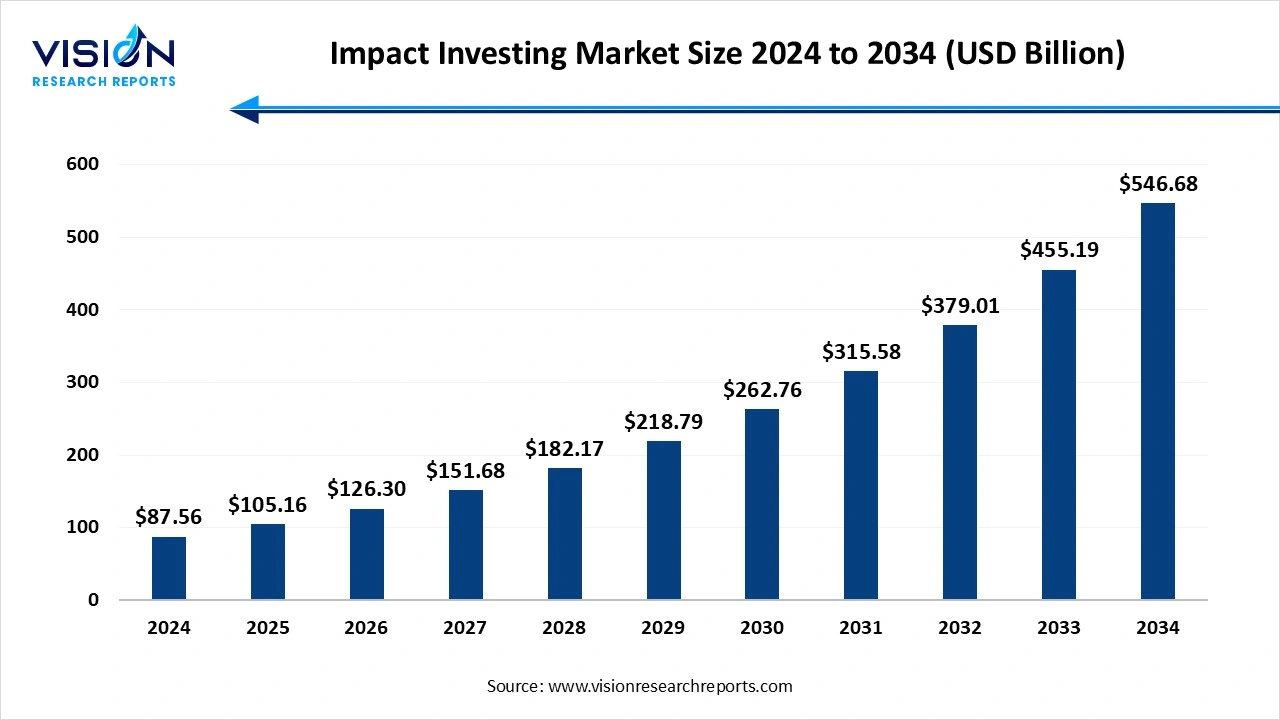
The global impact investing market size was estimated at around USD 87.56 billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 546.68 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 20.10% from 2025 to 2034.
 Key Pointers
Key PointersThe impact investing market is experiencing rapid expansion as investors increasingly seek to align financial returns with positive social and environmental outcomes. This investment approach directs capital toward companies, organizations, and funds that intentionally generate measurable impact alongside financial performance. Once a niche strategy, impact investing has evolved into a mainstream component of asset allocation, driven by rising global awareness of sustainability, equity, and climate change.Institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, and development finance institutions are fueling this momentum by integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria into their investment decisions.
One of the key growth drivers of the impact investing market is the increasing demand for responsible and sustainable investment options from both institutional and retail investors. As environmental and social challenges become more visible ranging from climate change to income inequality investors are seeking to fund solutions that address these global issues while achieving competitive returns.
Supportive government policies and regulatory frameworks are playing a crucial role in accelerating market growth. Initiatives such as the EU’s Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) and global ESG reporting standards are pushing companies and financial institutions to enhance transparency and sustainability disclosures. At the same time, innovations in financial instruments such as green bonds, social impact bonds, and blended finance are improving the scalability and accessibility of impact investing.
Investors are increasingly incorporating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) data into their investment strategies to enhance accountability and effectively track real-world impact alongside financial performance. This integration allows investors to make more informed decisions and align their portfolios with broader sustainability goals. As ESG metrics become more standardized and widely accepted, they are transforming the way capital is allocated across various industries and markets.There is a growing interest in thematic investing, where funds specifically target social or environmental issues such as clean energy, gender equality, and affordable housing. Thematic impact funds enable investors to focus on particular challenges they are passionate about, offering a more concentrated approach to driving positive change. This trend reflects a shift toward investment strategies that are not only financially rewarding but also purpose-driven.
Mainstream institutional adoption is another significant trend, with large asset managers, pension funds, and other institutional investors increasingly allocating substantial capital to impact investments. This movement marks a transition from impact investing being a niche practice to becoming a core component of mainstream financial portfolios. The participation of these large investors provides the sector with greater resources and credibility.
Advancements in impact measurement are enhancing the ability to quantify and compare outcomes across investments. Frameworks and tools such as the Impact Management Project (IMP) and IRIS+ are playing a critical role in improving transparency and fostering investor trust. By enabling standardized reporting and benchmarking, these innovations help ensure that impact investing delivers on its promises of generating meaningful social and environmental benefits.
One of the major challenges facing the impact investing market is the lack of standardized metrics for measuring social and environmental outcomes. Without universally accepted frameworks, it becomes difficult for investors to compare performance across different investments or accurately assess the true impact being generated. This inconsistency can lead to confusion and hinder the scaling of impact investments. Concerns around greenwashing where some firms overstate their sustainability efforts without delivering measurable results further undermine investor confidence and raise questions about the credibility of impact claims.
Another significant challenge is the limited availability of scalable and investment-ready projects, particularly in developing markets where capital deployment could have substantial social benefits. Despite growing demand from investors, the pipeline of viable opportunities that meet both financial and impact criteria remains constrained. Furthermore, balancing the dual objectives of generating competitive financial returns while achieving meaningful social or environmental impact continues to be complex. In some sectors, social goals may not align with short-term profitability, making it difficult for investors to navigate trade-offs between profit and purpose effectively.
North America dominated the global market with highest share of 38% in 2024. The region benefits from a mature investment infrastructure and a well-established culture of philanthropy and social entrepreneurship. U.S.-based investors have led the development of metrics, standards, and reporting frameworks that have shaped global practices, while Canada has shown growing interest in sustainable finance and community-based investments through government-backed initiatives and public-private partnerships.
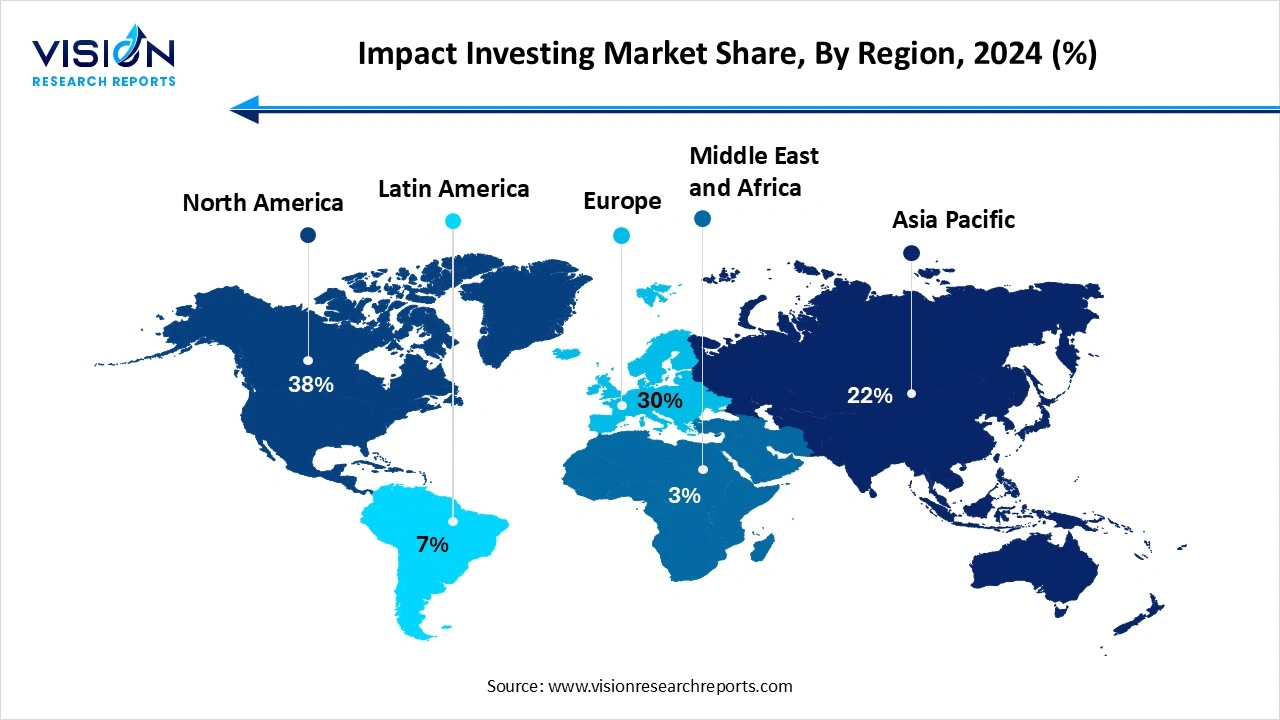 In the Asia-Pacific region, impact investing is gaining momentum amid rising awareness of climate vulnerability, income inequality, and social inclusion. Countries like India, China, Japan, and Australia are seeing increased participation from development finance institutions, family offices, and impact-driven venture capital. Asia-Pacific markets often focus on microfinance, sustainable agriculture, healthcare, and education, addressing the region’s specific socioeconomic challenges. Governments in the region are also encouraging responsible investing through favorable regulations and national sustainability agendas.
In the Asia-Pacific region, impact investing is gaining momentum amid rising awareness of climate vulnerability, income inequality, and social inclusion. Countries like India, China, Japan, and Australia are seeing increased participation from development finance institutions, family offices, and impact-driven venture capital. Asia-Pacific markets often focus on microfinance, sustainable agriculture, healthcare, and education, addressing the region’s specific socioeconomic challenges. Governments in the region are also encouraging responsible investing through favorable regulations and national sustainability agendas.
The equity segment held the largest share at 49% in 2024. Equity investments provide investors with ownership in companies that are actively tackling social and environmental issues. This enables investors to drive meaningful change by supporting enterprises aligned with their values and impact objectives. Additionally, equity investments present the opportunity for strong financial returns, appealing to those aiming to achieve both social impact and monetary gains.
The fixed income segment is projected to register the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. Fixed-income investments provide a steady and predictable return, making them a preferred choice for risk-averse investors aiming for both financial performance and positive impact. This investment approach aligns closely with the principles of impact investing, which targets measurable social and environmental benefits alongside returns. Additionally, the rising interest in sustainable and responsible investing has led to the emergence of green and social bonds designed to finance projects that deliver meaningful environmental or social outcomes.
The equity segment held the highest market share in 2024. Equity funds in impact investing are primarily focused on allocating capital to companies that are actively addressing critical global challenges such as climate change, education, clean water, and health care. These funds provide investors with an opportunity to participate in the growth of mission-driven businesses, from early-stage social enterprises to publicly listed firms with robust ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices. Through equity investments, impact investors not only seek long-term capital appreciation but also engage in active ownership, using shareholder influence to drive corporate accountability and strategic alignment with sustainability goals.
The bond funds segment is projected to register the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) over the forecast period. These include green bonds, social bonds, and sustainability-linked bonds, which are designed to fund specific outcomes such as renewable energy development, affordable housing, or access to education. Bond funds offer a more stable and predictable income stream for investors, making them an attractive option for those seeking lower-risk exposure to impactful projects. The rising popularity of these fixed-income instruments reflects the growing institutional and governmental support for integrating social responsibility into financial systems.
The active investment style in impact investing is characterized by a deliberate, research-intensive approach, where fund managers select individual securities based on a comprehensive assessment of their potential to generate measurable impact. These managers engage directly with companies, nonprofit organizations, or development projects to influence decision-making, improve sustainability practices, and monitor long-term impact outcomes. This style offers a tailored investment experience, with portfolios often focused on specific impact themes such as clean energy, sustainable agriculture, or financial inclusion. The active style allows for dynamic asset allocation and adjustment in response to evolving market conditions and impact objectives, making it suitable for investors who prioritize customization, engagement, and accountability.
The passive segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. Instead of attempting to outperform the market through active security selection, passive strategies aim to replicate the performance of established indices composed of companies that meet specific sustainability or ethical standards. This approach is generally more cost-effective and transparent, making it accessible to a wider range of investors, including those new to impact investing. Passive impact investing supports the scaling of sustainable capital allocation by offering diversified portfolios with consistent ESG alignment, even without direct shareholder intervention. As the demand for impact-oriented investment options grows, both active and passive styles are playing complementary roles in deepening the integration of social and environmental goals into global financial markets.
In the global impact investing market, institutional investors represent a significant force driving the allocation of capital toward socially and environmentally responsible initiatives. These investors include pension funds, insurance companies, endowments, sovereign wealth funds, and development finance institutions. With their vast financial resources and long-term investment horizons, institutional investors are well-positioned to support large-scale impact projects such as renewable energy infrastructure, sustainable agriculture, and inclusive financial systems. They typically engage in rigorous due diligence processes and demand robust impact measurement and reporting to ensure that their investments align with both fiduciary responsibilities and broader ESG goals.
The retail investors are also playing an increasingly vital role in the evolution of the impact investing market. Empowered by greater access to information, digital investment platforms, and a rising awareness of global challenges, individual investors are seeking to align their personal values with their financial decisions. Retail demand is fueling the creation of impact-focused mutual funds, ETFs, and micro-investment platforms that allow smaller-scale investors to participate in meaningful change. Unlike institutional investors, retail participants may prioritize purpose-driven investing over maximum financial returns, especially among younger generations who are more motivated by environmental and social outcomes.
By Asset Class
By Offerings
By Investment Style
By Investor Type
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Impact Investing Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Impact Investing Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Impact Investing Market, By Asset Class
8.1. Impact Investing Market, by Asset Class
8.1.1. Equity
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Fixed income
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Multi-asset
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.4. Alternatives
8.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global Impact Investing Market, By Offerings
9.1. Impact Investing Market, by Offerings
9.1.1. Equity
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Bond Funds
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. ETFs/Index Fund
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.4. Alternatives/Hedge Funds
9.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Global Impact Investing Market, By Investment Style
10.1. Impact Investing Market, by Investment Style
10.1.1. Active
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.2. Passive
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 11. Global Impact Investing Market, By Investor Type
11.1. Impact Investing Market, by Investor Type
11.1.1. Institutional Investors
11.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.2. Retail Investors
11.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 12. Global Impact Investing Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
12.1. North America
12.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.1.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.1.5. U.S.
12.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.1.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.1.6. Rest of North America
12.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.1.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.1.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.1.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.2. Europe
12.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.2.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.2.5. UK
12.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.2.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.2.6. Germany
12.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.2.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.2.7. France
12.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.2.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.2.8. Rest of Europe
12.2.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.2.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.2.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.2.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.3. APAC
12.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.3.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.3.5. India
12.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.3.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.3.6. China
12.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.3.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.3.7. Japan
12.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.3.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.3.8. Rest of APAC
12.3.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.3.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.3.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.3.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.4. MEA
12.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.4.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.4.5. GCC
12.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.4.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.4.6. North Africa
12.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.4.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.4.7. South Africa
12.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.4.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.4.8. Rest of MEA
12.4.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.4.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.4.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.4.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.5. Latin America
12.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.5.5. Brazil
12.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.5.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
12.5.6. Rest of LATAM
12.5.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Asset Class
12.5.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Offerings
12.5.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investment Style
12.5.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Investor Type
Chapter 13. Company Profiles
13.1. BlackRock
13.1.1. Company Overview
13.1.2. Product Offerings
13.1.3. Financial Performance
13.1.4. Recent Initiatives
13.2. Goldman Sachs Asset Management
13.2.1. Company Overview
13.2.2. Product Offerings
13.2.3. Financial Performance
13.2.4. Recent Initiatives
13.3. Bain Capital Double Impact
13.3.1. Company Overview
13.3.2. Product Offerings
13.3.3. Financial Performance
13.3.4. Recent Initiatives
13.4. TPG Rise Fund
13.4.1. Company Overview
13.4.2. Product Offerings
13.4.3. Financial Performance
13.4.4. Recent Initiatives
13.5. Bridges Fund Management
13.5.1. Company Overview
13.5.2. Product Offerings
13.5.3. Financial Performance
13.5.4. Recent Initiatives
13.6. Generation Investment Management
13.6.1. Company Overview
13.6.2. Product Offerings
13.6.3. Financial Performance
13.6.4. Recent Initiatives
13.7. BlueOrchard Finance
13.7.1. Company Overview
13.7.2. Product Offerings
13.7.3. Financial Performance
13.7.4. Recent Initiatives
13.8. Global Impact Investing Network (GIIN)
13.8.1. Company Overview
13.8.2. Product Offerings
13.8.3. Financial Performance
13.8.4. Recent Initiatives
13.9. Calvert Impact Capital
13.9.1. Company Overview
13.9.2. Product Offerings
13.9.3. Financial Performance
13.9.4. Recent Initiatives
13.10. Triodos Investment Management
13.10.1. Company Overview
13.10.2. Product Offerings
13.10.3. Financial Performance
13.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 14. Research Methodology
14.1. Primary Research
14.2. Secondary Research
14.3. Assumptions
Chapter 15. Appendix
15.1. About Us
15.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others