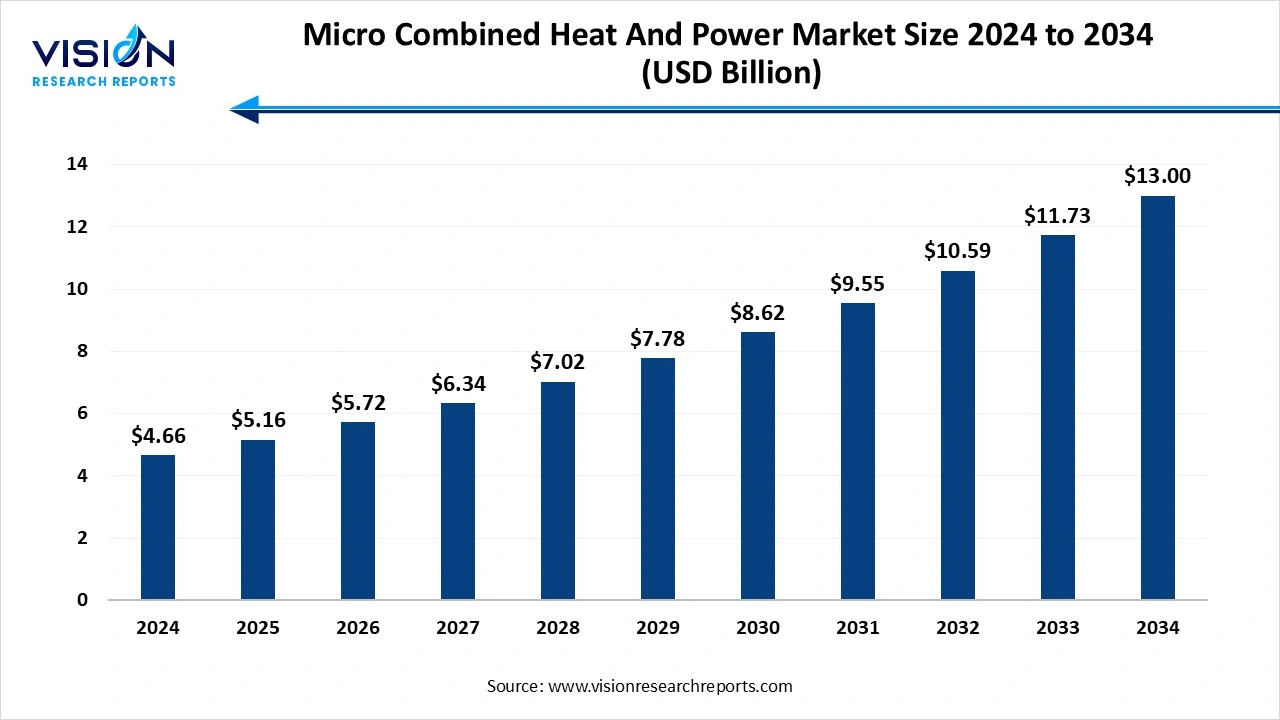
The global micro combined heat and power market size was surpassed at around USD 4.66 billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 13 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.80% from 2025 to 2034.
The micro combined heat and power (micro-CHP) market is experiencing steady growth due to increasing global emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability. Micro-CHP systems are small-scale energy generation units that simultaneously produce electricity and useful heat, making them highly efficient for residential, commercial, and small industrial applications. These systems are gaining popularity as they help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and lower energy costs by utilizing fuel more efficiently compared to conventional systems. Growing demand for decentralized energy systems and the rising adoption of cleaner energy solutions are key factors driving the market. Governments around the world are also offering incentives and regulatory support to promote the use of micro-CHP technologies, particularly in regions aiming to reduce dependence on centralized power grids and fossil fuels.
The growth of the micro combined heat and power (micro-CHP) market is primarily fueled by the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions that reduce both energy costs and carbon emissions. These systems offer higher overall efficiency compared to traditional methods of separate heat and power production, making them an attractive choice for residential and commercial buildings.
Another major growth factor is the rapid advancement in technology, which is improving the reliability, compactness, and cost-effectiveness of micro-CHP systems. The integration of renewable and low-carbon fuels such as hydrogen and bioenergy is making these systems even more appealing for future energy infrastructure. Growing urbanization, the need for distributed energy solutions, and increasing electricity demand in off-grid or remote areas are also contributing to the expanding market.
One of the key trends in the micro combined heat and power (micro-CHP) market is the shift toward renewable and low-carbon fuel sources. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing systems that operate on hydrogen, biogas, and other sustainable fuels to align with global decarbonization goals. This trend is supported by investments in clean energy infrastructure and initiatives aimed at phasing out fossil fuel dependency. Additionally, fuel cell-based micro-CHP systems are gaining traction due to their higher efficiency and lower emissions, making them suitable for future-ready energy solutions, particularly in eco-conscious markets like Japan and parts of Europe.
Another significant trend is the integration of micro-CHP systems with smart grid technologies and home energy management systems. As buildings become more intelligent and energy self-sufficient, micro-CHP units are being designed to operate in sync with real-time energy demand and supply fluctuations. This enhances energy optimization, reduces reliance on centralized grids, and supports grid stability during peak loads.
One of the primary challenges facing the micro combined heat and power (micro-CHP) market is the high upfront cost associated with system installation and maintenance. Despite the long-term savings in energy costs, the initial investment can be a deterrent, particularly for small businesses and residential users. The cost of components, such as fuel cells and advanced engines, adds to the overall expense, making it less accessible in price-sensitive markets. Additionally, consumers may be hesitant to adopt new technologies without clear short-term financial benefits, which slows down widespread adoption.
Another significant challenge is the limited availability and infrastructure for alternative fuels like hydrogen and biogas in many regions. While these cleaner fuels are ideal for sustainable micro-CHP operation, their lack of widespread distribution networks hampers deployment. Furthermore, integration with existing energy systems can be complex, especially in older buildings not designed for distributed energy solutions. Regulatory uncertainty in some countries, along with inconsistent support policies, also poses a hurdle, making it difficult for manufacturers and consumers to plan long-term investments confidently.
The Asia Pacific region held the largest share of the micro combined heat and power (MCHP) market, accounting for 43% in 2024. This dominance is primarily driven by rapid urbanization and industrial growth in countries such as China, India, and those in Southeast Asia, which has significantly increased the demand for both electricity and heating. Additionally, the region’s pressing air pollution challenges have prompted the adoption of cleaner energy technologies.
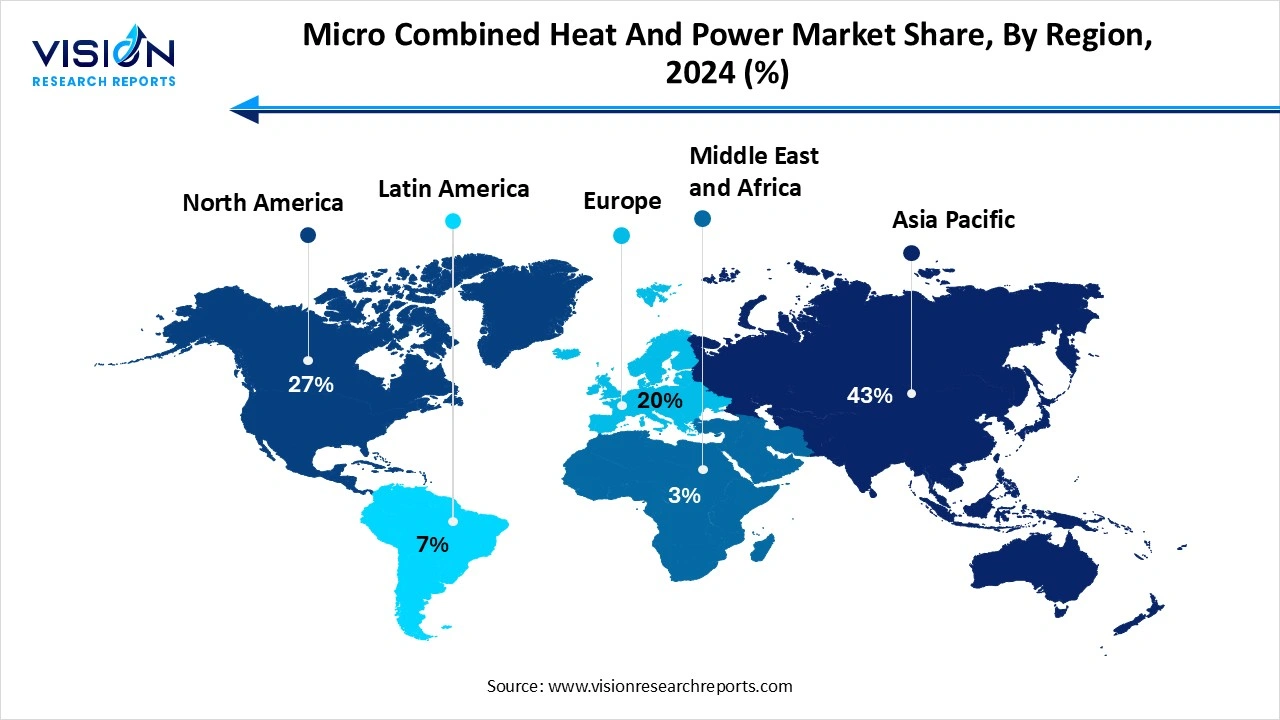 The North America micro combined heat and power (MCHP) market is projected to witness substantial growth over the forecast period, driven by rising concerns over fluctuating energy prices and a strong push for long-term energy cost stability. Both residential and commercial sectors are increasingly adopting MCHP systems to gain more control over their energy consumption and reduce dependence on conventional grid electricity. These systems not only offer enhanced energy efficiency by simultaneously generating electricity and heat but also provide a resilient solution amid rising utility costs.
The North America micro combined heat and power (MCHP) market is projected to witness substantial growth over the forecast period, driven by rising concerns over fluctuating energy prices and a strong push for long-term energy cost stability. Both residential and commercial sectors are increasingly adopting MCHP systems to gain more control over their energy consumption and reduce dependence on conventional grid electricity. These systems not only offer enhanced energy efficiency by simultaneously generating electricity and heat but also provide a resilient solution amid rising utility costs.
The engine-based segment dominated the market, accounting for the highest revenue share of 69% in 2024. Engine-based micro-CHP systems are widely used due to their well-established design, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability for various applications, particularly in residential and small commercial settings. These systems typically use internal combustion engines or Stirling engines to generate electricity and heat simultaneously. They are preferred in regions with existing gas infrastructure, and they offer relatively easy maintenance and proven performance reliability.
The fuel cell-based segment is projected to experience strong growth, with a robust CAGR of 16.4% during the forecast period. These systems use electrochemical reactions to produce electricity and heat, offering higher efficiency and significantly lower emissions compared to combustion-based models. Fuel cell technology is gaining momentum in markets focused on decarbonization and sustainability, especially in Japan and select European countries where government incentives support clean energy solutions. Although fuel cell-based micro-CHP systems come at a higher initial cost, their environmental benefits, quiet operation, and potential for integration with renewable hydrogen make them a strategic choice for future energy infrastructure.
The residential segment held the largest share of the market in 2024. These systems help businesses reduce utility costs and carbon emissions while providing a dependable source of heat and power. The commercial segment often favors engine-based systems because of their maturity, cost-efficiency, and compatibility with existing infrastructure. Additionally, in regions where energy regulations are stringent and sustainability goals are prioritized, micro-CHP systems offer an effective means to comply with environmental standards. Commercial buildings such as hotels, hospitals, office complexes, and educational institutions benefit greatly from micro-CHP systems due to their consistent energy and heating needs. These systems help businesses reduce utility costs and carbon emissions while providing a dependable source of heat and power. The commercial segment often favors engine-based systems because of their maturity, cost-efficiency, and compatibility with existing infrastructure. Additionally, in regions where energy regulations are stringent and sustainability goals are prioritized, micro-CHP systems offer an effective means to comply with environmental standards.
The micro-CHP is increasingly being adopted in individual homes and multi-family housing complexes. These systems provide a decentralized energy solution that allows homeowners to reduce dependence on grid power, lower electricity bills, and enhance overall energy efficiency. In areas with high energy prices and strong government incentives, residential adoption is particularly notable. Fuel cell-based micro-CHP units are gaining popularity in residential settings due to their compact design, quiet operation, and low emissions. As consumers become more environmentally conscious and energy costs continue to rise, the residential application of micro-CHP systems is expected to expand, especially in technologically advanced and environmentally proactive countries.
By Product
By Application
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Micro Combined Heat And Power Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Micro Combined Heat And Power r Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Micro Combined Heat And Power Market, By Product
8.1. Micro Combined Heat And Power Market, by proudct, 2024-2033
8.1.1. Engine-based
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
8.1.2. Fuel Cell-based
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 9. Micro Combined Heat And Power Market, By Application
9.1. Micro Combined Heat And Power Market, by Application, 2024-2033
9.1.1. Commercial
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.2. Residential
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 10. U.S. Pharmaceutical Water Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
10.1. U.S.
10.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product (2021-2033)
10.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application (2021-2033)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1. Yanmar Co., Ltd.
11.1.1. Company Overview
11.1.2. Product Offerings
11.1.3. Financial Performance
11.1.4. Recent Initiatives
11.2. BDR Thermea Group
11.2.1. Company Overview
11.2.2. Product Offerings
11.2.3. Financial Performance
11.2.4. Recent Initiatives
11.3. Viessmann Group
11.3.1. Company Overview
11.3.2. Product Offerings
11.3.3. Financial Performance
11.3.4. Recent Initiatives
11.4. Vaillant Group
11.4.1. Company Overview
11.4.2. Product Offerings
11.4.3. Financial Performance
11.4.4. LTE Scientific
11.5. Panasonic Corporation
11.5.1. Company Overview
11.5.2. Product Offerings
11.5.3. Financial Performance
11.5.4. Recent Initiatives
11.6. Aisin Seiki Co., Ltd.
11.6.1. Company Overview
11.6.2. Product Offerings
11.6.3. Financial Performance
11.6.4. Recent Initiatives
11.7. Ceres Power Holdings plc
11.7.1. Company Overview
11.7.2. Product Offerings
11.7.3. Financial Performance
11.7.4. Recent Initiatives
11.8. 2G Energy AG
11.8.1. Company Overview
11.8.2. Product Offerings
11.8.3. Financial Performance
11.8.4. Recent Initiatives
11.9. Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
11.9.1. Company Overview
11.9.2. Product Offerings
11.9.3. Financial Performance
11.9.4. Ener-G Holdings Plc
11.10. Nexus Pharmaceuticals
11.10.1. Company Overview
11.10.2. Product Offerings
11.10.3. Financial Performance
11.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 12. Research Methodology
12.1. Primary Research
12.2. Secondary Research
12.3. Assumptions
Chapter 13. Appendix
13.1. About Us
13.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others