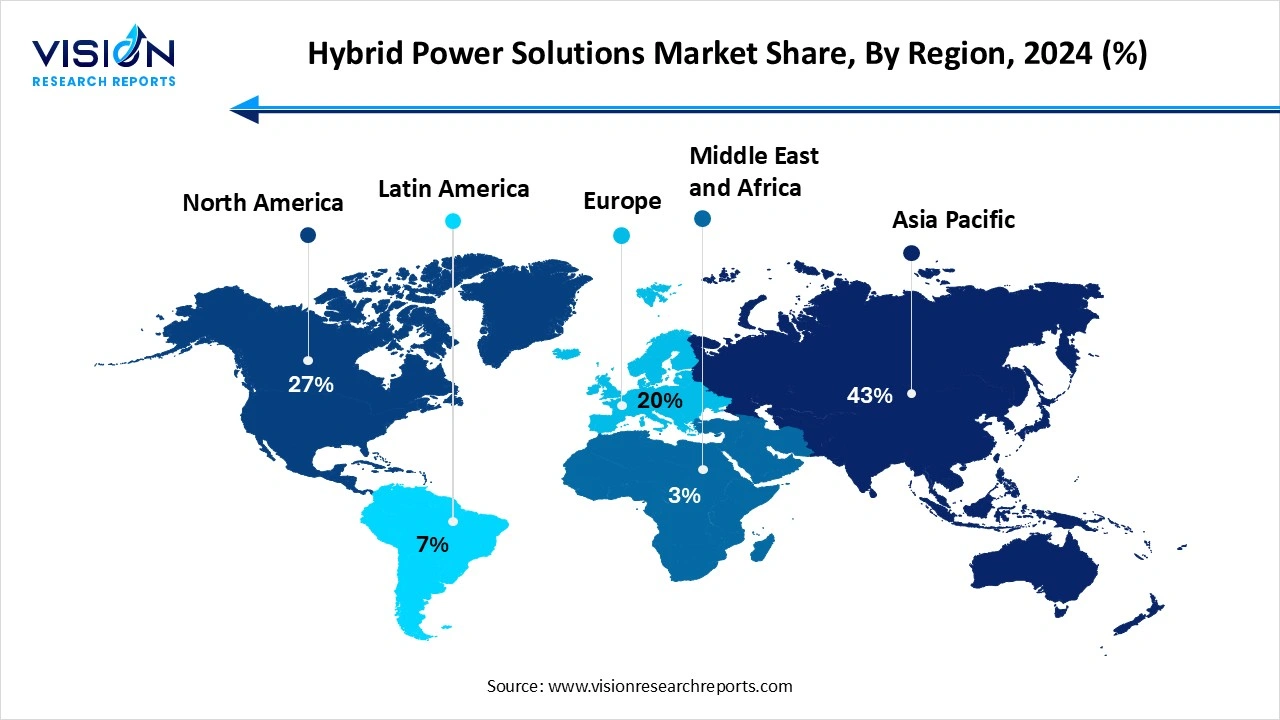 The North America hybrid power solutions market is projected to experience the fastest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.6% between 2025 and 2034. In North America, the United States and Canada are investing in hybrid systems for both commercial and industrial applications, particularly in regions prone to grid instability and harsh weather conditions. 
The North America hybrid power solutions market is projected to experience the fastest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.6% between 2025 and 2034. In North America, the United States and Canada are investing in hybrid systems for both commercial and industrial applications, particularly in regions prone to grid instability and harsh weather conditions. 
The solar-diesel systems led the market with a revenue share of 37% in 2024, driven by their superior efficiency and cost-effectiveness. These systems offer a reliable and economical power solution, making them especially suitable for remote and off-grid applications. These systems combine the reliability of diesel generators with the sustainability of solar power, offering an efficient solution for areas with inconsistent grid access or complete off-grid needs. Solar-diesel hybrid systems reduce fuel dependency and operational costs by offsetting diesel usage during daylight hours, leading to lower carbon emissions and enhanced fuel savings. 
The wind-diesel system segment is projected to experience notable growth, with a compound annual growth rate CAGR of 10.4% anticipated over the forecast period. Wind-diesel hybrid systems, on the other hand, are proving to be a reliable alternative in areas with strong and consistent wind resources. These systems integrate wind turbines with diesel generators to ensure a stable power supply, even during periods of low wind activity. Wind-diesel hybrids are especially suitable for island communities, remote coastal regions, and high-altitude locations where wind conditions are favorable.
The power ratings ranging from 11 kW to 100 kW dominated the market capturing a revenue share of 58% in 2024. These systems are particularly ideal for powering remote villages, telecom infrastructure, small industrial operations, and agricultural sites where moderate energy demand exists but reliable grid connectivity is lacking. The flexibility and relatively lower capital requirement of this power range make it an attractive choice for governments and private organizations focused on rural electrification and decentralized energy projects.
The power rating segment above 100 kW is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 10.3% throughout the forecast period. These high-capacity hybrid systems are engineered to meet substantial and continuous power demands while minimizing diesel consumption and reducing environmental impact. Increasing global efforts toward decarbonization, paired with the financial savings from reduced fuel usage over time, are prompting industries to invest in hybrid systems above 100 kW.
The commercial end users accounted for the largest revenue share, contributing 39% to the market in 2024. Commercial facilities such as office buildings, shopping complexes, educational institutions, and healthcare centers are increasingly adopting hybrid systems to ensure uninterrupted operations while reducing energy expenses and carbon footprints. The integration of renewable energy sources like solar or wind with backup diesel or battery storage systems provides a dependable power supply that supports sustainability goals and regulatory compliance.
The telecommunication segment is projected to record the second-highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.6% during the forecast period. With the rapid expansion of telecom infrastructure, especially in remote and off-grid locations, ensuring continuous power supply for network towers and data transmission equipment is critical. Hybrid systems combining renewable energy with diesel generators or batteries are increasingly used to power telecom towers, reducing fuel dependency and lowering operational costs. These solutions also support telecom companies’ objectives to improve energy efficiency and reduce emissions.
By System 
By Power Rating 
By End Use 
By Regional 
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution System Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Hybrid Power Solutions Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Hybrid Power Solutions Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Hybrid Power Solutions Market, By System
8.1. Hybrid Power Solutions Market, by System
8.1.1 Solar-Diesel
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Wind-Diesel
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Solar-Wind-Diesel
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.4. Others
8.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global Hybrid Power Solutions Market, By Power Rating
9.1. Hybrid Power Solutions Market, by Power Rating
9.1.1. Up to 10 kW
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. 11 kW-100 kW
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Above 100 kW
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Global Hybrid Power Solutions Market, By End Use
10.1. Hybrid Power Solutions Market, by End Use
10.1.1. Residential
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.2. Commercial
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.3. Telecommunication
10.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.4. Others
10.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 11. Global Hybrid Power Solutions Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
11.1. North America
11.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.1.4. U.S.
11.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.1.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.1.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.1.5. Rest of North America
11.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.2. Europe
11.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.2.4. UK
11.2.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.2.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.2.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.2.5. Germany
11.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.2.6. France
11.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.2.7. Rest of Europe
11.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.3. APAC
11.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.3.4. India
11.3.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.3.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.3.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.3.5. China
11.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.3.6. Japan
11.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.3.7. Rest of APAC
11.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.4. MEA
11.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.4.4. GCC
11.4.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.4.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.4.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.4.5. North Africa
11.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.4.6. South Africa
11.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.4.7. Rest of MEA
11.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.5. Latin America
11.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.5.4. Brazil
11.5.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.5.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.5.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.5.5. Rest of LATAM
11.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by System
11.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Power Rating
11.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1. Siemens AG
12.1.1. Company Overview
12.1.2. Product Offerings
12.1.3. Financial Performance
12.1.4. Recent Initiatives
12.2. General Electric (GE) Company
12.2.1. Company Overview
12.2.2. Product Offerings
12.2.3. Financial Performance
12.2.4. Recent Initiatives
12.3. Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
12.3.1. Company Overview
12.3.2. Product Offerings
12.3.3. Financial Performance
12.3.4. Recent Initiatives
12.4. SMA Solar Technology AG
12.4.1. Company Overview
12.4.2. Product Offerings
12.4.3. Financial Performance
12.4.4. Recent Initiatives
12.5. Eaton Corporation plc
12.5.1. Company Overview
12.5.2. Product Offerings
12.5.3. Financial Performance
12.5.4. Recent Initiatives
12.6. Aggreko PLC
12.6.1. Company Overview
12.6.2. Product Offerings
12.6.3. Financial Performance
12.6.4. Recent Initiatives
12.7. ZTE Corporation.
12.7.1. Company Overview
12.7.2. Product Offerings
12.7.3. Financial Performance
12.7.4. Recent Initiatives
12.8. Eltek (a Delta Group Company)
12.8.1. Company Overview
12.8.2. Product Offerings
12.8.3. Financial Performance
12.8.4. Recent Initiatives
12.9. HOMER Energy (a UL company).
12.9.1. Company Overview
12.9.2. Product Offerings
12.9.3. Financial Performance
12.9.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 13. Research Methodology
13.1. Primary Research
13.2. Secondary Research
13.3. Assumptions
Chapter 14. Appendix
14.1. About Us
14.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others