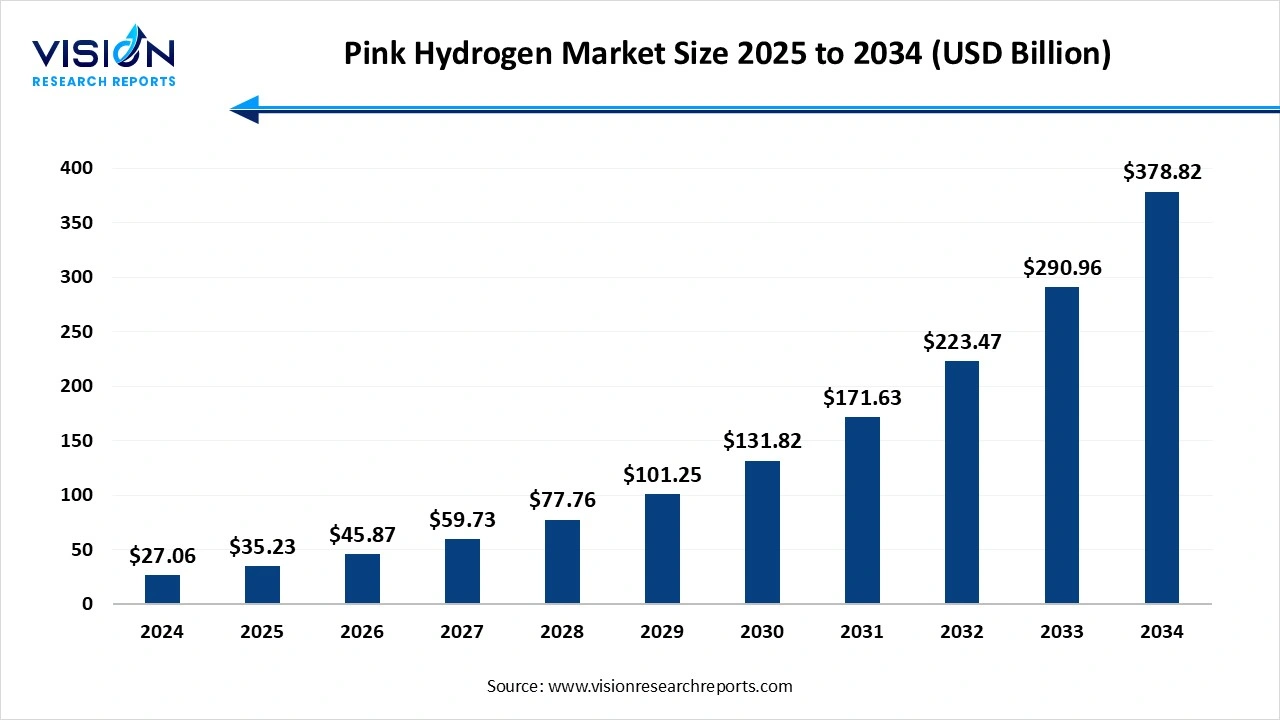
The global pink hydrogen market size was valued at around USD 27.06 billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 78.82 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 30.2% from 2025 to 2034. The market growth is driven by increasing demand for zero-emission fuel and strong government support for nuclear-powered hydrogen production, the Pink Hydrogen Market is witnessing notable growth. 
| Report Coverage     | Details |
| Market Size in 2024     | USD 27.06 billion |
| Revenue Forecast by 2034     | USD  78.82 billion |
| Growth rate from 2025 to 2034    | CAGR of 30.2% |
| Base Year     | 2024 |
| Forecast Period    2025 to 2034 |   |
| Regions     | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Companies Covered¬† ¬†¬† | Air Liquide,¬†Linde plc,¬†Siemens Energy, Hydrogenics (a subsidiary of Cummins Inc.,¬†NEL ASA,¬†Plug Power Inc.,¬†Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation General Electric GE Power, Rosatom EDF (√Člectricit√© de France),¬†Westinghouse Electric Company,¬†Bloom Energy INEOS Group,¬†Areva H2Gen,Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power (KHNP) |
Pink hydrogen, produced through electrolysis powered by nuclear energy, is gaining significant attention as a clean and sustainable alternative in the global hydrogen landscape. As countries aim to decarbonize heavy industries and transition to low-emission energy sources, pink hydrogen stands out due to its zero-carbon production process and consistent power supply capabilities. Unlike green hydrogen, which depends on variable renewable sources, pink hydrogen benefits from the steady and high-capacity output of nuclear power, making it a reliable option for large-scale industrial applications and grid stability.
The pink hydrogen market is primarily driven by the global push for decarbonization and the rising need for clean, sustainable energy sources. As governments and industries commit to achieving net-zero emissions targets, pink hydrogen has emerged as a strategic solution. Its production through nuclear-powered electrolysis ensures a low-carbon footprint while offering a steady and high-capacity energy supply ideal for sectors like steel, chemicals, and long-haul transport.
Growing investments in nuclear energy infrastructure and advancements in electrolysis technologies are accelerating the commercialization of pink hydrogen. Countries with established nuclear power capacities, such as France, the U.S., and Japan, are exploring pink hydrogen as a means to diversify their clean energy portfolios. Supportive government policies, funding initiatives, and public-private collaborations are also encouraging innovation in this space, further boosting market growth prospects over the coming decade.
One of the primary challenges facing the pink hydrogen market is the high capital cost associated with nuclear-powered electrolysis. Building and maintaining nuclear power plants is expensive and time-consuming, often requiring extensive regulatory approvals and safety measures. Additionally, integrating electrolyzers with nuclear reactors demands advanced engineering solutions and significant upfront investment, which can limit scalability especially in countries with limited nuclear infrastructure or public opposition to nuclear energy.
Another challenge lies in public perception and regulatory hurdles. Nuclear energy continues to face skepticism due to safety concerns, radioactive waste disposal, and past incidents such as Fukushima. These factors create resistance to new nuclear projects, potentially slowing down the adoption of pink hydrogen. Moreover, the lack of specific regulatory frameworks for pink hydrogen and limited international standards hinder market development and cross-border collaboration, delaying its commercialization and widespread deployment.
North America dominated the pink hydrogen market, accounting for over 38% of the total revenue share in 2024. This leadership position is driven by the region’s well-established nuclear infrastructure, strong government backing for clean hydrogen initiatives, and growing efforts to decarbonize industrial sectors. The United States is playing a pivotal role, supported by its extensive nuclear power capacity and impactful legislation such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), which offers tax incentives and public funding to promote clean hydrogen production.
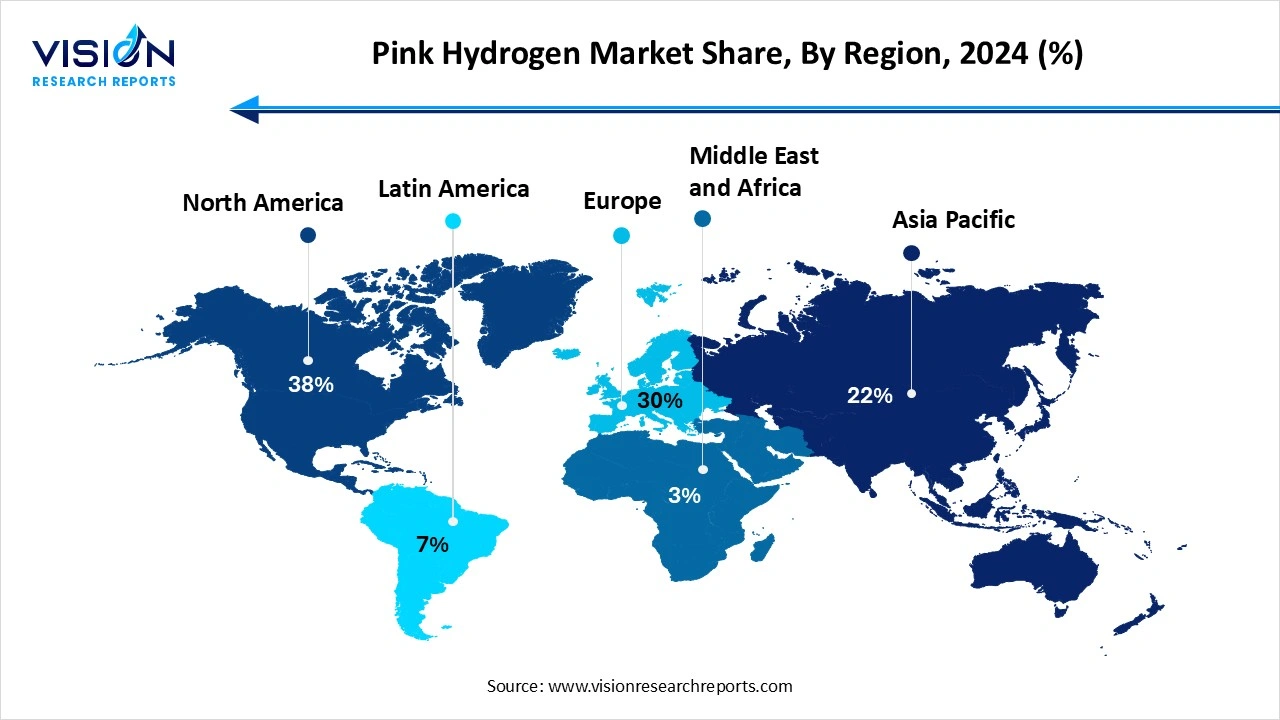 in Asia-Pacific, nations such as Japan and South Korea are actively pursuing nuclear-based hydrogen strategies to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and enhance energy security. These countries are focusing on technological advancements and international partnerships to build a sustainable pink hydrogen ecosystem. Overall, the regional outlook reflects growing momentum across developed economies, with pink hydrogen expected to play an integral role in shaping low-carbon energy portfolios.
in Asia-Pacific, nations such as Japan and South Korea are actively pursuing nuclear-based hydrogen strategies to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and enhance energy security. These countries are focusing on technological advancements and international partnerships to build a sustainable pink hydrogen ecosystem. Overall, the regional outlook reflects growing momentum across developed economies, with pink hydrogen expected to play an integral role in shaping low-carbon energy portfolios.
The alkaline electrolysis segment led the market, capturing more than 69% of the total revenue share in 2024. This process involves splitting water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen using an alkaline electrolyte typically potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide as the medium to conduct electricity. Alkaline electrolysis is known for its technological maturity, cost-effectiveness, and ability to operate continuously, which makes it an ideal fit for integration with the stable and round-the-clock energy supply provided by nuclear power plants.
The use of alkaline electrolysis in pink hydrogen production supports large-scale applications due to its scalability and relatively lower operational costs compared to other electrolysis technologies like PEM or solid oxide electrolysis. Its long-standing industrial use and proven reliability make it a preferred choice in regions with established nuclear infrastructure. However, continuous R&D is being directed toward improving the efficiency and flexibility of alkaline systems to better match the dynamic demands of hydrogen markets.
The refinery segment accounted for the highest revenue share, reaching 45% in 2024. Refineries represent one of the key end-use segments for the global pink hydrogen market, as the sector heavily relies on hydrogen for various processes such as hydrocracking, hydrotreating, and desulfurization. Traditionally, this hydrogen has been produced from fossil fuels like natural gas through steam methane reforming, which contributes significantly to carbon emissions. However, with increasing pressure to decarbonize and meet stringent environmental regulations, refineries are beginning to explore cleaner hydrogen alternatives.
As global energy policies shift toward sustainability, the integration of pink hydrogen into refinery operations is gaining traction, especially in regions with established nuclear infrastructure. The use of pink hydrogen not only helps refiners meet emission targets but also aligns with broader net-zero commitments being adopted worldwide. Moreover, the stable and continuous supply of nuclear energy supports uninterrupted hydrogen production, which is crucial for the continuous processes in refineries.
By Process 
By End Use 
By Regional 
Pink Hydrogen Market
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Pink Hydrogen Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Pink Hydrogen r Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Pink Hydrogen Market, By Process
8.1. Pink Hydrogen Market, by Process, 2024-2033
8.1.1. PEM Electrolysis
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
8.1.2. Alkaline Electrolysis
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
8.1.3. Solid Oxide Electrolysis
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 9. Pink Hydrogen Market, By End Use
9.1. Pink Hydrogen Market, by End Use, 2024-2033
9.1.1. Refinery
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.2. Ammonia
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.3. Methanol
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.4. Steel Production
9.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.5. Transport
9.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.6. Others
9.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 10. U.S. Pharmaceutical Water Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
10.1. U.S.
10.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process (2021-2033)
10.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use (2021-2033)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1. Air Liquide
11.1.1. Company Overview
11.1.2. Product Offerings
11.1.3. Financial Performance
11.1.4. Recent Initiatives
11.2. Linde plc
11.2.1. Company Overview
11.2.2. Product Offerings
11.2.3. Financial Performance
11.2.4. Recent Initiatives
11.3. Hydrogenics (a subsidiary of Cummins Inc.)
11.3.1. Company Overview
11.3.2. Product Offerings
11.3.3. Financial Performance
11.3.4. Recent Initiatives
11.4. NEL ASA
11.4.1. Company Overview
11.4.2. Product Offerings
11.4.3. Financial Performance
11.4.4. LTE Scientific
11.5. Plug Power Inc.
11.5.1. Company Overview
11.5.2. Product Offerings
11.5.3. Financial Performance
11.5.4. Recent Initiatives
11.6. General Electric (GE Power)
11.6.1. Company Overview
11.6.2. Product Offerings
11.6.3. Financial Performance
11.6.4. Recent Initiatives
11.7. Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation
11.7.1. Company Overview
11.7.2. Product Offerings
11.7.3. Financial Performance
11.7.4. Recent Initiatives
11.8. General Electric (GE Power)
11.8.1. Company Overview
11.8.2. Product Offerings
11.8.3. Financial Performance
11.8.4. Recent Initiatives
11.9. Rosatom
11.9.1. Company Overview
11.9.2. Product Offerings
11.9.3. Financial Performance
11.9.4. EDF (Électricité de France)
11.10. Nexus Pharmaceuticals
11.10.1. Company Overview
11.10.2. Product Offerings
11.10.3. Financial Performance
11.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 12. Research Methodology
12.1. Primary Research
12.2. Secondary Research
12.3. Assumptions
Chapter 13. Appendix
13.1. About Us
13.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others