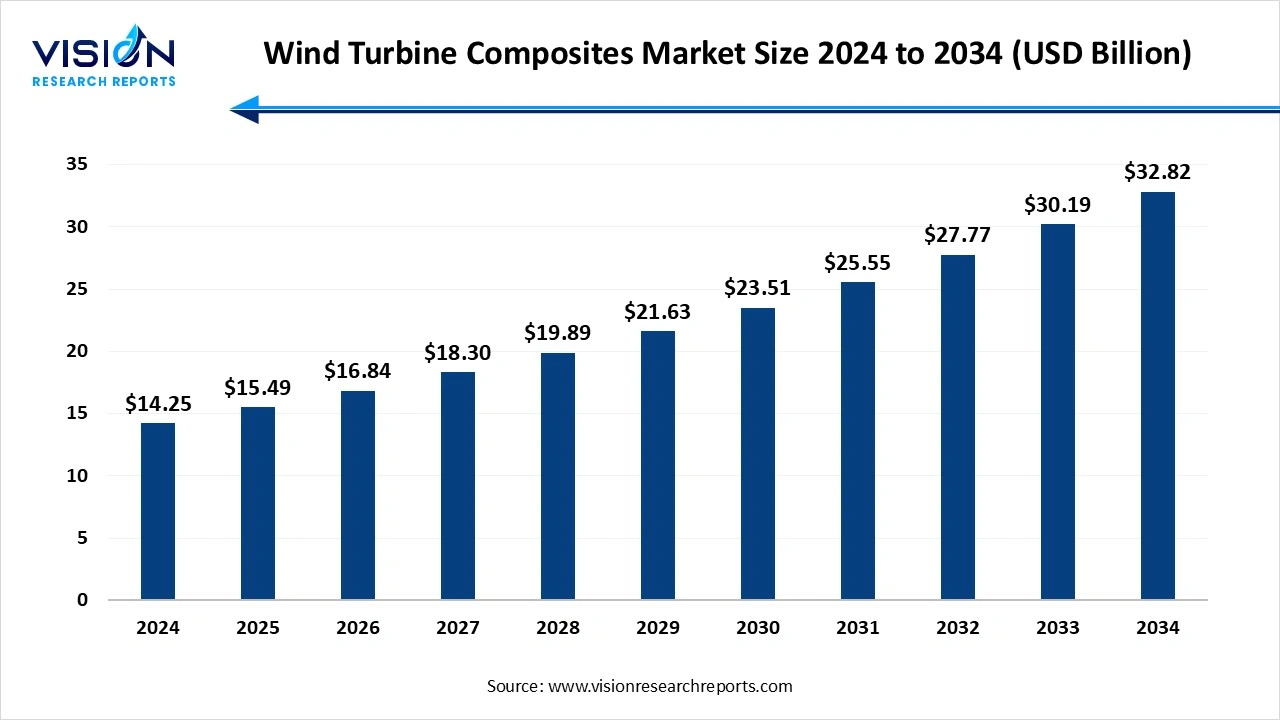
The global wind turbine composites market size was estimated at around USD 14.25 billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 32.82 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.70% from 2025 to 2034.
The wind turbine composites market is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for renewable energy and advancements in composite materials technology. Composites, primarily made from glass fiber and carbon fiber reinforced polymers, are integral in manufacturing wind turbine blades due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. These materials enhance turbine efficiency and lifespan while reducing maintenance costs. The global shift toward sustainable energy solutions, coupled with government incentives and ambitious wind energy capacity targets, is propelling investments in the wind turbine composites sector.
The growth of the wind turbine composites market is primarily fueled by the global transition toward renewable energy sources. Governments worldwide are implementing stringent regulations and offering incentives to reduce carbon emissions, thereby accelerating the adoption of wind energy. Composites, especially glass fiber and carbon fiber reinforced polymers, play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and reliability of wind turbines by providing lightweight yet strong and durable blades. This demand for high-performance materials to improve turbine output and reduce operational costs is driving market expansion.
In addition to environmental and regulatory drivers, technological advancements in composite manufacturing processes are also propelling market growth. Innovations such as resin transfer molding, vacuum-assisted resin infusion, and automated fiber placement are enhancing production efficiency and reducing costs, making composites more accessible for large-scale turbine blade fabrication. Furthermore, ongoing research into bio-based and recyclable composite materials aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability, providing the market with eco-friendly alternatives that meet both performance and environmental standards.
The Asia Pacific wind turbine composites market led the global industry in 2024, capturing the largest revenue share of approximately 32%, primarily fueled by China’s substantial investments in renewable energy infrastructure. This region benefits from ambitious wind energy targets, robust government backing, and an extensive manufacturing base. Composite producers here leverage economies of scale alongside advancing technical expertise. Additionally, rapid urbanization and growing electricity demand continue to strengthen the region’s dominance in wind energy development.
The wind turbine composites market in Europe is propelled by robust environmental regulations and cutting-edge technological innovation. Nations such as Germany, Denmark, and the UK have taken the lead in adopting wind energy, especially in offshore installations. European companies are at the forefront of advancements in blade recycling and the development of high-performance carbon fiber. The European Union's unified energy strategy promotes cross-border collaboration and facilitates the export of composite technology and expertise.
The glass fiber segment dominated the market, capturing the largest revenue share at 73% in 2024. It offers a favorable balance between strength, durability, and affordability, making it the preferred choice for the majority of onshore wind turbine blades. Its widespread availability and well-established manufacturing processes also contribute to its dominant market share. Additionally, advancements in glass fiber technology, such as the development of high-modulus variants, have enhanced its stiffness and fatigue resistance, enabling longer blade designs and improved energy efficiency.
Carbon fiber is the fastest-growing segment, experiencing a CAGR of 9%, fueled by the demand for longer, lighter, and more efficient turbine blades. Carbon fiber composites provide a superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to glass fiber, which translates into lighter blades with greater structural integrity and reduced fatigue. This enables turbines to capture more wind energy while maintaining reliability and safety in harsh environmental conditions. Although carbon fiber is more expensive than glass fiber, its advantages in performance, especially for next-generation wind turbines, are driving increased adoption.
The blades segment led the industry, generating the highest revenue share at 80% in 2024. Composite materials, particularly glass fiber and carbon fiber reinforced polymers, are extensively used in blade manufacturing due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and resistance to environmental stressors. These properties enable the production of longer, lighter blades that improve aerodynamic efficiency and energy capture, directly enhancing the overall performance of wind turbines. The increasing demand for larger turbine blades, driven by the growth of both onshore and offshore wind projects, has further propelled the use of advanced composites.
Nacelles, which house the turbine’s critical components such as the gearbox, generator, and control systems, also utilize composite materials for various structural parts, including covers and housings. The use of composites in nacelle construction offers several advantages, such as reduced weight, enhanced corrosion resistance, and improved mechanical strength, which contribute to the overall reliability and efficiency of the turbine. Glass fiber composites are commonly preferred for nacelle applications because of their cost-effectiveness and favorable performance characteristics.
By Fiber Type
By Application
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approachx
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Wind Turbine Composites Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Wind Turbine Composites Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Wind Turbine Composites Market, By Fiber Type
8.1. Wind Turbine Composites Market, by Fiber Type
8.1.1. Glass fiber
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Carbon fiber
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Others
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Wind Turbine Composites Market, By Application
9.1. Wind Turbine Composites Market, by Application
9.1.1. Blades
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Nacelles
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Others
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Wind Turbine Composites Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
10.1. U.S.
10.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Fiber Type
10.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1. Owens Corning
11.1.1. Company Overview
11.1.2. Product Offerings
11.1.3. Financial Performance
11.1.4. Recent Initiatives
11.2. Hexcel Corporation
11.2.1. Company Overview
11.2.2. Product Offerings
11.2.3. Financial Performance
11.2.4. Recent Initiatives
11.3. Gurit Holding AG
11.3.1. Company Overview
11.3.2. Product Offerings
11.3.3. Financial Performance
11.3.4. Recent Initiatives
11.4. Jushi Group Co., Ltd.
11.4.1. Company Overview
11.4.2. Product Offerings
11.4.3. Financial Performance
11.4.4. LTE Scientific
11.5. Toray Industries, Inc.
11.5.1. Company Overview
11.5.2. Product Offerings
11.5.3. Financial Performance
11.5.4. Recent Initiatives
11.6. SGL Carbon SE
11.6.1. Company Overview
11.6.2. Product Offerings
11.6.3. Financial Performance
11.6.4. Recent Initiatives
11.7. Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Corporation
11.7.1. Company Overview
11.7.2. Product Offerings
11.7.3. Financial Performance
11.7.4. Recent Initiatives
11.8. AOC Aliancys Chemicals
11.8.1. Company Overview
11.8.2. Product Offerings
11.8.3. Financial Performance
11.8.4. Recent Initiatives
11.9. Teijin Limited
11.9.1. Company Overview
11.9.2. Product Offerings
11.9.3. Financial Performance
11.9.4. Recent Initiatives
11.10. Zhejiang Hengyi Group Co., Ltd
11.10.1. Company Overview
11.10.2. Product Offerings
11.10.3. Financial Performance
11.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 12. Research Methodology
12.1. Primary Research
12.2. Secondary Research
12.3. Assumptions
Chapter 13. Appendix
13.1. About Us
13.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others