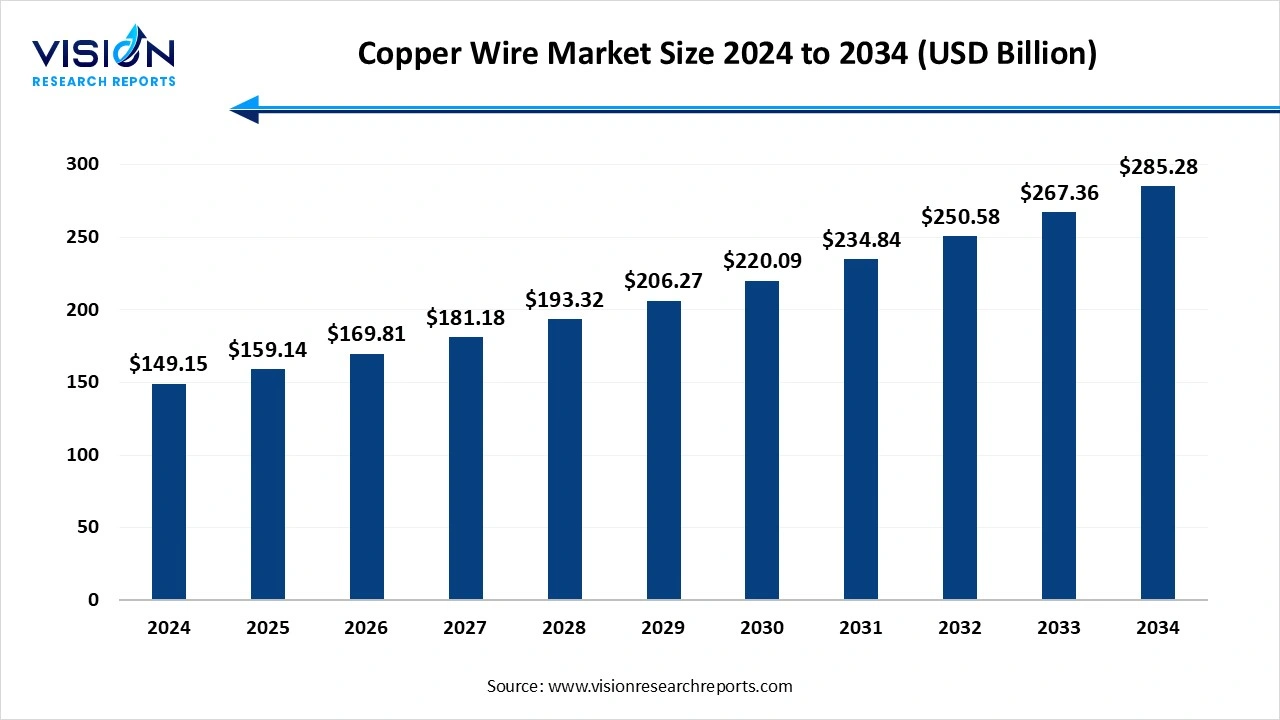
The global copper wire market size was estimated at USD 149.15 billion in 2024 and it is expected to surpass around USD 285.28 billion by 2034, poised to grow at a CAGR of 6.70% from 2025 to 2034.
The copper wire market plays a vital role in the global economy, driven by its extensive use across electrical, construction, telecommunications, and automotive industries. Copper wire is valued for its superior electrical conductivity, ductility, and corrosion resistance, making it a fundamental material in power generation, transmission, and distribution systems. As nations expand infrastructure and transition toward renewable energy sources, demand for copper wire continues to grow steadily. Additionally, rapid urbanization and industrial development especially in emerging economies are fueling market expansion. The rise of electric vehicles (EVs), 5G networks, and smart grid technologies further enhances copper wire consumption. With sustainability gaining prominence, the market is also witnessing increased recycling efforts, helping to stabilize supply and reduce environmental impact.
The growth of the copper wire market is primarily driven by the increasing demand for electricity and the expansion of power infrastructure worldwide. As both developed and developing nations invest heavily in upgrading their transmission and distribution networks, copper wire remains the preferred choice due to its excellent conductivity and durability. The global shift toward renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, also contributes significantly to market growth, as these systems rely heavily on copper wiring for energy transmission and grid integration.
Another key growth factor is the rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and advancements in the automotive and electronics industries. EVs require significantly more copper wiring than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, particularly in motors, battery packs, and charging systems. Moreover, the proliferation of smart devices, IoT technologies, and 5G networks is fueling demand for high- rformance electrical components, further accelerating copper wire usage across various sectors.
The global copper wire market exhibits notable regional variations, with Asia Pacific emerging as the dominant player due to its massive industrial base, high population density, and ongoing urban infrastructure development. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are witnessing robust demand for copper wire across sectors such as construction, consumer electronics, power generation, and automotive. China, in particula, holds a significant share of global copper consumption, driven by its leadership in manufacturing and renewable energy capacity additions. The rapid pace of electrification and infrastructure modernization in Southeast Asia also contributes to regional market growth.
The U.S. copper wire market is witnessing strong growth fueled by several important factors. Rising electricity demand is driving extensive use of copper wire in power generation, transmission, and distribution networks. Additionally, significant investments in construction projects spanning residential, commercial, and industrial sectors are propelling market expansion, as copper wire remains a critical component for electrical wiring. Furthermore, the ongoing development of smart grids and efforts to modernize power infrastructure are increasing the need for advanced copper wiring solutions that improve efficiency and ensure system reliability.
Low voltage copper wires are extensively used in residential, commercial, and light industrial settings. These wires are essential for powering everyday electrical systems, including household appliances, lighting fixtures, and small-scale machinery. Due to copper's high conductivity and flexibility, low voltage copper wires offer reliable performance in environments where safety and efficiency are critical. Additionally, the growing demand for smart homes, increased urbanization, and the proliferation of electronic devices have significantly contributed to the rising consumption of low voltage copper wires across the globe.
Hand, high voltage copper wires are crucial in large-scale power transmission and distribution systems. They are primarily utilized in utility grids, renewable energy installations, and heavy industrial applications where electricity needs to be transferred over long distances with minimal loss. The ongoing expansion of national and cross-border grid infrastructure, along with the integration of wind and solar power plants, has spurred the demand for high voltage copper wires. These wires are engineered to withstand extreme mechanical and thermal stress, ensuring stable performance under heavy electrical loads.
In the global copper wire market, the building wire segment plays a fundamental role, driven by the rising demand for safe and efficient electrical wiring systems in residential, commercial, and industrial construction projects. Copper building wires are widely preferred for their superior conductivity, flexibility, and long-term reliability. They are integral to the internal electrical infrastructure of buildings, supporting lighting, HVAC systems, and general power distribution. Rapid urbanization, increasing construction of smart buildings, and the growth of real estate development particularly in emerging economies are key factors fueling the demand for copper building wires.
The renewable energy segment represents another dynamic area of growth for the copper wire market. As countries invest in clean energy infrastructure to meet sustainability goals and reduce carbon emissions, copper wires are playing a crucial role in the development and operation of solar, wind, and hydropower projects. These renewable systems require extensive wiring networks to connect generation units with energy storage systems and power grids. Copper's high thermal and electrical conductivity ensures efficient energy transfer, making it indispensable in harsh outdoor environments typical of renewable installations.
By Voltage
By Application
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Copper Wire Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Copper Wire Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Copper Wire Market, By Voltage
8.1. Copper Wire Market, by Voltage
8.1.1. Low
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Medium
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. High
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Copper Wire Market, By Application
9.1. Copper Wire Market, by Application
9.1.1. Building Wire
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Power Distribution
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Automotive
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.4. Communication
9.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.5. Renewable Energy
9.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Copper Wire Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
10.1. U.S.
10.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage
10.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1. Southwire Company, LLC
11.1.1. Company Overview
11.1.2. Product Offerings
11.1.3. Financial Performance
11.1.4. Recent Initiatives
11.2. Prysmian Group
11.2.1. Company Overview
11.2.2. Product Offerings
11.2.3. Financial Performance
11.2.4. Recent Initiatives
11.3. Nexans S.A.
11.3.1. Company Overview
11.3.2. Product Offerings
11.3.3. Financial Performance
11.3.4. Recent Initiatives
11.4. LS Cable & System Ltd.
11.4.1. Company Overview
11.4.2. Product Offerings
11.4.3. Financial Performance
11.4.4. LTE Scientific
11.5. General Cable Technologies Corporation (part of Prysmian Group)
11.5.1. Company Overview
11.5.2. Product Offerings
11.5.3. Financial Performance
11.5.4. Recent Initiatives
11.6. Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd.
11.6.1. Company Overview
11.6.2. Product Offerings
11.6.3. Financial Performance
11.6.4. Recent Initiatives
11.7. Encore Wire Corporation
11.7.1. Company Overview
11.7.2. Product Offerings
11.7.3. Financial Performance
11.7.4. Recent Initiatives
11.8. Superior Essex Inc.
11.8.1. Company Overview
11.8.2. Product Offerings
11.8.3. Financial Performance
11.8.4. Recent Initiatives
11.9. Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd.
11.9.1. Company Overview
11.9.2. Product Offerings
11.9.3. Financial Performance
11.9.4. Recent Initiatives
11.10. Havells India Limited
11.10.1. Company Overview
11.10.2. Product Offerings
11.10.3. Financial Performance
11.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 12. Research Methodology
12.1. Primary Research
12.2. Secondary Research
12.3. Assumptions
Chapter 13. Appendix
13.1. About Us
13.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others