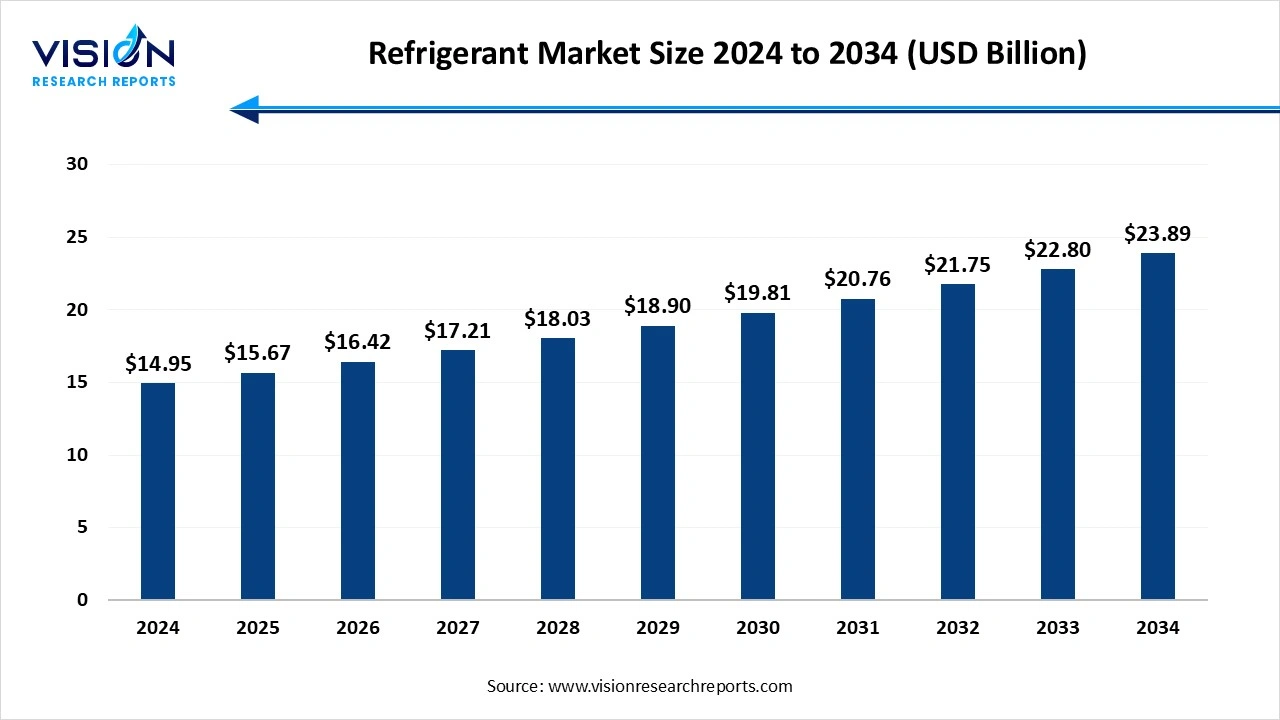
The global refrigerant market size was estimated at USD 14.95 billion in 2024 and it is expected to surpass around USD 23.89 billion by 2034, poised to grow at a CAGR of 4.80% from 2025 to 2034.
The global refrigerant market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for air conditioning and refrigeration systems across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Increasing urbanization, expanding middle-class populations, and growing temperature extremes due to climate change are key factors fueling this demand. technological advancements and the transition toward eco-friendly and low-global-warming-potential (GWP) refrigerants, in compliance with international environmental regulations such as the Kigali Amendment and the Montreal Protocol, are shaping market dynamics. While traditional refrigerants like hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) continue to dominate in many applications, the market is witnessing a significant shift toward natural and sustainable alternatives, including hydrocarbons, ammonia, and carbon dioxide.
Rising demand for cooling solutions one of the primary growth drivers of the refrigerant market is the escalating global demand for air conditioning and refrigeration systems. Rapid urbanization, particularly in developing economies, coupled with increasing disposable incomes, has significantly boosted the adoption of HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems in residential and commercial buildings. Moreover, the expansion of the cold chain logistics industry, particularly for food preservation and pharmaceuticals, is contributing to increased refrigerant consumption.
Regulatory push toward eco-friendly Refrigerants environmental regulations and sustainability goals are playing a crucial role in reshaping the refrigerant market landscape. Governments and international bodies are enforcing stringent regulations to phase out ozone-depleting substances and high-GWP refrigerants, in line with agreements such as the Montreal Protocol and the Kigali Amendment. This regulatory shift is encouraging the adoption of low-GWP and natural refrigerants, such as ammonia, carbon dioxide, and hydrocarbons. In response, manufacturers are investing in R&D to develop next-generation refrigerants that are both efficient and environmentally responsible, thereby fostering innovation and opening new market opportunities.
Europe accounted for a significant 32% share of global refrigerant revenue, making it one of the leading consumers worldwide in 2024. The European Union’s F-Gas Regulation aims to reduce the use of fluorinated gases with high global warming potential, leading to a significant increase in the adoption of natural refrigerants like CO₂, ammonia, and hydrocarbons. Countries such as Germany, France, and the United Kingdom are at the forefront of this transition, investing in green technologies and encouraging energy-efficient cooling systems. The region’s strong regulatory framework and commitment to sustainability are pushing manufacturers to innovate and adopt low-impact refrigerant alternatives.
The Asia-Pacific region holds the largest share of the global refrigerant market, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing demand for air conditioning and refrigeration systems. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are witnessing a surge in residential and commercial construction, which, in turn, fuels the need for HVAC systems and cold storage solutions. China, in particular, is a major producer and consumer of refrigerants, with a well-established manufacturing base and strong government support for low-emission technologies. The region is also experiencing a gradual shift toward environmentally friendly refrigerants, spurred by both domestic environmental policies and international agreements.
The fluorocarbon segment generated the maximum market share of 54% in 2024. Products such as R-134a, R-410A, and R-404A are commonly used due to their stability, non-corrosive properties, and effective cooling performance. These refrigerants have been widely adopted because of their compatibility with existing system designs and ease of use. However, environmental concerns over their high global warming potential have prompted regulatory bodies to implement gradual phase-down measures. In response, newer fluorocarbon products like R-32 and various HFO (hydrofluoroolefin) blends with lower GWP are emerging as transitional solutions.
The hydrocarbon segment is projected to experience the highest CAGR during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. Products such as R-290 (propane), R-600a (isobutane), and R-1270 (propylene) are particularly popular in domestic refrigeration and light commercial cooling applications. These hydrocarbons are naturally occurring substances with negligible ozone depletion potential and very low GWP, making them a strong choice for industries seeking to reduce environmental impact. Their superior thermodynamic efficiency contributes to reduced energy consumption, which is increasingly valued in sustainability-driven markets.
The stationary air conditioning, heat pumps, and chillers segment led the market in 2024. Stationary air conditioning remains the largest segment, fueled by growing urbanization and demand for energy-efficient cooling in residential and commercial buildings. Heat pumps are gaining traction as sustainable solutions for both heating and cooling, supported by increasing environmental awareness and government incentives promoting clean energy technologies. Chillers serve vital industrial and commercial purposes, providing large-scale cooling for manufacturing, data centers, and institutional facilities.
Domestic refrigeration remains a stable and essential segment of the global refrigerant market, supported by consistent demand for household appliances such as refrigerators and freezers. In this category, hydrocarbons like R-600a and R-290 have become the preferred refrigerants due to their low global warming potential and high energy efficiency. These natural refrigerants are particularly suited for use in compact systems and have gained widespread acceptance in both developed and developing markets
By Product
By Application
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Refrigerant Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Refrigerant Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Refrigerant Market, By Product
8.1. Refrigerant Market, by Product
8.1.1. Fluorocarbon
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Hydrocarbon
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Inorganic
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.4. Others
8.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Refrigerant Market, By Application
9.1. Refrigerant Market, by Application
9.1.1. Industrial Refrigeration
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Domestic Refrigeration
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Transport Refrigeration
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.4. Commercial Refrigeration
9.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.5. Stationary Air Conditioning, Heat Pumps, Chillers
9.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.5. Mobile Air Conditioner
9.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Refrigerant Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
10.1. U.S.
10.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
10.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1. Chemours Company
11.1.1. Company Overview
11.1.2. Product Offerings
11.1.3. Financial Performance
11.1.4. Recent Initiatives
11.2. Honeywell International Inc.
11.2.1. Company Overview
11.2.2. Product Offerings
11.2.3. Financial Performance
11.2.4. Recent Initiatives
11.3. Daikin Industries, Ltd.
11.3.1. Company Overview
11.3.2. Product Offerings
11.3.3. Financial Performance
11.3.4. Recent Initiatives
11.4. Arkema S.A.
11.4.1. Company Overview
11.4.2. Product Offerings
11.4.3. Financial Performance
11.4.4. LTE Scientific
11.5. Linde plc
11.5.1. Company Overview
11.5.2. Product Offerings
11.5.3. Financial Performance
11.5.4. Recent Initiatives
11.6. Mexichem S.A.B. de C.V. (now part of Orbia)
11.6.1. Company Overview
11.6.2. Product Offerings
11.6.3. Financial Performance
11.6.4. Recent Initiatives
11.7. Gujarat Fluorochemicals Limited
11.7.1. Company Overview
11.7.2. Product Offerings
11.7.3. Financial Performance
11.7.4. Recent Initiatives
11.8. Koura Global (formerly part of Honeywell)
11.8.1. Company Overview
11.8.2. Product Offerings
11.8.3. Financial Performance
11.8.4. Recent Initiatives
11.9. SRF Limited
11.9.1. Company Overview
11.9.2. Product Offerings
11.9.3. Financial Performance
11.9.4. Recent Initiatives
11.10. Sinochem Group
11.10.1. Company Overview
11.10.2. Product Offerings
11.10.3. Financial Performance
11.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 12. Research Methodology
12.1. Primary Research
12.2. Secondary Research
12.3. Assumptions
Chapter 13. Appendix
13.1. About Us
13.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others