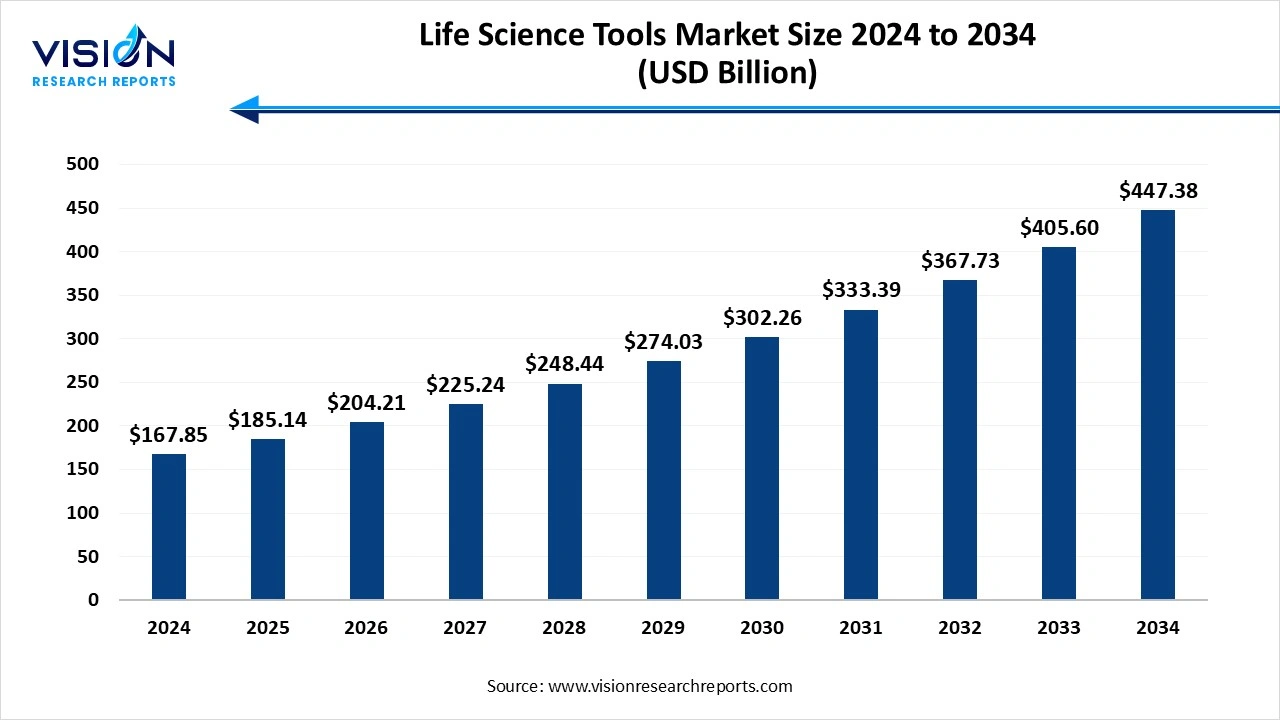
The global life science tools market size was reached at around USD 167.85 billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 447.38 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.30% from 2025 to 2034.
By region, North America dominated the global market with highest share of 45% in 2024.
By technology, the cell biology technology segment registered the maximum market share of 34% in 2024.
By technology, the genomic technology segment isegment is predicted to grow at the remarkable CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
The cell culture systems and 3D cell culture segment accounted for the highest revenue share, reaching 17% in 2024.
The next-generation sequencing segment is projected to register the fastest CAGR of 13.80%
The healthcare segment captured the largest share of revenue in the life science market, accounting for 33% in 2025.
The biopharmaceutical segment is anticipated to witness the fastest growth over the forecast period.
The life science tools market encompasses a broad range of instruments, reagents, consumables, and services used in the study of living organisms and biological processes. It plays a critical role in driving advancements across biotechnology, pharmaceutical development, academic research, and clinical diagnostics. In recent years, the market has experienced substantial growth, fueled by rising investments in research and development, growing demand for precision medicine, and technological innovations such as high-throughput sequencing, CRISPR gene editing, and mass spectrometry.
The growth of the life science tools market is driven primarily by increased funding and investments in biomedical research, pharmaceutical development, and biotechnology innovation. Governments, private organizations, and academic institutions across the globe are consistently investing in life sciences to support advancements in disease research, drug discovery, and personalized medicine. Additionally, the rising prevalence of chronic and infectious diseases has created a surge in demand for diagnostic solutions and therapeutic development, further fueling the need for cutting-edge life science instruments and reagents.
Another key growth factor is the rapid technological evolution in genomics, proteomics, and cell biology. Innovations such as next-generation sequencing (NGS), single-cell analysis, and CRISPR gene-editing technologies are transforming the research landscape, requiring more sophisticated and efficient tools.
One of the prominent trends in the life science tools market is the increasing adoption of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) in laboratory workflows. Laboratories are integrating robotic systems, AI-driven data analysis, and digital platforms to enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and speed of research processes. This digital transformation is especially evident in areas like genomics, where high-throughput sequencing requires advanced computational tools to manage and interpret massive datasets.
Another significant trend is the rising emphasis on personalized and precision medicine, which is reshaping how life science tools are designed and used. As healthcare moves toward individualized treatment strategies based on genetic and molecular profiles, researchers require advanced tools for biomarker discovery, genomic sequencing, and proteomic analysis. Additionally, there is a growing focus on single-cell technologies and 3D cell culture systems, which provide deeper biological insights and more accurate disease modeling.
One of the primary challenges facing the life science tools market is the high cost associated with advanced instruments and technologies. Many cutting-edge tools, such as next-generation sequencing platforms, mass spectrometers, and high-throughput screening systems, require significant capital investment, limiting their accessibility to smaller research institutions and laboratories, particularly in developing regions.
Another key challenge is the regulatory and compliance complexity in the life sciences industry. As research increasingly involves human data, genetic information, and clinical applications, companies must navigate strict regulations related to data privacy, safety standards, and product validation. These regulatory requirements can delay product development and market entry, especially when targeting multiple geographic regions with varying compliance frameworks.
North America led the life science tools industry, accounting for the highest revenue share of 45% in 2024. The United States, in particular, is a major contributor to the region’s market growth, supported by substantial government funding for biomedical research and high demand for advanced diagnostic and therapeutic technologies. The region also benefits from strong collaborations between academic institutions, biotechnology firms, and pharmaceutical companies, which drive innovation and early adoption of cutting-edge life science tools.
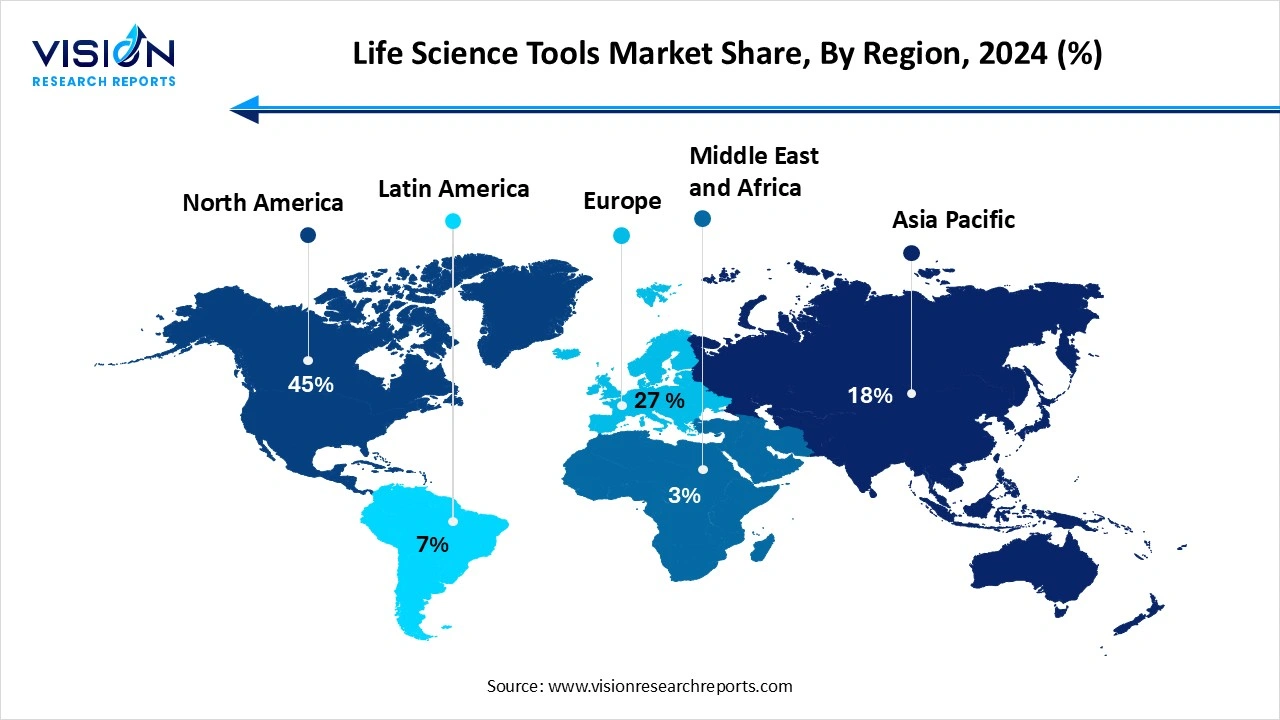 Asia Pacific, on the other hand, is emerging as the fastest-growing region, owing to rapid industrialization, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and increasing government initiatives to boost life science research. China, India, and Japan are at the forefront of this growth, with rising demand for genomics, proteomics, and cell-based research tools. The region is also witnessing a surge in biopharmaceutical manufacturing and clinical trials, creating new opportunities for life science tool providers.
Asia Pacific, on the other hand, is emerging as the fastest-growing region, owing to rapid industrialization, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and increasing government initiatives to boost life science research. China, India, and Japan are at the forefront of this growth, with rising demand for genomics, proteomics, and cell-based research tools. The region is also witnessing a surge in biopharmaceutical manufacturing and clinical trials, creating new opportunities for life science tool providers.
The cell biology technology segment accounted for the highest revenue share of 34% in 2024. This segment includes a variety of tools such as flow cytometry, microscopy systems, cell imaging platforms, and cell culture technologies that help researchers analyze cellular structures, functions, and interactions. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, especially cancer, has driven the demand for advanced cell biology tools that allow scientists to understand disease mechanisms at the cellular level.
The genomic technology segment is anticipated to register the highest CAGR throughout the forecast period. Technologies such as next-generation sequencing (NGS), polymerase chain reaction (PCR), microarrays, and gene editing tools like CRISPR are extensively used to analyze DNA and RNA sequences with high speed and accuracy. The expanding application of genomics in disease diagnosis, prenatal screening, infectious disease detection, and oncology research has led to a surge in demand for high-throughput and cost-effective genomic tools.
The cell culture systems and 3D cell culture segment accounted for the highest revenue share, reaching 17% in 2024. These systems are essential for studying cellular behavior, drug development, cancer biology, stem cell research, and vaccine production. Cell culture tools include bioreactors, flasks, media, reagents, and other consumables that support the in vitro growth and maintenance of cells. The growing demand for biologics and personalized therapeutics has increased the adoption of advanced cell culture technologies, such as 3D culture systems and organoids, which more accurately mimic in vivo conditions.
The next-generation sequencing segment is projected to register the fastest CAGR of 13.80% throughout the forecast period. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) and genomic technology represent a rapidly evolving area within the life science tools market, revolutionizing the way researchers understand genetics and molecular biology. These technologies allow for the comprehensive sequencing and analysis of DNA and RNA, enabling breakthroughs in areas such as disease diagnosis, pharmacogenomics, and microbial detection. NGS platforms have significantly reduced the cost and time required for sequencing, making them accessible to a wider range of research institutions and clinical laboratories.
The healthcare segment captured the largest share of revenue in the life science market, accounting for 33% in 2025. Hospitals, diagnostic laboratories, and clinical research organizations utilize life science tools extensively for clinical diagnostics, biomarker identification, and therapeutic monitoring. Technologies such as next-generation sequencing, PCR, and advanced imaging systems are integral in diagnosing genetic disorders, infectious diseases, and various types of cancer. As the healthcare industry moves toward precision medicine, the demand for accurate, efficient, and scalable life science tools continues to rise.
The biopharmaceutical segment is anticipated to witness the fastest growth over the forecast period. The biopharmaceutical segment is another major end-user of life science tools, as these technologies are fundamental to every stage of the drug development process from discovery and preclinical testing to manufacturing and quality control. Biopharmaceutical companies rely heavily on high-throughput screening, genomic and proteomic tools, cell-based assays, and analytical instruments to discover new drug targets, evaluate compound efficacy, and ensure product safety. The increasing complexity of biologics, such as monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and gene therapies, requires advanced tools that can support scalable and reproducible research.
By Product & Service
By Technology
By End-use
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Product & Service Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Life Science Tools Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Life Science Tools Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Life Science Tools Market, By Product & Service
8.1. Life Science Tools Market, by Product & Service
8.1.1 Cell Culture Systems & 3D Cell Culture
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Liquid Chromatography
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Mass Spectrometry
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.4. Flow Cytometry
8.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.5. Cloning & Genome Engineering
8.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.6. Microscopy & Electron Microscopy
8.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.7. Next Generation Sequencing
8.1.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.8. PCR & qPCR
8.1.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.9. Nucleic Acid Preparation
8.1.9.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.10.1. Nucleic Acid Microarray
8.1.10.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.11.1. Sanger Sequencing
8.1.11.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.12.1. Transfection Devices & Gene Delivery Technologies
8.1.12.1.Market Revenue and Forecast
1.13. Other Separation Technologies
8.1.13.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.14. Other Products & Services
8.1.14.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global Life Science Tools Market, By Technology
9.1. Life Science Tools Market, by Technology
9.1.1. Genomic Technology
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Proteomics Technology
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Cell Biology Technology
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.4. Other Analytical & Sample Preparation Technology
9.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.5. Lab Supplies & Technologies
9.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Global Life Science Tools Market, By End-use
10.1. Life Science Tools Market, by End-use
10.1.1. Government & Academic
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.2. Biopharmaceutical Company
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.3. Healthcare
10.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.4. Industrial Applications
10.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.5. Others
10.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 11. Global Life Science Tools Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
11.1. North America
11.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.1.4. U.S.
11.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.1.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.1.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.1.5. Rest of North America
11.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.2. Europe
11.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.2.4. UK
11.2.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.2.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.2.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.2.5. Germany
11.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.2.6. France
11.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.2.7. Rest of Europe
11.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.3. APAC
11.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.3.4. India
11.3.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.3.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.3.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.3.5. China
11.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.3.6. Japan
11.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.3.7. Rest of APAC
11.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.4. MEA
11.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.4.4. GCC
11.4.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.4.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.4.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.4.5. North Africa
11.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.4.6. South Africa
11.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.4.7. Rest of MEA
11.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.5. Latin America
11.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.5.4. Brazil
11.5.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.5.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.5.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
11.5.5. Rest of LATAM
11.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product & Service
11.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1. Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
12.1.1. Company Overview
12.1.2. Product Offerings
12.1.3. Financial Performance
12.1.4. Recent Initiatives
12.2. Agilent Technologies, Inc.
12.2.1. Company Overview
12.2.2. Product Offerings
12.2.3. Financial Performance
12.2.4. Recent Initiatives
12.3Danaher Corporation
12.3.1. Company Overview
12.3.2. Product Offerings
12.3.3. Financial Performance
12.3.4. Recent Initiatives
12.4. Illumina, Inc.
12.4.1. Company Overview
12.4.2. Product Offerings
12.4.3. Financial Performance
12.4.4. Recent Initiatives
12.5. Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
12.5.1. Company Overview
12.5.2. Product Offerings
12.5.3. Financial Performance
12.5.4. Recent Initiatives
12.6. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
12.6.1. Company Overview
12.6.2. Product Offerings
12.6.3. Financial Performance
12.6.4. Recent Initiatives
12.7. Merck KGaA.
12.7.1. Company Overview
12.7.2. Product Offerings
12.7.3. Financial Performance
12.7.4. Recent Initiatives
12.8. Bruker Corporation
12.8.1. Company Overview
12.8.2. Product Offerings
12.8.3. Financial Performance
12.8.4. Recent Initiatives
12.9. PerkinElmer Inc.
12.9.1. Company Overview
12.9.2. Product Offerings
12.9.3. Financial Performance
12.9.4. Recent Initiatives
12.10. Waters Corporation
12.10.1. Company Overview
12.10.2. Product Offerings
12.10.3. Financial Performance
12.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 13. Research Methodology
13.1. Primary Research
13.2. Secondary Research
13.3. Assumptions
Chapter 14. Appendix
14.1. About Us
14.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others