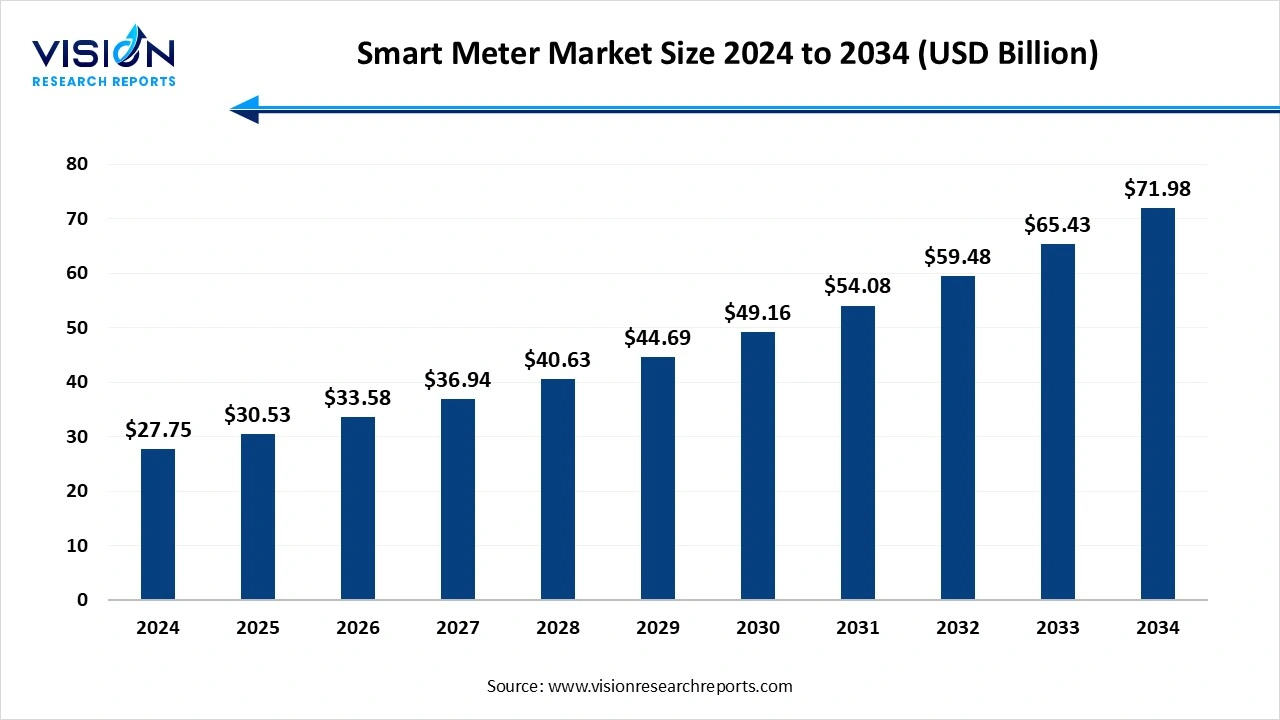
The global smart meter market size was reached at around USD 27.75 billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 71.98 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10% from 2025 to 2034
The smart meter market has been experiencing steady growth as utility companies worldwide adopt advanced metering technologies to improve energy management and grid efficiency. Smart meters are electronic devices that record consumption of electricity, water, or gas in real-time and communicate the information to the utility provider for monitoring and billing. This shift from traditional analog meters to smart meters is being driven by the rising need for accurate billing, reduction in energy theft, and support for dynamic pricing models.
The growth of the smart meter market is largely driven by increasing government mandates and policy support for smart grid infrastructure. Many countries are investing heavily in modernizing their energy systems to enhance efficiency, reduce carbon emissions, and ensure better demand-response capabilities. Programs such as smart city initiatives and digital transformation of utility services are encouraging large-scale deployment of smart meters.
Another major growth factor is the rising demand for energy efficiency and real-time data analytics. Smart meters play a crucial role in enabling two-way communication between utilities and consumers, allowing for remote monitoring, automated billing, and predictive maintenance. As the need for sustainable energy management grows, industries and households are adopting smart meters to track consumption and integrate renewable sources like solar and wind.
One of the prominent trends in the smart meter market is the integration of IoT and advanced data analytics. Modern smart meters are increasingly being designed to connect with IoT platforms, enabling utilities to gather large volumes of real-time consumption data. This data is then analyzed to detect usage patterns, forecast demand, and quickly identify system faults or outages. The shift toward digital platforms has also led to the emergence of cloud-based smart metering solutions, allowing for remote management, system scalability, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Another key trend is the growing demand for smart electric meters driven by the global transition toward renewable energy. As more households and industries install solar panels and other renewable sources, smart meters are becoming essential tools to manage bidirectional energy flows and net metering. These devices help balance grid load and allow users to monitor the energy they consume and generate, promoting more sustainable energy usage.
One of the primary challenges facing the smart meter market is the high initial investment cost associated with deployment and infrastructure upgrades. Implementing smart metering systems requires substantial funding for device installation, communication networks, and software platforms. For utility providers in developing regions or those with limited budgets, this upfront expenditure can be a major barrier. Additionally, the cost of maintaining and upgrading the smart grid infrastructure over time adds to the financial burden, slowing down mass adoption in some areas.
Data privacy and cybersecurity concerns also pose significant challenges in the smart meter market. Since smart meters collect and transmit sensitive consumer usage data over digital networks, they become vulnerable targets for cyberattacks. Any breach in data security could lead to unauthorized access, fraud, or disruption of energy services. To address these issues, utilities and vendors must invest in robust security frameworks and comply with data protection regulations efforts that can be both complex and costly.
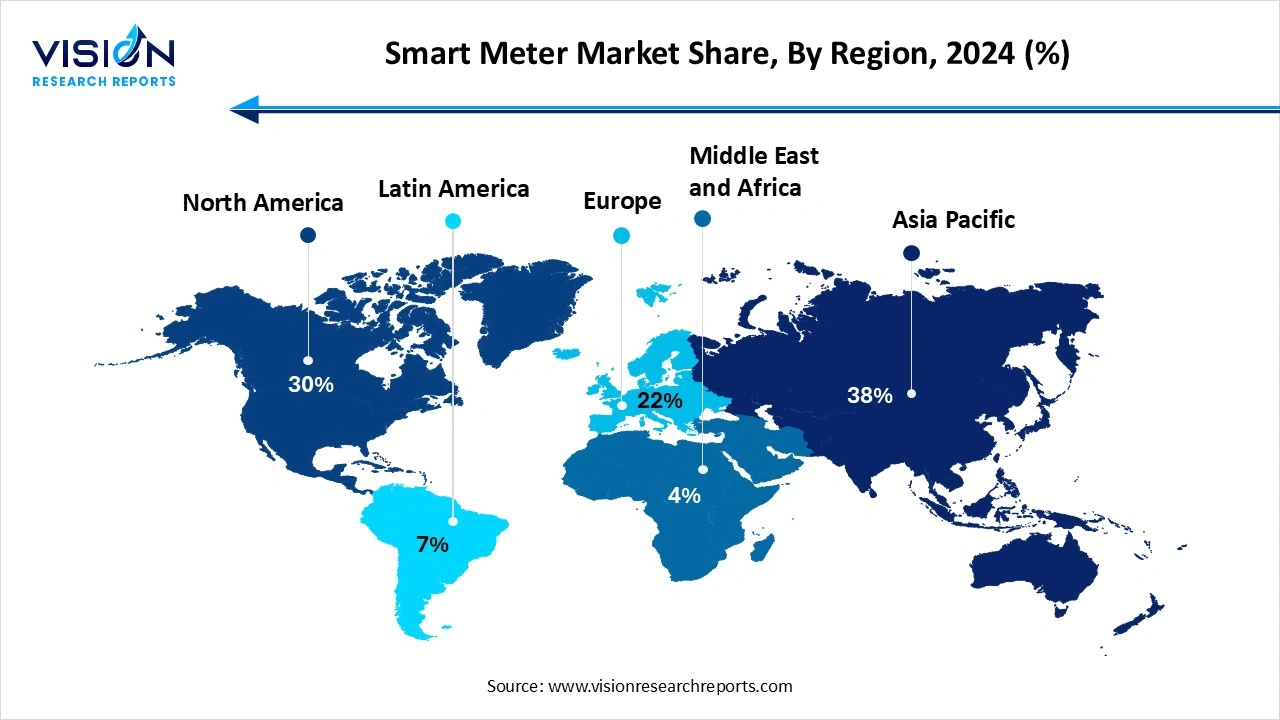
The Asia Pacific region dominated the smart meter market, accounting for the largest share of 38% in 2024. Its leadership is attributed to rapid urbanization, government-driven initiatives for energy efficiency, and significant investments in smart grid and metering technologies. The Asia Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the smart meter market, fueled by rapid urbanization, rising energy demand, and government-led digitalization initiatives. China and India are key markets in this region, with large-scale government programs aimed at modernizing utility infrastructure and improving energy access.
 The European smart meter market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 8.1% from 2025 to 2034, driven by stringent regulatory mandates aimed at promoting energy efficiency and achieving carbon neutrality. Initiatives under the European Green Deal are accelerating investments in smart grid modernization and advanced energy management solutions.
The European smart meter market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 8.1% from 2025 to 2034, driven by stringent regulatory mandates aimed at promoting energy efficiency and achieving carbon neutrality. Initiatives under the European Green Deal are accelerating investments in smart grid modernization and advanced energy management solutions.
The hardware segment led the market, accounting for over 77% of the total share in 2024. This segment includes smart meters themselves, along with communication modules, sensors, and related devices that facilitate accurate measurement and real-time data transmission. Hardware components are critical in ensuring the effectiveness and reliability of smart metering solutions, particularly in large-scale deployments across utility grids. The growing demand for electricity, water, and gas management solutions has driven utilities to upgrade from traditional metering systems to intelligent hardware capable of two-way communication and remote monitoring.
The software segment is projected to register the highest CAGR of over 15.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. Software platforms are responsible for collecting, processing, and analyzing data transmitted by smart meters, providing utilities with actionable insights to enhance grid performance and customer service. These platforms support functionalities such as meter data management (MDM), outage detection, energy usage analytics, and billing automation. As utilities seek to optimize energy distribution and improve consumer engagement, demand for intelligent, cloud-based software solutions continues to rise.
The smart electric meter segment led the market, accounting for the highest revenue share in 2024. These meters are designed to record and transmit real-time electricity usage data to utility providers, enabling better load management, accurate billing, and detection of energy theft. With the growing global emphasis on reducing carbon emissions and enhancing energy efficiency, smart electric meters have become a critical component of modern power grids. Governments and utilities across various regions are actively implementing smart grid initiatives, where smart electric meters play a central role in enabling two-way communication and supporting demand-response programs.
The smart water meters segment is anticipated to record the highest CAGR between 2025 and 2034. These meters provide accurate and timely data on water consumption, allowing utilities and consumers to monitor usage patterns and detect leaks or anomalies in real time. With the growing challenges of water scarcity and aging water infrastructure in many regions, smart water meters are emerging as a vital solution for sustainable water management. Municipalities and utility companies are increasingly investing in these technologies to optimize water distribution, improve billing accuracy, and promote water conservation.
The automated meter reading (AMR) segment held a 51% share of the market in 2024. AMR technology enables the remote collection of consumption data from utility meters without requiring manual readings. This system significantly reduces operational costs and enhances billing accuracy by automating data collection. AMR systems typically rely on one-way communication, where data is transmitted from the meter to the utility provider but does not allow for two-way interaction.
The advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) segment is projected to register the highest CAGR during the period from 2025 to 2034. AMI supports two-way communication between the meter and the utility provider, enabling a broader range of functions such as real-time monitoring, remote connect/disconnect, outage detection, and dynamic pricing. This advanced technology plays a vital role in smart grid development by providing utilities with detailed consumption data and analytics, which can be used to improve grid reliability, enhance energy efficiency, and engage consumers more effectively.
The residential segment captured the largest share of the market in 2024. Smart meters in residential settings enable consumers to gain detailed insights into their electricity, water, or gas consumption, which in turn promotes conscious usage and cost savings. With rising awareness about energy conservation and the introduction of dynamic pricing models, homeowners are increasingly adopting smart meters to track usage patterns and manage utility bills more effectively.
The industrial segment is projected to record the fastest CAGR during the period from 2025 to 2034. Industries consume high volumes of electricity, water, and gas, making accurate monitoring and control of resource usage critical to cost control and environmental compliance. Smart meters offer industrial users real-time data analytics, enabling better load distribution, process optimization, and early detection of inefficiencies or system failures. In addition, smart meters play a key role in supporting industries' shift toward renewable energy integration and sustainability goals.
By Smart Meter Component
By Smart Meter Type
By Smart Meter Technology
By Smart Meter End-use
By Smart Meter Market Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Smart Meter Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Smart Meter Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Smart Meter Market, By Component
8.1. Smart Meter Market, by Component
8.1.1. Hardware
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Software
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global Smart Meter Market, By Type
9.1. Smart Meter Market, by Type
9.1.1. Smart Electric Meter
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Smart Water Meter
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Smart Gas Meter
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Global Smart Meter Market, By Technology
10.1. Smart Meter Market, by Technology
10.1.1. Automatic Meter Reading (AMR)
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.2. Advanced Meter Infrastructure (AMI)
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 11. Global Smart Meter Market, By End-use
11.1. Smart Meter Market, by End-use
11.1.1. Residential
11.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.2. Commercial
11.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.3. Industrial
11.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 12. Global Smart Meter Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
12.1. North America
12.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.1.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.1.5. U.S.
12.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.1.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.1.6. Rest of North America
12.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.1.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.1.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.1.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.2. Europe
12.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.2.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.2.5. UK
12.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.2.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.2.6. Germany
12.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.2.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.2.7. France
12.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.2.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.2.8. Rest of Europe
12.2.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.2.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.2.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.2.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.3. APAC
12.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.3.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.3.5. India
12.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.3.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.3.6. China
12.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.3.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.3.7. Japan
12.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.3.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.3.8. Rest of APAC
12.3.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.3.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.3.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.3.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.4. MEA
12.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.4.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.4.5. GCC
12.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.4.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.4.6. North Africa
12.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.4.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.4.7. South Africa
12.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.4.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.4.8. Rest of MEA
12.4.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.4.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.4.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.4.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.5. Latin America
12.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.5.5. Brazil
12.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.5.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
12.5.6. Rest of LATAM
12.5.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component
12.5.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
12.5.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
12.5.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End-use
Chapter 13. Company Profiles
13.1. Itron Inc.
13.1.1. Company Overview
13.1.2. Product Offerings
13.1.3. Financial Performance
13.1.4. Recent Initiatives
13.2. Siemens AG
13.2.1. Company Overview
13.2.2. Product Offerings
13.2.3. Financial Performance
13.2.4. Recent Initiatives
13.3. Landis+Gyr Group AG
13.3.1. Company Overview
13.3.2. Product Offerings
13.3.3. Financial Performance
13.3.4. Recent Initiatives
13.4. Honeywell International Inc.
13.4.1. Company Overview
13.4.2. Product Offerings
13.4.3. Financial Performance
13.4.4. Recent Initiatives
13.5. Schneider Electric SE
13.5.1. Company Overview
13.5.2. Product Offerings
13.5.3. Financial Performance
13.5.4. Recent Initiatives
13.6. Sensus (a Xylem brand)
13.6.1. Company Overview
13.6.2. Product Offerings
13.6.3. Financial Performance
13.6.4. Recent Initiatives
13.7. Aclara Technologies LLC
13.7.1. Company Overview
13.7.2. Product Offerings
13.7.3. Financial Performance
13.7.4. Recent Initiatives
13.8. EDMI Limited
13.8.1. Company Overview
13.8.2. Product Offerings
13.8.3. Financial Performance
13.8.4. Recent Initiatives
13.9. Kamstrup A/S
13.9.1. Company Overview
13.9.2. Product Offerings
13.9.3. Financial Performance
13.9.4. Recent Initiatives
13.10. Badger Meter, Inc.
13.10.1. Company Overview
13.10.2. Product Offerings
13.10.3. Financial Performance
13.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 14. Research Methodology
14.1. Primary Research
14.2. Secondary Research
14.3. Assumptions
Chapter 15. Appendix
15.1. About Us
15.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others