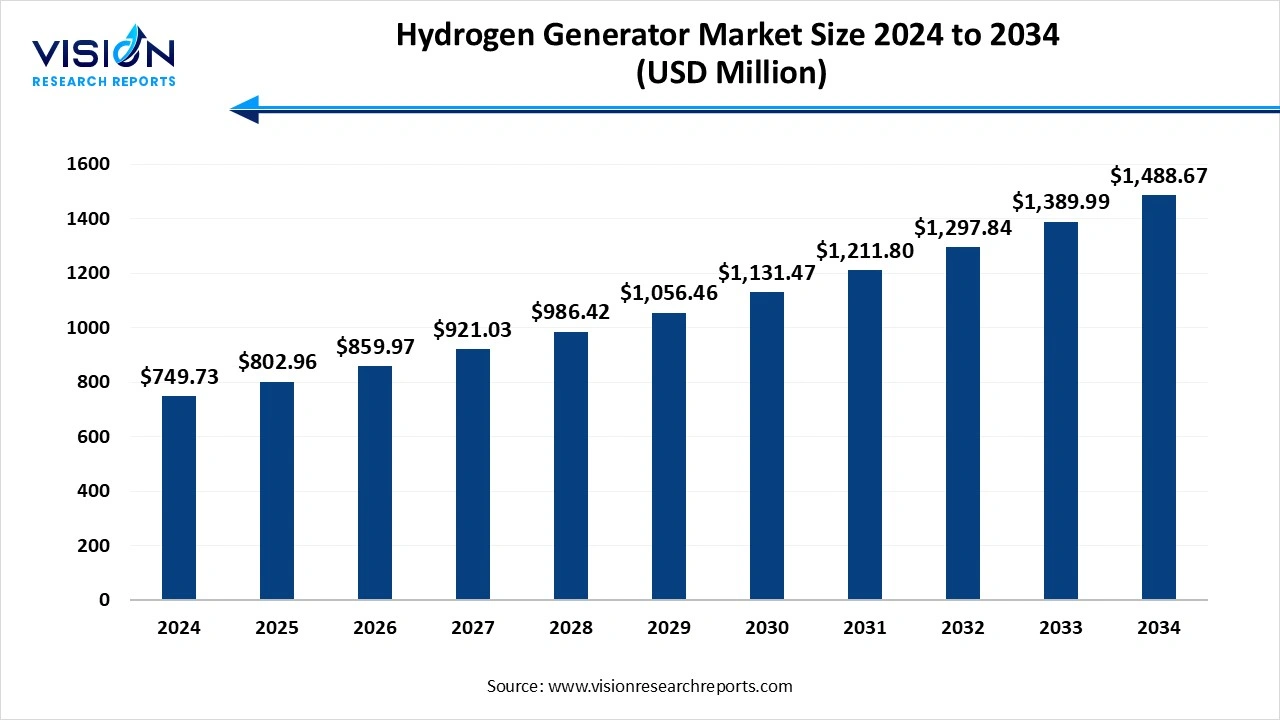
The global hydrogen generator market size was reached at around USD 749.73 million in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 1,488.67 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 7.10% from 2025 to 2034.
 Key Pointers
Key Pointers
The hydrogen generator market is gaining significant momentum as industries and governments worldwide pivot toward cleaner energy solutions. Hydrogen generators, which produce hydrogen on-site through processes like electrolysis or steam methane reforming, are increasingly being adopted across sectors such as chemicals, oil & gas, power generation, and transportation. This shift is driven by the growing demand for sustainable fuel alternatives and the need to reduce dependency on fossil fuels.
One of the primary growth factors driving the hydrogen generator market is the increasing global focus on clean and sustainable energy solutions. Governments across the world are implementing stringent environmental regulations and offering incentives to reduce carbon emissions, which has significantly accelerated the adoption of hydrogen as a green energy carrier. Hydrogen generators, particularly those based on electrolysis using renewable energy, play a vital role in decarbonizing sectors like transportation, industrial processing, and power generation.
Another key factor is the rising demand for on-site hydrogen production to ensure safety, cost-efficiency, and supply reliability. On-site hydrogen generators eliminate the need for storage and transportation of compressed gas, making them a preferred solution across industries such as chemical manufacturing, oil refining, and electronics. Additionally, technological advancements in compact and modular hydrogen generators have made them more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises.
The hydrogen generator market is witnessing several emerging trends that are reshaping its landscape. One notable trend is the rapid development and adoption of green hydrogen technologies, especially electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind. This shift is driven by the need to reduce carbon emissions and align with global decarbonization goals. Many countries are investing heavily in green hydrogen infrastructure and pilot projects, positioning electrolysis-based hydrogen generators as a key technology for the future.
Another major trend is the integration of hydrogen generators in distributed energy systems and industrial clusters. Companies are increasingly deploying modular and scalable hydrogen generators for on-site applications, which enhances energy efficiency and reduces logistic costs. In sectors like mobility, there is growing interest in pairing hydrogen generators with fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) infrastructure.
One of the major challenges faced by the hydrogen generator market is the high capital and operational costs associated with hydrogen production technologies, particularly electrolysis. While green hydrogen is seen as a sustainable solution, the cost of electrolyzers, along with the need for renewable energy inputs, often makes it less economically competitive compared to conventional hydrogen derived from fossil fuels. This cost disparity limits widespread adoption, especially in price-sensitive markets. Moreover, the infrastructure required for production, storage, and distribution of hydrogen adds to the overall investment burden, creating barriers for small and medium enterprises.
Another critical challenge is the lack of standardized regulations and infrastructure to support hydrogen deployment at scale. Many regions still lack well-defined safety standards, certification processes, and transport logistics tailored for hydrogen applications. This regulatory uncertainty discourages investment and slows the commercialization of advanced hydrogen generation technologies.
Asia Pacific led the global hydrogen generator market, accounting for 35% of the total revenue share in 2024. Countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India are actively promoting hydrogen as a part of their long-term energy strategies. China, in particular, is investing in hydrogen production to support its vast manufacturing base and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Meanwhile, Japan and South Korea are focusing on hydrogen fuel cells and related infrastructure, encouraging the deployment of compact and portable hydrogen generators.
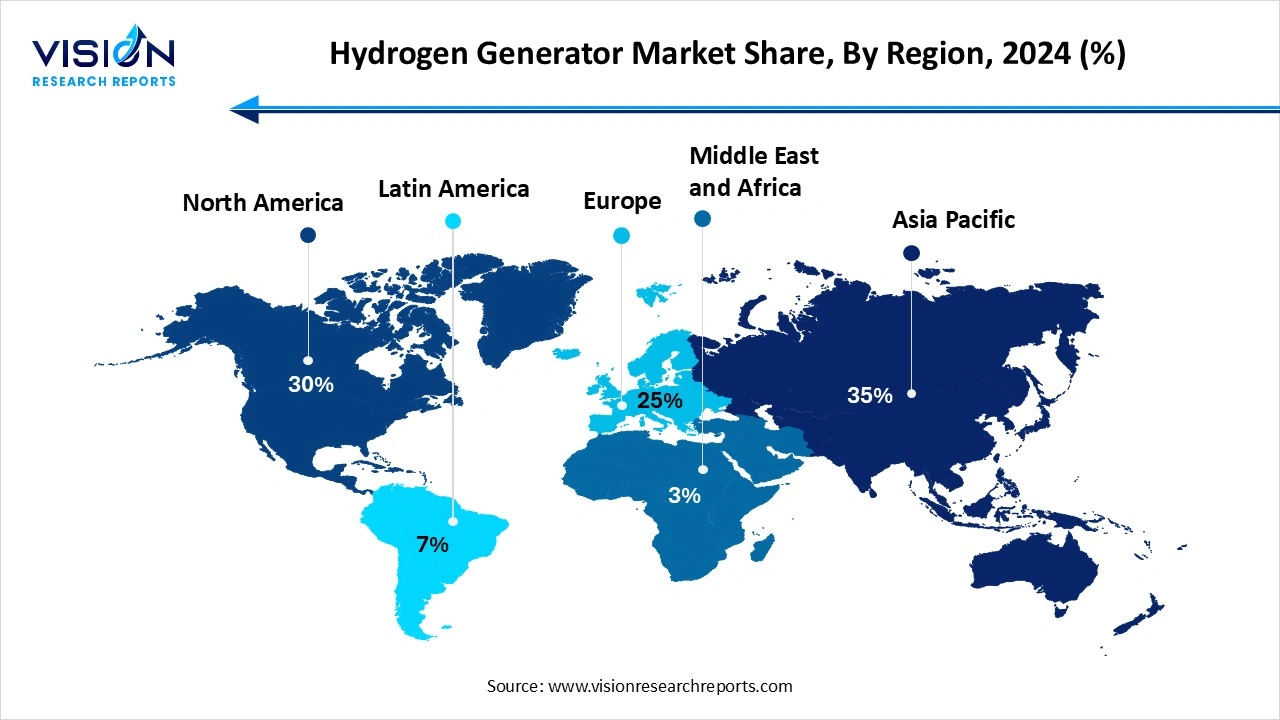 The North American hydrogen generator market is projected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The United States, in particular, is at the forefront with supportive government initiatives, pilot projects, and partnerships aimed at expanding hydrogen production capacity. The region’s focus on reducing carbon emissions and transitioning to clean energy solutions has bolstered the adoption of both steam reforming and electrolysis-based hydrogen generators across multiple sectors.
The North American hydrogen generator market is projected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The United States, in particular, is at the forefront with supportive government initiatives, pilot projects, and partnerships aimed at expanding hydrogen production capacity. The region’s focus on reducing carbon emissions and transitioning to clean energy solutions has bolstered the adoption of both steam reforming and electrolysis-based hydrogen generators across multiple sectors.
The on-site segment accounted for the highest revenue share of 75% in 2024, primarily fueled by increasing demand for immediate hydrogen generation at industrial locations and the benefits of reduced transportation costs. These systems are widely used in industrial settings such as chemical manufacturing, oil refining, metal processing, and electronics, where continuous and high-volume hydrogen supply is essential. On-site generation provides enhanced safety, cost-effectiveness, and operational efficiency, especially for businesses aiming to reduce reliance on external hydrogen sources. 
The portable hydrogen generator segment is projected to experience the highest growth rate during the forecast period. These compact systems are increasingly used in military operations, disaster response, and mobile laboratories, as well as for backup power in off-grid locations. With the growing interest in hydrogen fuel cell technology for mobile and off-grid power applications, the demand for portable hydrogen generators is witnessing steady growth. These units are typically powered by lightweight and efficient technologies such as proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis and are designed for easy deployment and low maintenance.
The steam reforming segment accounted for the largest share of market revenue in 2024. Steam reforming is currently the most widely used process, especially in large-scale industrial settings, due to its cost-efficiency and established infrastructure. This method involves extracting hydrogen from hydrocarbons such as natural gas by reacting them with steam at high temperatures. It is particularly prevalent in the chemical and petrochemical industries, where hydrogen is needed in significant volumes for processes such as ammonia production and hydrocracking.
The electrolysis segment is projected to witness significant growth throughout the forecast period. This method uses electrical energy to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, and when powered by renewable sources like solar or wind, it produces what is known as green hydrogen. Electrolysis is increasingly being adopted for its ability to enable decentralized hydrogen production and reduce carbon footprints. Technological advancements and decreasing costs of renewable energy are making this method more competitive, especially in regions with strong climate action goals.
The chemical processing emerged as the leading segment in the hydrogen generator industry, capturing the largest share of revenue in 2024. Hydrogen is a critical feedstock in the production of ammonia, methanol, and other key chemicals. On-site hydrogen generators are increasingly being utilized in chemical plants to ensure a continuous and reliable supply of hydrogen, which is essential for uninterrupted production operations. The integration of hydrogen generators into chemical processing facilities also helps reduce dependence on external suppliers and minimizes the risks associated with transportation and storage of compressed hydrogen gas.
The refinery segment is anticipated to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period. These processes are vital for refining crude oil into cleaner fuels that meet stringent environmental regulations. Refineries have traditionally relied on large-scale, centralized hydrogen production units; however, there is a growing shift toward on-site hydrogen generation systems that provide flexibility and reduce operational costs. The rising global demand for low-sulfur fuels, driven by tightening emission standards, has further amplified the need for consistent hydrogen supply within refineries.
By Product 
By Process 
By Application 
By Regional 
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Product Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Hydrogen Generator Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Hydrogen Generator Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Hydrogen Generator Market, By Product
8.1. Hydrogen Generator Market, by Product
8.1.1 On-site
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Portable
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global Hydrogen Generator Market, By Process
9.1. Hydrogen Generator Market, by Process
9.1.1. Steam Reforming
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Electrolysis
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Global Hydrogen Generator Market, By Application
10.1. Hydrogen Generator Market, by Application
10.1.1. Chemical Processing
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.2. Petroleum Recovery
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.3. Fuel Cells
10.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.4. Refinery
10.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.5. Others
10.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 11. Global Hydrogen Generator Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
11.1. North America
11.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.1.4. U.S.
11.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.1.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.1.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.1.5. Rest of North America
11.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.2. Europe
11.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.2.4. UK
11.2.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.2.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.2.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.2.5. Germany
11.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.2.6. France
11.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.2.7. Rest of Europe
11.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.3. APAC
11.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.3.4. India
11.3.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.3.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.3.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.3.5. China
11.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.3.6. Japan
11.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.3.7. Rest of APAC
11.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.4. MEA
11.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.4.4. GCC
11.4.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.4.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.4.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.4.5. North Africa
11.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.4.6. South Africa
11.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.4.7. Rest of MEA
11.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.5. Latin America
11.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.5.4. Brazil
11.5.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.5.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.5.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
11.5.5. Rest of LATAM
11.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
11.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Process
11.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Application
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1. Air Liquide S.A.
12.1.1. Company Overview
12.1.2. Product Offering
12.1.3. Financial Performance
12.1.4. Recent Initiatives
12.2. Air Products and Chemicals, Inc.
12.2.1. Company Overview
12.2.2. Product Offerings
12.2.3. Financial Performance
12.2.4. Recent Initiatives
12.3. Linde plc.
12.3.1. Company Overview
12.3.2. Product Offerings
12.3.3. Financial Performance
12.3.4. Recent Initiatives
12.4. Nel ASA.
12.4.1. Company Overview
12.4.2. Product Offerings
12.4.3. Financial Performance
12.4.4. Recent Initiatives
12.5 Proton OnSite (a part of Nel ASA)
12.5.1. Company Overview
12.5.2. Product Offerings
12.5.3. Financial Performance
12.5.4. Recent Initiatives
12.6. Plug Power Inc.
12.6.1. Company Overview
12.6.2. Product Offerings
12.6.3. Financial Performance
12.6.4. Recent Initiatives
12.7. Hydrogenics Corporation (a Cummins Inc. company).
12.7.1. Company Overview
12.7.2. Product Offerings
12.7.3. Financial Performance
12.7.4. Recent Initiatives
12.8. McPhy Energy S.A.
12.8.1. Company Overview
12.8.2. Product Offerings
12.8.3. Financial Performance
12.8.4. Recent Initiatives
12.9. Teledyne Energy Systems, Inc.
12.9.1. Company Overview
12.9.2. Product Offerings
12.9.3. Financial Performance
12.9.4. Recent Initiatives
12.10. Peak Scientific Instruments Ltd.
12.10.1. Company Overview
12.10.2. Product Offerings
12.10.3. Financial Performance
12.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 13. Research Methodology
13.1. Primary Research
13.2. Secondary Research
13.3. Assumptions
Chapter 14. Appendix
14.1. About Us
14.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others