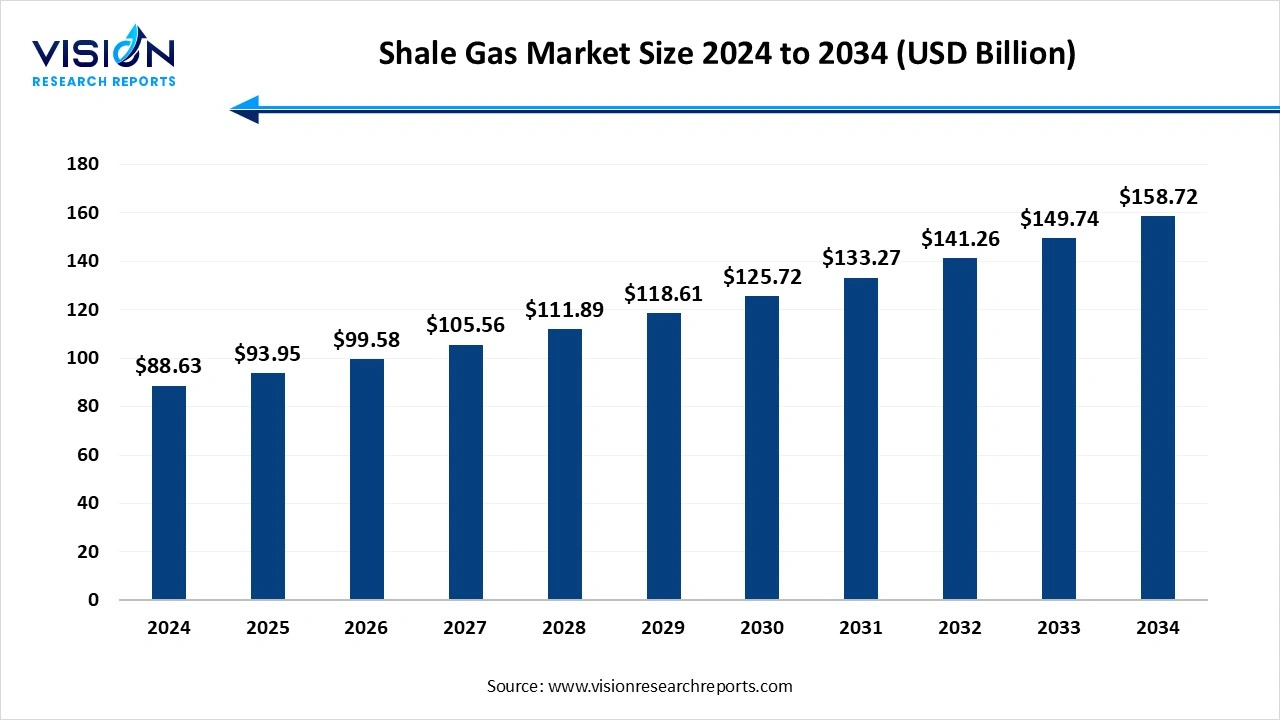
The global shale gas market size was valued at around USD 88.63 billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 158.72 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 6% from 2025 to 2034.
 Key Pointers
Key Pointers
The shale gas market has emerged as a transformative segment within the global energy landscape, driven by advancements in horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing technologies. These innovations have unlocked vast reserves of unconventional natural gas trapped in shale formations, particularly in regions such as North America, China, and Argentina. As a result, shale gas has significantly contributed to energy security, reduced dependency on coal, and enhanced the availability of cleaner-burning fuel alternatives in many developed and emerging economies.
Several key growth factors are driving the expansion of the shale gas market globally. Technological advancements in hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling have significantly improved extraction efficiency and cost-effectiveness, making shale gas production commercially viable even in complex geological formations. These technologies have enabled energy companies to access previously untapped reserves, particularly in countries like the United States, Canada, and China.
Government policies and regulatory support have also played a crucial role in market growth. Many countries are focusing on enhancing energy security and reducing carbon emissions by shifting from coal to gas-based energy solutions. Incentives such as tax breaks, subsidies for upstream exploration, and the development of gas distribution infrastructure have stimulated investment in shale gas projects.
One of the prominent trends in the shale gas market is the increasing integration of digital technologies and automation in exploration and production activities. Oil and gas companies are leveraging tools such as real-time data analytics, artificial intelligence, and remote monitoring systems to enhance operational efficiency and minimize production costs. These digital advancements allow for more precise well placement, predictive maintenance, and optimized resource management, leading to higher yields and lower environmental impact. This trend is expected to continue as operators focus on improving recovery rates and maintaining profitability amid volatile energy prices.
Another key trend is the global diversification of shale gas production beyond North America. While the United States continues to dominate the market, countries like China, Argentina, and the United Kingdom are investing in shale exploration and development to boost domestic energy supply and reduce reliance on imports. At the same time, growing concerns over environmental sustainability are pushing stakeholders to adopt cleaner extraction techniques and implement stricter regulatory standards.
One of the primary challenges facing the shale gas market is the environmental and regulatory scrutiny associated with hydraulic fracturing, or fracking. The process requires large volumes of water mixed with chemicals to fracture shale formations, which can lead to groundwater contamination, seismic activity, and surface pollution if not managed properly. These environmental risks have led to public opposition and stricter government regulations in various regions, making it more complex and costly for companies to obtain permits and operate within legal compliance. In some areas, bans or moratoriums on fracking have slowed down exploration and development activities significantly.
Another major challenge is the economic volatility tied to fluctuating natural gas prices and high production costs. Shale gas extraction, though more advanced today, still demands significant capital investment in drilling, infrastructure, and transport. During periods of low global energy prices, the profitability of shale operations can be severely impacted, leading to project delays or cancellations.
North America led the global shale gas market, holding the highest revenue share of 46% in 2024. The U.S. has witnessed a shale gas revolution over the past decade, fueled by the widespread adoption of hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling technologies. This has transformed the U.S. from a major energy importer to a leading natural gas exporter. The abundance of shale reserves in basins such as the Marcellus, Barnett, and Haynesville has significantly contributed to domestic energy security, economic growth, and the transition to cleaner energy sources. Canada also plays a vital role in North America’s shale gas landscape, with active exploration and development in regions such as British Columbia and Alberta.
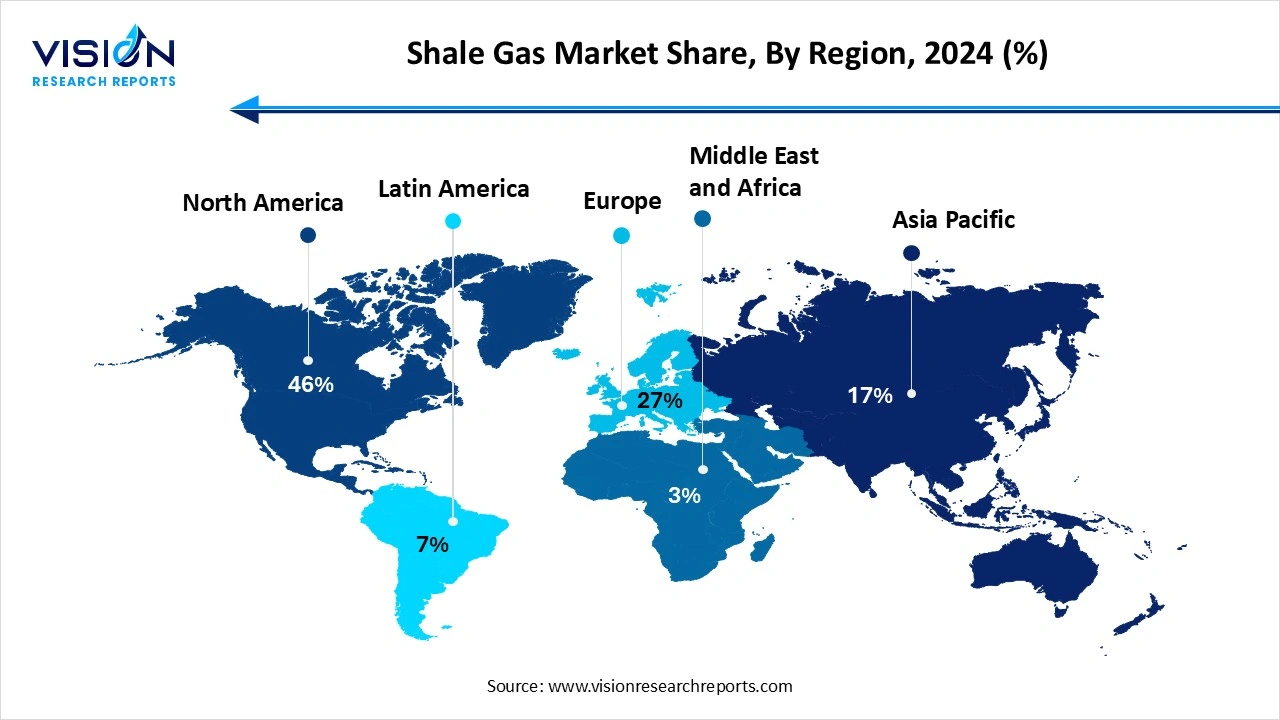 In the Asia Pacific region, China is emerging as a key player in the shale gas market due to its strategic focus on energy diversification and reducing reliance on coal. Despite facing technical and geological challenges, China is investing heavily in shale gas exploration and infrastructure development. The Chinese government has introduced policy incentives and partnerships with foreign firms to accelerate the commercialization of shale resources.
In the Asia Pacific region, China is emerging as a key player in the shale gas market due to its strategic focus on energy diversification and reducing reliance on coal. Despite facing technical and geological challenges, China is investing heavily in shale gas exploration and infrastructure development. The Chinese government has introduced policy incentives and partnerships with foreign firms to accelerate the commercialization of shale resources.
The power generation segment led the market, capturing the largest revenue share of 28% in 2024. Shale gas, as a low-carbon alternative to coal, is widely used in gas-fired power plants to produce electricity with reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Countries striving to transition from coal-based energy systems to more environmentally friendly solutions are increasingly adopting shale gas for electricity generation. Its abundance, relatively low cost, and compatibility with existing power infrastructure make it a viable fuel source for base-load and peak-load electricity needs.
The industrial application segment is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6% between 2025 and 2034. Industries such as chemicals, fertilizers, cement, and glass rely heavily on natural gas as both a feedstock and a source of energy. Shale gas provides a cost-effective and reliable alternative to conventional fuels, enhancing energy security and operational efficiency across various industrial sectors. In the chemical industry, for example, natural gas liquids derived from shale gas such as ethane and propane are key raw materials for the production of plastics and other petrochemicals.
By Application
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Shale Gas Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Shale Gas Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Shale Gas Market, By Application
8.1.Shale Gas Market, by Application Type
8.1.1. Aerospace & Defense
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Medical
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Automotive
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.4. Consumer Products & Industrial
8.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.5. Others
8.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global Shale Gas Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
9.1. North America
9.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.1.2. U.S.
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.1.3. Rest of North America
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.2. Europe
9.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.2.2. UK
9.2.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.2.3. Germany
9.2.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.2.4. France
9.2.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.2.5. Rest of Europe
9.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.3. APAC
9.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.3.2. India
9.3.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.3.3. China
9.3.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.3.4. Japan
9.3.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.3.5. Rest of APAC
9.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.4. MEA
9.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.4.2. GCC
9.4.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.4.3. North Africa
9.4.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.4.4. South Africa
9.4.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.4.5. Rest of MEA
9.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.5. Latin America
9.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.5.2. Brazil
9.5.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
9.5.3. Rest of LATAM
9.5.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
Chapter 10. Company Profiles
10.1. ExxonMobil Corporation
10.1.1. Company Overview
10.1.2. Product Offerings
10.1.3. Financial Performance
10.1.4. Recent Initiatives
10.2. Chevron Corporation
10.2.1. Company Overview
10.2.2. Product Offerings
10.2.3. Financial Performance
10.2.4. Recent Initiatives
10.3. ConocoPhillips
10.3.1. Company Overview
10.3.2. Product Offerings
10.3.3. Financial Performance
10.3.4. Recent Initiatives
10.4. Royal Dutch Shell plc
10.4.1. Company Overview
10.4.2. Product Offerings
10.4.3. Financial Performance
10.4.4. Recent Initiatives
10.5. BP plc
10.5.1. Company Overview
10.5.2. Product Offerings
10.5.3. Financial Performance
10.5.4. Recent Initiatives
10.6. TotalEnergies SE
10.6.1. Company Overview
10.6.2. Product Offerings
10.6.3. Financial Performance
10.6.4. Recent Initiatives
10.7. Cabot Oil & Gas Corporation
10.7.1. Company Overview
10.7.2. Product Offerings
10.7.3. Financial Performance
10.7.4. Recent Initiatives
10.8. Devon Energy Corporation
10.8.1. Company Overview
10.8.2. Product Offerings
10.8.3.Financial Performance
10.8.4. Recent Initiatives
10.9. Chesapeake Energy Corporation
10.9.1. Company Overview
10.9.2. Product Offerings
10.9.3. Financial Performance
10.9.4. Recent Initiatives
10.10. EQT Corporation
10.10.1. Company Overview
10.10.2. Product Offerings
10.10.3. Financial Performance
10.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 11. Research Methodology
11.1. Primary Research
11.2. Secondary Research
11.3. Assumptions
Chapter 12. Appendix
12.1. About Us
12.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others