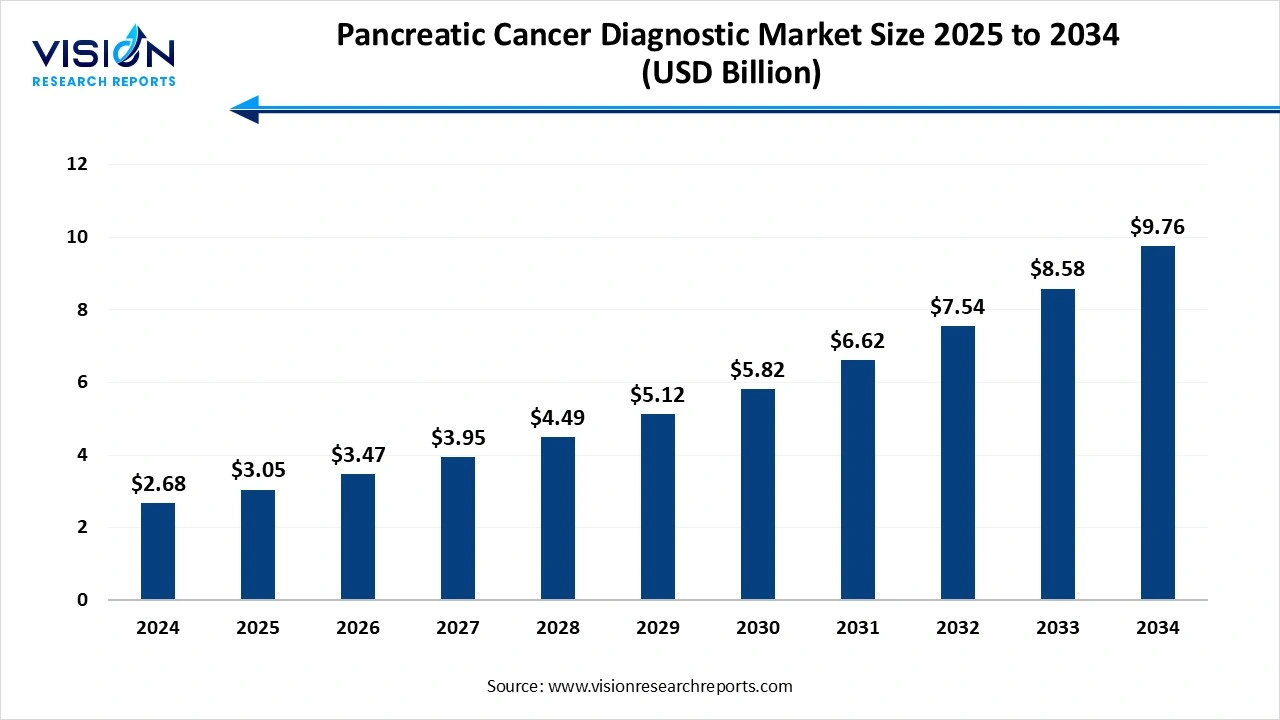
The global pancreatic cancer diagnostic market size stood at USD 2.68 billion in 2024 and is estimated to reach USD 3.05 billion in 2025. It is projected to hit USD 9.76 billion by 2034, registering a robust CAGR of 13.8% from 2025 to 2034. The market growth is driven by the rising incidence of pancreatic cancer, growing awareness about early diagnosis, and advancements in imaging technologies, the Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market is experiencing significant growth.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.68 Billion |
| Revenue Forecast by 2034 | USD 9.76 Billion |
| Growth rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 13.8% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Regions | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Companies Covered | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; QIAGEN; Illumina, Inc.; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Agilent Technologies, Inc.; Abbott; BD; Myriad Genetics, Inc; Koninklijke Philips N.V.; Hitachi, Ltd; Danaher; Prestige Biopharma Ltd; BioMarker Strategies; ASURAGEN, INC |
The pancreatic cancer diagnostic market is witnessing significant growth due to the rising incidence of pancreatic cancer globally, coupled with increased awareness and advancements in diagnostic technologies. Pancreatic cancer is known for its poor prognosis and late-stage detection, which makes early and accurate diagnosis crucial. This growing need for early detection is fueling demand for innovative diagnostic methods, including imaging techniques, molecular testing, and biomarker analysis.
Technological innovations such as liquid biopsies, next-generation sequencing (NGS), and AI-driven diagnostic tools are further transforming the landscape of pancreatic cancer diagnostics. These advanced tools offer higher sensitivity and specificity, enabling healthcare providers to detect cancer at earlier stages, which improves treatment outcomes.
Several key factors are driving the growth of the pancreatic cancer diagnostic market, with the foremost being the rising global prevalence of pancreatic cancer. As one of the deadliest forms of cancer with a high mortality rate, there is a critical need for early and precise diagnostic solutions. The increasing incidence of risk factors such as chronic pancreatitis, diabetes, obesity, and smoking is contributing to a surge in pancreatic cancer cases, thereby intensifying the demand for advanced diagnostic tools.
Another significant growth driver is the continuous advancement in diagnostic technologies. Innovations such as liquid biopsies, biomarker testing, imaging techniques like endoscopic ultrasound (EUS), and next-generation sequencing (NGS) are enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of pancreatic cancer detection. These methods allow for minimally invasive and early-stage diagnosis, which is crucial for improving patient survival rates.
The pancreatic cancer diagnostic market faces several critical challenges, with late-stage detection being one of the most significant. Pancreatic cancer often presents with vague or non-specific symptoms in its early stages, leading to delayed diagnosis and limited treatment options. This lack of early warning signs makes timely detection difficult, thereby reducing the effectiveness of available diagnostic tools and negatively impacting patient survival rates. Furthermore, there is a shortage of highly specific and sensitive biomarkers for early-stage pancreatic cancer, which hampers accurate diagnosis and screening efforts.
Another major challenge is the high cost and limited accessibility of advanced diagnostic technologies. Cutting-edge tools like next-generation sequencing (NGS), liquid biopsies, and molecular imaging techniques require substantial financial investment and technical expertise, which may not be readily available in low- and middle-income countries.
North America accounted for 41% of the market share in 2024. The global pancreatic cancer diagnostic market exhibits notable regional variation, with North America dominating due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high prevalence of pancreatic cancer, and strong presence of leading diagnostic companies. The United States, in particular, contributes significantly to market growth, driven by increased awareness, high adoption of advanced diagnostic technologies, and supportive healthcare reimbursement policies. Continuous investment in research and development, along with growing demand for early detection tools, further fuels the expansion of the market across the region.
Asia Pacific: Fastest-Growing Region in the Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market
Pancreatic cancer continues to be one of the most difficult cancers to detect and treat, particularly across the Asia-Pacific region where healthcare infrastructure varies significantly. However, advancements in diagnostics and therapeutics are steadily improving patient outcomes by supporting earlier detection and more precise treatment pathways. The effectiveness of these solutions increasingly relies on interoperability standards and APIs that enable seamless healthcare data exchange. Standards such as FHIR and HL7 ensure that electronic health records (EHRs) communicate smoothly across platforms and healthcare systems.
India Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market – Key Insights
The pancreatic cancer diagnostics landscape in India is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by the rising prevalence of the disease and continuous improvements in healthcare infrastructure. A notable industry shift is toward advanced, minimally invasive, and highly precise diagnostic approaches. This includes the adoption of liquid biopsies, advanced imaging techniques, and early-detection technologies, all of which contribute to better clinical outcomes.
Liquid biopsies are gaining strong momentum as an emerging diagnostic tool, enabling the detection of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and other biomarkers from blood samples — offering a less invasive and highly informative method for disease monitoring and early identification.
The consumables segment accounted for the largest revenue share, representing 49% in 2024. Ask ChatGPT Consumables play a crucial role in diagnostic procedures, comprising reagents, assay kits, testing tubes, and other lab essentials used in various testing formats such as molecular diagnostics, immunoassays, and histopathology. The increasing demand for early and accurate diagnostic outcomes has driven the frequent use of these consumables in clinical laboratories, research institutions, and hospitals. As new tests are developed and adopted more widely, the need for high-quality, reliable consumables continues to rise.
The services segment is projected to achieve a strong growth rate throughout the forecast period. This segment has gained substantial traction due to the surge in outsourcing diagnostic testing to specialized laboratories and the integration of advanced technologies such as AI-assisted imaging and next-generation sequencing. Service providers offer comprehensive diagnostic packages that support the early detection, staging, and monitoring of pancreatic cancer, helping physicians design effective treatment strategies. Additionally, the emphasis on value-based healthcare and the growing trend toward personalized medicine have led to increased reliance on service-based diagnostics, particularly in urban healthcare infrastructures.
The imaging test segment led the global market, capturing a revenue share of 58% in 2024. These tests include modalities such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS). Imaging allows for detailed visualization of the pancreas and surrounding tissues, aiding in the identification of tumors, metastasis, and abnormalities. Among these, CT scans are widely used due to their high-resolution output and accessibility, while EUS has gained prominence for its superior sensitivity in detecting small tumors. The growing prevalence of pancreatic cancer, coupled with technological advancements in imaging systems, such as AI-assisted image interpretation and real-time 3D imaging, continues to drive the growth of this segment.
Blood tests also play an increasingly important role in the pancreatic cancer diagnostic landscape. These tests are typically used to detect tumor markers such as carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9), which is often elevated in individuals with pancreatic cancer. Although not definitive on their own, blood tests serve as valuable tools for monitoring disease progression and treatment response. In recent years, the emergence of liquid biopsy techniques has significantly enhanced the capabilities of blood-based diagnostics by allowing the detection of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and other molecular markers with high precision. These non-invasive methods offer convenience and quicker turnaround times, making them suitable for regular monitoring.
The exocrine cancer segment led the market, capturing a dominant revenue share of 94% in 2024. Exocrine pancreatic cancer is the most prevalent form, accounting for the vast majority of diagnosed cases. The most common subtype within this category is pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, which originates in the ducts that carry digestive enzymes. Due to its aggressive nature and tendency to remain asymptomatic in the early stages, exocrine cancer is often diagnosed at an advanced stage, making early detection particularly challenging. As a result, there is a high demand for advanced diagnostic tools that can detect the disease earlier and more accurately.
The endocrine pancreatic cancer, also known as pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs), is less common but is gaining increasing attention due to improved diagnostic capabilities and growing awareness. Unlike exocrine cancers, endocrine tumors develop in the hormone-producing cells of the pancreas and tend to grow more slowly. However, their diagnosis can be complex, as symptoms are often non-specific and may mimic other conditions. Diagnostic strategies for PNETs typically involve a combination of blood hormone level testing, imaging, and histological examination. Recent advancements in genetic and molecular profiling have further enhanced the ability to accurately diagnose and classify these tumors.
The hospitals segment led the pancreatic cancer diagnostics market, accounting for 57% of the revenue share in 2024. Hospitals are typically the first point of care for patients presenting with symptoms indicative of pancreatic cancer, making them critical centers for early diagnosis and disease management. Equipped with sophisticated imaging systems, endoscopic tools, and pathology labs, hospitals offer a full spectrum of diagnostic services, including imaging tests, biopsies, and molecular diagnostics. The presence of multidisciplinary medical teams further enhances the diagnostic process, ensuring accurate interpretation and timely clinical decision-making.
The laboratories segment is expected to experience the highest growth rate throughout the forecast period. These laboratories, which may operate independently or in partnership with healthcare institutions, specialize in conducting a wide range of tests including genetic analysis, biomarker testing, and advanced pathology services. With the rise in demand for precision diagnostics, laboratories are increasingly adopting high-throughput technologies such as next-generation sequencing and liquid biopsy platforms. These labs support both early detection and ongoing monitoring of pancreatic cancer by delivering reliable and detailed diagnostic information.
By Product
By Test Type
By Cancer Type
By End-use
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market, By Product
8.1. Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market, by Product,
8.1.1. Instruments
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Consumables
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Services
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market, By Test Type
9.1. Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market, by Test Type,
9.1.1. Imaging Test
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Biopsy
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Blood Test
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.4. Others
9.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Global Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market, By Cancer Type
10.1. Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market, by Cancer Type,
10.1.1. Exocrine
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.2. Endocrine
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 11. Global Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market, By End-use
11.1. Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market, by End-use,
11.1.1. Hospitals
11.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.2. Clinics
11.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.3. Laboratories
11.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.4. Others
11.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 12. Global Pancreatic Cancer Diagnostic Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
12.1. North America
12.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.1.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.1.5. U.S.
12.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.1.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.1.6. Rest of North America
12.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.1.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.1.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.1.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.2. Europe
12.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.2.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.2.5. UK
12.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.2.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.2.6. Germany
12.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.2.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.2.7. France
12.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.2.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.2.8. Rest of Europe
12.2.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.2.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.2.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.2.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.3. APAC
12.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.3.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.3.5. India
12.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.3.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.3.6. China
12.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.3.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.3.7. Japan
12.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.3.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.3.8. Rest of APAC
12.3.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.3.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.3.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.3.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.4. MEA
12.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.4.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.4.5. GCC
12.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.4.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.4.6. North Africa
12.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.4.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.4.7. South Africa
12.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.4.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.4.8. Rest of MEA
12.4.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.4.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.4.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.4.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.5. Latin America
12.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.5.5. Brazil
12.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.5.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.5.6. Rest of LATAM
12.5.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
12.5.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Test Type
12.5.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Cancer Type
12.5.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
Chapter 13. Company Profiles
13.1. Roche Diagnostics
13.1.1. Company Overview
13.1.2. Product Offerings
13.1.3. Financial Performance
13.1.4. Recent Initiatives
13.2. Siemens Healthineers
13.2.1. Company Overview
13.2.2. Product Offerings
13.2.3. Financial Performance
13.2.4. Recent Initiatives
13.3. Hologic, Inc.
13.3.1. Company Overview
13.3.2. Product Offerings
13.3.3. Financial Performance
13.3.4. Recent Initiatives
13.4. F. Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
13.4.1. Company Overview
13.4.2. Product Offerings
13.4.3. Financial Performance
13.4.4. Recent Initiatives
13.5. Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
13.5.1. Company Overview
13.5.2. Product Offerings
13.5.3. Financial Performance
13.5.4. Recent Initiatives
13.6. QIAGEN N.V.
13.6.1. Company Overview
13.6.2. Product Offerings
13.6.3. Financial Performance
13.6.4. Recent Initiatives
13.7. Agilent Technologies, Inc.
13.7.1. Company Overview
13.7.2. Product Offerings
13.7.3. Financial Performance
13.7.4. Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD)
13.8. Sysmex Corporation
13.8.1. Company Overview
13.8.2. Product Offerings
13.8.3. Financial Performance
13.8.4. Recent Initiatives
13.9. Koninklijke Philips N.V.
13.9.1. Company Overview
13.9.2. Product Offerings
13.9.3. Financial Performance
13.9.4. Recent Initiatives
13.10. Hitachi, Ltd
13.10.1. Company Overview
13.10.2. Product Offerings
13.10.3. Financial Performance
13.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 14. Research Methodology
14.1. Primary Research
14.2. Secondary Research
14.3. Assumptions
Chapter 15. Appendix
15.1. About Us
15.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others