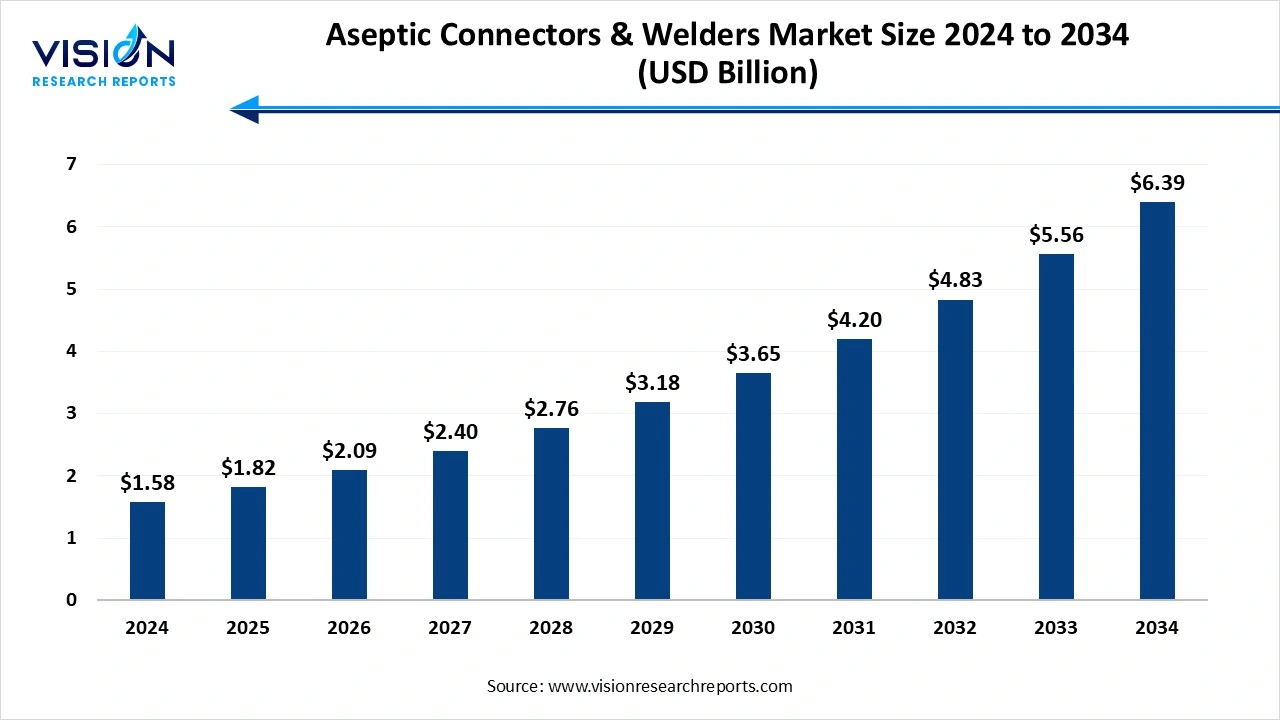
The global aseptic connectors & welders market size was accounted at around USD 1.58 billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 6.39 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 15% from 2025 to 2034.
The aseptic connectors and welders market plays a crucial role in maintaining sterility and integrity in fluid transfer processes, particularly within the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and food & beverage industries. These components are essential for preventing contamination during the handling and transfer of sensitive liquids under sterile conditions. Market growth is primarily driven by the rising demand for biologics and personalized medicines, which require high-precision and contamination-free manufacturing environments. Additionally, the increasing adoption of single-use technologies and the expansion of bioprocessing facilities worldwide are contributing significantly to the demand for advanced aseptic connectors and welders.
The growth of the aseptic connectors and welders market is largely fueled by the expanding biopharmaceutical industry, which demands sterile and reliable fluid handling solutions for manufacturing processes. As biologics, vaccines, and cell and gene therapies gain momentum, there is an increasing need for systems that can support closed, sterile environments to prevent cross-contamination. This demand is further bolstered by the shift toward single-use technologies in bioprocessing, which require aseptic connectors and welders to ensure fluid integrity and streamline operations.
Another significant growth factor is the rapid technological innovation in aseptic processing equipment. Modern connectors and welders are being designed with improved ergonomics, faster setup times, and enhanced compatibility with various tubing and bag systems, all of which contribute to greater operational efficiency. Regulatory pressures and industry standards are also prompting pharmaceutical and biotech companies to upgrade their systems to ensure compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP).
One of the most notable trends in the aseptic connectors and welders market is the growing adoption of single-use systems (SUS) in biopharmaceutical manufacturing. As companies aim to reduce cleaning validation costs and increase production flexibility, single-use technologies have become a preferred choice. This shift has led to higher demand for aseptic connectors and welders that are compatible with disposable systems, offering ease of use, reduced risk of cross-contamination, and improved scalability.
Another key trend is the integration of automation and digital monitoring into aseptic welding and connection systems. Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating features such as automated welding cycles, digital validation, and real-time data logging to ensure traceability and compliance with stringent regulatory requirements. This technological evolution not only enhances process reliability but also aligns with the broader trend of smart manufacturing in the pharmaceutical sector.
One of the primary challenges faced by the aseptic connectors and welders market is the high cost associated with advanced aseptic technologies. Implementing sophisticated equipment and single-use systems requires significant investment, which can be a barrier for small- to mid-sized biopharmaceutical companies, particularly in emerging markets. In addition, the cost of training personnel to operate and maintain these systems effectively adds to the overall expenditure. This financial burden can slow down the adoption rate, especially in regions where capital resources are limited or where traditional systems are still prevalent.
Another critical challenge is the complexity of regulatory compliance. The aseptic processing environment is governed by strict standards such as cGMP, ISO certifications, and other health authority guidelines, which require rigorous validation and documentation. Navigating these regulatory frameworks can be both time-consuming and resource-intensive, particularly as global requirements vary.
The North American aseptic connectors and welders industry led the global market, capturing the highest revenue share of 49% in 2024. The United States, in particular, plays a dominant role in regional market growth, supported by favorable regulatory frameworks, increased investments in biologics, and the expansion of single-use technologies in pharmaceutical production.
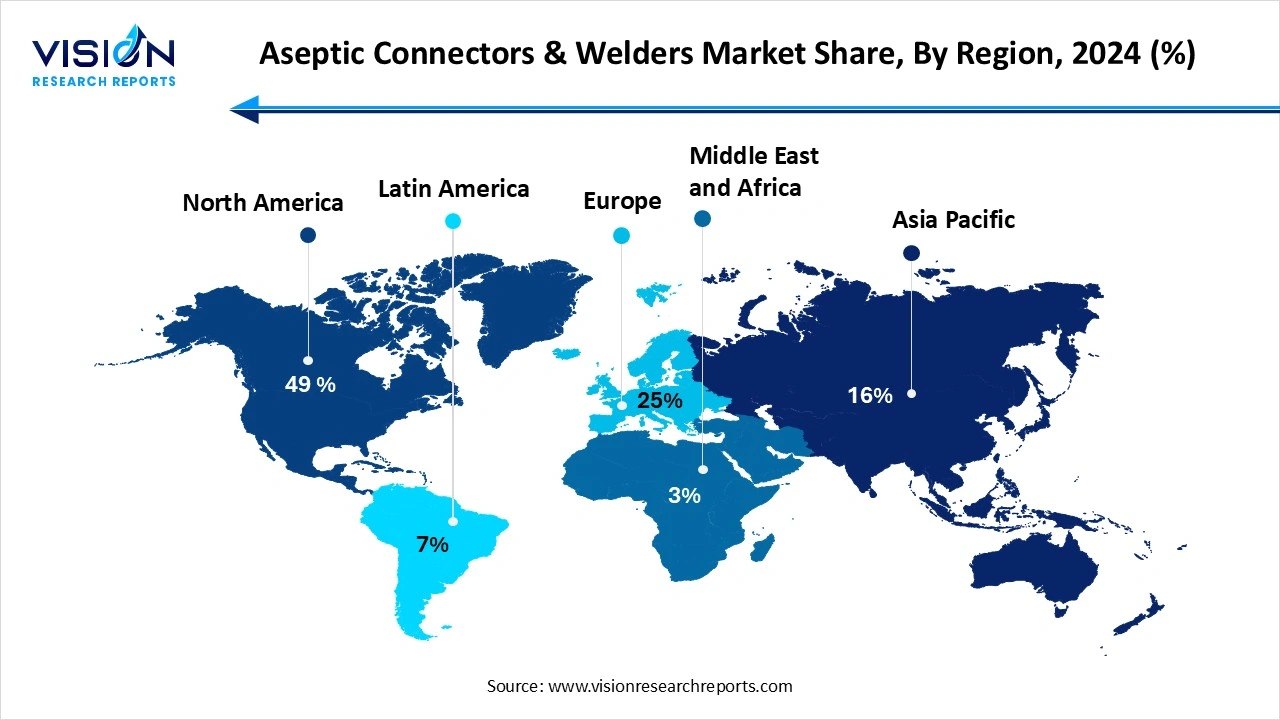 The Asia Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market due to increased pharmaceutical outsourcing, rapid industrialization, and government support for biotech and healthcare infrastructure. Countries like China, India, and South Korea are investing heavily in pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities, leading to greater demand for sterile processing equipment, including aseptic connectors and welders.
The Asia Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market due to increased pharmaceutical outsourcing, rapid industrialization, and government support for biotech and healthcare infrastructure. Countries like China, India, and South Korea are investing heavily in pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities, leading to greater demand for sterile processing equipment, including aseptic connectors and welders.
The aseptic connectors segment held the dominant position in the market, accounting for the largest share in 2024. Aseptic connectors are designed to facilitate contamination-free connections between various systems and components, ensuring the integrity of sterile processes. These connectors are widely used in upstream and downstream bioprocessing, enabling flexible and closed systems that reduce the risk of microbial ingress.
The aseptic welders segment is anticipated to register a substantial CAGR throughout the forecast period. These devices are used to thermally bond tubing in a way that maintains sterility, making them essential for processes that involve fluid transfers under stringent cleanroom conditions. The aseptic welders market is benefiting from increasing automation in bioprocessing operations and the need for scalable solutions that support high-volume production without compromising safety or quality. Modern aseptic welders are being developed with enhanced control systems, faster cycle times, and digital documentation capabilities to meet regulatory compliance and improve traceability.
The upstream bioprocessing segment accounted for the highest revenue share, capturing 46% of the market in 2024. These components ensure closed and contamination-free fluid transfers, which are critical for preserving cell viability and ensuring consistent process performance. Aseptic connectors allow seamless integration of various single-use and stainless-steel systems, making it easier to scale operations and improve production flexibility. Similarly, aseptic welders are used to form sterile bonds between tubing systems without the need for cleanroom breaks, helping maintain the aseptic environment required for sensitive upstream operations.
The downstream bioprocessing segment is projected to experience the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. These stages require ultra-clean environments to avoid any contamination that could compromise the safety or efficacy of the end product. Aseptic connectors provide safe and sterile fluid transfers between different components and systems, such as chromatography skids, buffer vessels, and single-use containers. Aseptic welders, on the other hand, are widely used to join fluid paths securely and hygienically, ensuring leak-proof connections even during high-volume processing.
The OEMs segment led the market, securing the highest revenue share of 40% in 2024. These companies are responsible for designing and producing bioprocessing equipment and integrated systems used across pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. OEMs rely on high-quality aseptic connectors and welders to incorporate into their machines and modular systems, ensuring sterility, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. As the demand for automated and single-use bioprocessing systems grows, OEMs are increasingly sourcing advanced connectors and welding technologies that support seamless integration, offer user-friendly interfaces, and enhance process scalability.
The CROs & CMOs segment is expected to register the highest CAGR over the course of the forecast period. These organizations play a crucial role in accelerating time-to-market for new biologics and biosimilars by providing specialized, flexible, and scalable production capabilities. To maintain the integrity and sterility of drug products across varying production volumes and project scopes, CROs and CMOs require reliable aseptic connectors and welders that support closed-system processing and comply with international quality standards.
By Product
By Application
By End Use
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Product Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Aseptic Connectors & Welders Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Aseptic Connectors & Welders Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Aseptic Connectors & Welders Market, By Product
8.1. Aseptic Connectors & Welders Market, by Product
8.1.1 Aseptic Connectors
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Tubing Size
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Aseptic Welders
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global Aseptic Connectors & Welders Market, By Application
9.1. Aseptic Connectors & Welders Market, by Application
9.1.1. Upstream Bioprocessing
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Downstream Bioprocessing
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Harvest & Fill-finish Operations
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Global Aseptic Connectors & Welders Market, By End Use
10.1. Aseptic Connectors & Welders Market, by End Use
10.1.1. Biopharmaceutical & Pharmaceutical Companies
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.2. OEMs
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.3. CROs & CMOs
10.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.4. Academic & Research Institutes
10.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 11. Global Aseptic Connectors & Welders Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
11.1. North America
11.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.1.4. U.S.
11.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.1.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.1.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.1.5. Rest of North America
11.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.2. Europe
11.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.2.4. UK
11.2.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.2.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.2.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.2.5. Germany
11.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.2.6. France
11.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.2.7. Rest of Europe
11.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.3. APAC
11.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.3.4. India
11.3.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.3.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.3.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.3.5. China
11.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.3.6. Japan
11.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.3.7. Rest of APAC
11.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.4. MEA
11.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.4.4. GCC
11.4.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.4.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.4.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.4.5. North Africa
11.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.4.6. South Africa
11.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.4.7. Rest of MEA
11.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.5. Latin America
11.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.5.4. Brazil
11.5.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.5.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.5.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
11.5.5. Rest of LATAM
11.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1. Sartorius AG.
12.1.1. Company Overview
12.1.2. Product Offerings
12.1.3. Financial Performance
12.1.4. Recent Initiatives
12.2. Merck KGaA.
12.2.1. Company Overview
12.2.2. Product Offerings
12.2.3. Financial Performance
12.2.4. Recent Initiatives
12.3. Pall Corporation (a Danaher company).
12.3.1. Company Overview
12.3.2. Product Offerings
12.3.3. Financial Performance
12.3.4. Recent Initiatives
12.4. Saint-Gobain Life Sciences.
12.4.1. Company Overview
12.4.2. Product Offerings
12.4.3. Financial Performance
12.4.4. Recent Initiatives
12.5. CPC – Colder Products Company.
12.5.1. Company Overview
12.5.2. Product Offerings
12.5.3. Financial Performance
12.5.4. Recent Initiatives
12.6. Terumo BCT
12.6.1. Company Overview
12.6.2. Product Offerings
12.6.3. Financial Performance
12.6.4. Recent Initiatives
12.7. Meissner Filtration Products.
12.7.1. Company Overview
12.7.2. Product Offerings
12.7.3. Financial Performance
12.7.4. Recent Initiatives
12.8. Entegris, Inc.
12.8.1. Company Overview
12.8.2. Product Offerings
12.8.3. Financial Performance
12.8.4. Recent Initiatives
12.9. Parker Hannifin Corporation.
12.9.1. Company Overview
12.9.2. Product Offerings
12.9.3. Financial Performance
12.9.4. Recent Initiatives
12.10. Repligen Corporation
12.10.1. Company Overview
12.10.2. Product Offerings
12.10.3. Financial Performance
12.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 13. Research Methodology
13.1. Primary Research
13.2. Secondary Research
13.3. Assumptions
Chapter 14. Appendix
14.1. About Us
14.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others