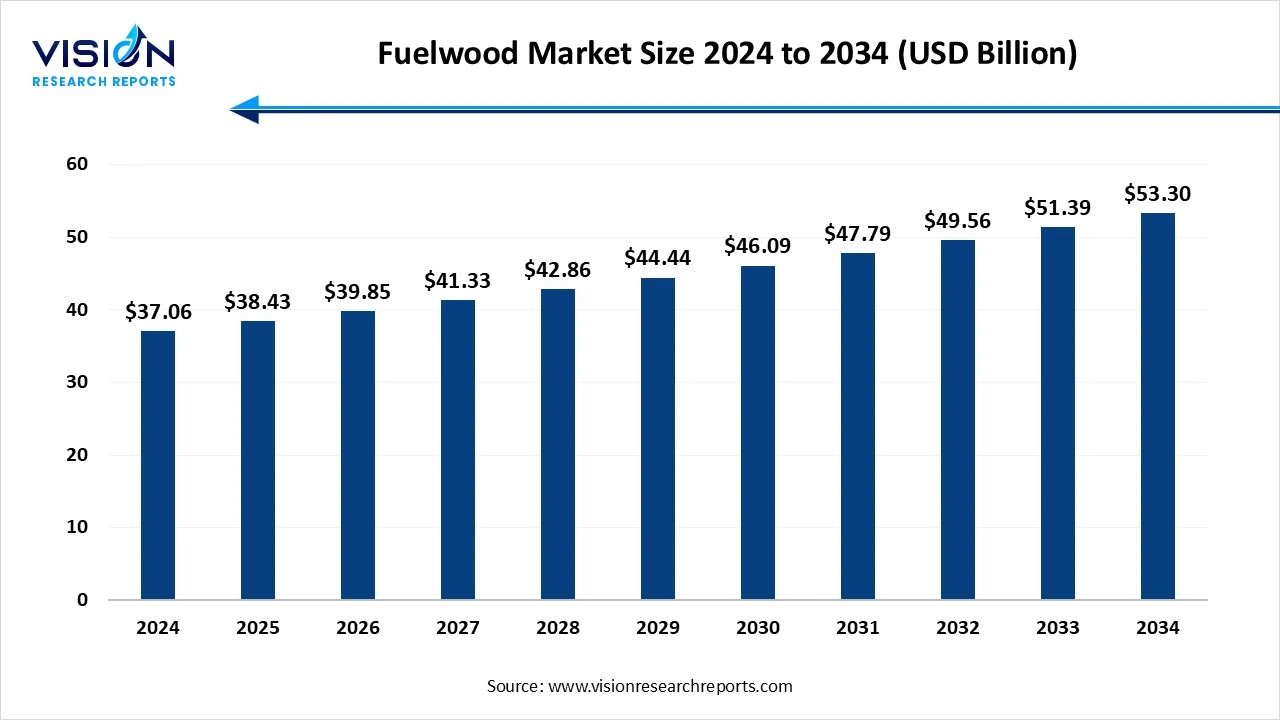
The global fuelwood market size was estimated at around USD 37.06 billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 53.30 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 3.70% from 2025 to 2034.
 Key Pointers
Key PointersThe fuelwood market plays a vital role in the global energy landscape, particularly in rural and developing regions where it remains a primary source of heating and cooking fuel. Fuelwood, derived from sustainably managed forests, woodlots, and agricultural residues, is widely used due to its accessibility, affordability, and cultural familiarity. It serves both domestic households and small industries, especially in regions lacking reliable access to modern energy alternatives.
Despite increasing urbanization and the rise of cleaner energy technologies, the demand for fuelwood continues to hold strong in many parts of Asia, Africa, and Latin America. It also contributes to local economies through informal supply chains, providing livelihoods for woodcutters, traders, and transporters. However, unsustainable harvesting and inefficient usage practices pose environmental concerns, including deforestation and indoor air pollution.
The growth of the fuelwood market is primarily fueled by its widespread use in rural and off-grid communities, where access to electricity and alternative energy sources remains limited. In many parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and Latin America, fuelwood is an essential energy resource for daily cooking and heating needs. The affordability and easy availability of wood as a renewable biomass resource continue to drive its demand among low-income households.
The market benefits from the increasing recognition of biomass energy as a renewable and carbon-neutral source when harvested sustainably. Governments and development organizations are promoting community-based forest management and sustainable woodlot cultivation to meet growing energy needs while reducing environmental degradation. Technological advancements such as improved biomass stoves and better kiln designs for charcoal production are enhancing energy efficiency and reducing emissions, which in turn support market growth.
Europe led the fuelwood market, capturing the largest revenue share of 60% in 2024. This dominance is driven by the region’s substantial consumption of fuelwood and biomass products, supported by robust government initiatives aimed at promoting renewable energy and achieving climate objectives. Numerous European countries provide subsidies for biomass heating systems, boosting demand for fuelwood, pellets, and briquettes across residential and industrial sectors. Additionally, Europe’s commitment to lowering carbon emissions has accelerated the adoption of advanced biomass technologies and the implementation of stringent regulations focused on sustainable forestry management and emissions control.
The fuelwood market in the Asia Pacific region is primarily propelled by its vast rural population and heavy reliance on traditional biomass for energy. In countries such as India, Indonesia, and Bangladesh, millions of households depend on fuelwood as their main source of energy for cooking and heating, largely due to limited access to modern fuels. While government initiatives promoting clean cooking solutions and the adoption of improved biomass technologies are gradually reshaping the market, the use of traditional fuelwood remains deeply rooted, particularly in remote and low-income communities.
The natural forests segment dominated the market, capturing the largest revenue share of 52% in 2024. In numerous rural communities, especially in parts of Africa, Asia, and Latin America, people rely heavily on wood gathered directly from natural forests for their daily energy needs. These forests, often unmanaged or under community stewardship, provide an accessible and low-cost fuel source. However, this reliance on natural forests raises serious sustainability concerns. Overharvesting without adequate regeneration can lead to deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and soil degradation, which in turn threaten the long-term availability of fuelwood and the health of ecosystems. 
The plantation forests segment is expected to experience the fastest growth, with a CAGR of 4.2% over the forecast period. These plantations, established through planned forestry initiatives, offer a renewable and more controlled supply of wood biomass. They are designed to meet the growing energy demand while reducing the pressure on natural forest resources. Managed plantations enable the sustainable harvesting of wood with periodic replanting, ensuring a steady fuelwood supply for residential and industrial use. This source type is particularly prominent in countries with active forestry policies and investments in bioenergy. impacts, yet the transition away from traditional fuelwood remains gradual and uneven across regions.
The residential heating and cooking segment dominated the market, capturing the largest revenue share of 55% in 2024. In numerous low-income countries, fuelwood serves as the primary source of energy for daily household activities such as preparing meals and maintaining indoor warmth during colder months. Its accessibility, low upfront cost, and traditional usage make it an indispensable resource for millions of households lacking reliable access to electricity or cleaner fuels like LPG and natural gas.
The industrial heating segment is expected to experience the highest CAGR growth throughout the forecast period. Industries such as brick kilns, food processing units, and small-scale ceramics rely on fuelwood as a cost-effective and locally available fuel source. The use of fuelwood in industrial heating is especially prevalent in regions where alternative energy supplies are either scarce or prohibitively expensive. While this sector contributes significantly to the overall demand for fuelwood, it also presents challenges in terms of sustainability and emissions.
By Source Type 
By End Use 
By Regional 
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Source Type Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Source Type Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Source Type Market, By Source Type
8.1. Source Type Market, by Source Type
8.1.1. Natural Forests
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Plantation Forests
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Agroforestry
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.4. Others
8.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Source Type Market, By End Use
9.1. Source Type Market, by End Use
9.1.1. Residential Heating & Cooking
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Industrial Heating
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Power Generation
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.4. Others
9.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Source Type Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
10.1. U.S.
10.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Source Type
10.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1. Enviva Inc.
11.1.1. Company Overview
11.1.2. Product Offerings
11.1.3. Financial Performance
11.1.4. Recent Initiatives
11.2. Drax Group plc
11.2.1. Company Overview
11.2.2. Product Offerings
11.2.3. Financial Performance
11.2.4. Recent Initiatives
11.3. Pinnacle Renewable Energy Inc.
11.3.1. Company Overview
11.3.2. Product Offerings
11.3.3. Financial Performance
11.3.4. Recent Initiatives
11.4. Graanul Invest
11.4.1. Company Overview
11.4.2. Product Offerings
11.4.3. Financial Performance
11.4.4. LTE Scientific
11.5. Fram Renewable Fuels, LLC
11.5.1. Company Overview
11.5.2. Product Offerings
11.5.3. Financial Performance
11.5.4. Recent Initiatives
11.6. Westervelt Company
11.6.1. Company Overview
11.6.2. Product Offerings
11.6.3. Financial Performance
11.6.4. Recent Initiatives
11.7. Energex Corporation
11.7.1. Company Overview
11.7.2. Product Offerings
11.7.3. Financial Performance
11.7.4. Recent Initiatives
11.8. Andritz AG
11.8.1. Company Overview
11.8.2. Product Offerings
11.8.3. Financial Performance
11.8.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 12. Research Methodology
12.1. Primary Research
12.2. Secondary Research
12.3. Assumptions
Chapter 13. Appendix
13.1. About Us
13.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others