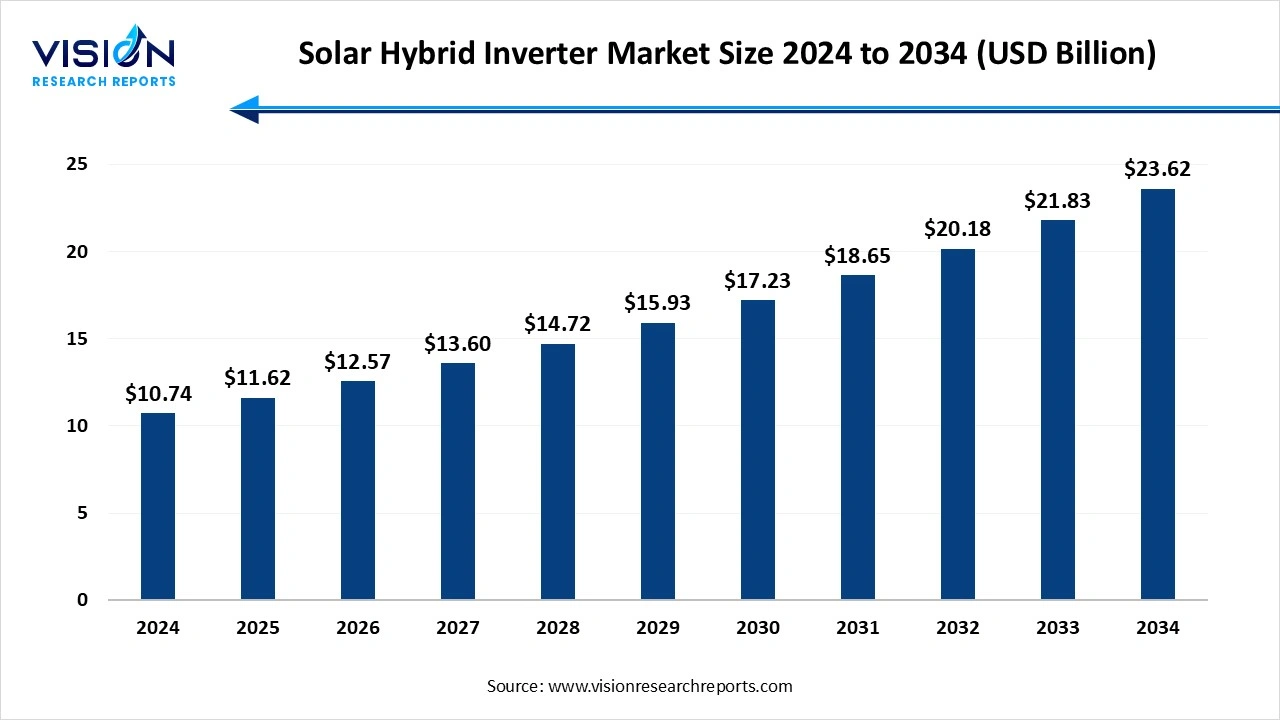
The global solar hybrid inverter market size was estimated at USD 10.74 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 23.62 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.20% from 2025 to 2034.
The solar hybrid inverter market is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for reliable and efficient renewable energy solutions worldwide. Solar hybrid inverters, which combine solar power with battery storage and grid connectivity, offer enhanced energy management capabilities, making them an attractive choice for both residential and commercial applications. The rising adoption of solar energy systems, supported by favorable government policies and incentives aimed at promoting clean energy, is fueling market expansion. Advancements in inverter technology, such as improved efficiency, smart monitoring features, and integration with IoT platforms, are further propelling market development. Growing concerns over energy security,
The growth of the solar hybrid inverter market is primarily driven by the rising global emphasis on renewable energy and sustainability. Governments across the world are implementing supportive policies, subsidies, and incentives to encourage the adoption of solar power systems, which directly boosts the demand for hybrid inverters. These inverters play a crucial role in optimizing energy consumption by efficiently managing power from solar panels, batteries, and the electrical grid. Furthermore, increasing electricity costs and frequent power outages, especially in developing regions, are prompting residential and commercial users to seek reliable backup power solutions, making hybrid inverters an essential component for uninterrupted power supply.
Technological advancements are also fueling market expansion by enhancing the performance and functionality of solar hybrid inverters. Innovations such as improved energy conversion efficiency, intelligent energy management systems, and seamless integration with smart home and IoT devices are making hybrid inverters more user-friendly and efficient. Additionally, the growing adoption of energy storage systems and microgrid installations supports the need for hybrid inverters that can effectively balance multiple power sources.
North America led the global market with highest share 43% in 2024. Frequent disruptions caused by weather events are encouraging both residential and commercial users to opt for hybrid inverters that offer backup power during outages. The United States is at the forefront of this growth, supported by federal tax incentives, net metering programs, and an increase in solar-plus-storage projects. Canada is also playing a key role, particularly in provinces that provide clean energy incentives and support electrification efforts in off-grid communities.
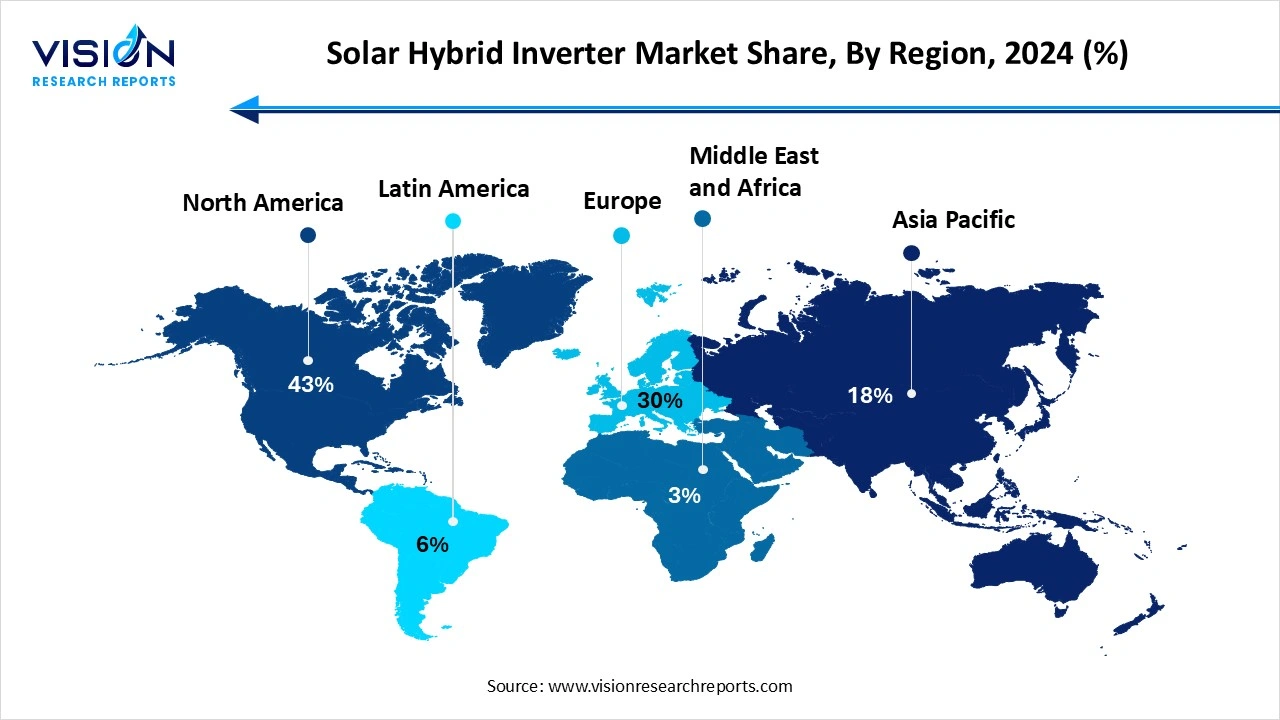 The Asia Pacific region leads the global solar hybrid inverter market, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing rooftop solar installations, and favorable government policies. Nations such as India and China are at the forefront of this growth, propelled by extensive solar projects, rural electrification efforts, and incentives promoting battery-backed solar solutions. In India, hybrid inverters play a vital role in addressing power shortages in rural and semi-urban regions. Simultaneously, China’s focus on distributed energy generation and advancements in battery technology is boosting adoption in both commercial and residential sectors.
The Asia Pacific region leads the global solar hybrid inverter market, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing rooftop solar installations, and favorable government policies. Nations such as India and China are at the forefront of this growth, propelled by extensive solar projects, rural electrification efforts, and incentives promoting battery-backed solar solutions. In India, hybrid inverters play a vital role in addressing power shortages in rural and semi-urban regions. Simultaneously, China’s focus on distributed energy generation and advancements in battery technology is boosting adoption in both commercial and residential sectors.
The three-phase hybrid inverter segment is pivotal in the solar hybrid inverter market. These inverters can handle larger loads and provide balanced power output across three phases, ensuring stable and reliable electricity supply for manufacturing units, office complexes, and large-scale solar installations. Their ability to integrate solar power with battery storage and grid supply makes them ideal for minimizing downtime and optimizing energy usage in demanding environments.
single-phase hybrid inverters are commonly deployed in residential and small commercial applications where power requirements are comparatively lower. These inverters combine solar energy, battery storage, and grid connectivity within a compact design that suits household electrical systems. Single-phase hybrid inverters offer cost-effective solutions for homeowners looking to reduce electricity bills and enhance energy security by ensuring backup power during outages. The growing adoption of rooftop solar systems and increasing awareness of energy independence are driving the demand for single-phase hybrid inverters, particularly in urban and suburban areas.
The commercial segment held the solar hybrid inverter market in 2024. The commercial sector is a significant contributor to the growth of the global solar hybrid inverter market due to its substantial energy consumption and increasing focus on sustainable power solutions. Businesses across manufacturing, retail, and office spaces are adopting solar hybrid inverters to reduce operational costs and ensure a stable power supply. These inverters help commercial establishments manage energy more efficiently by combining solar power generation with battery storage and grid connectivity, which enhances reliability and reduces dependence on conventional electricity sources. The rising emphasis on corporate sustainability and regulatory compliance regarding carbon emissions is further encouraging commercial users to integrate hybrid inverters into their energy infrastructure.
In the residential sector, solar hybrid inverters are gaining popularity as homeowners seek greater energy independence and protection against frequent power outages. With the increasing installation of rooftop solar systems, residential users are adopting hybrid inverters to maximize the use of solar energy while ensuring continuous power availability through battery backups. This not only lowers electricity bills but also provides resilience during grid failures. Government incentives, growing environmental awareness, and the desire for smart energy management solutions are key factors driving the adoption of solar hybrid inverters in homes.
By Product
By End Use
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Solar Hybrid Inverter Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Solar Hybrid Inverter Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Solar Hybrid Inverter Market, By Product
8.1. Solar Hybrid Inverter Market, by Product
8.1.1. Single-Phase Hybrid
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Three-Phase Hybrid
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Solar Hybrid Inverter Market, By End Use
9.1. Solar Hybrid Inverter Market, by End Use
9.1.1. Commercial
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Residential
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Others
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Solar Hybrid Inverter Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
10.1. U.S.
10.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
10.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1. Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
11.1.1. Company Overview
11.1.2. Product Offerings
11.1.3. Financial Performance
11.1.4. Recent Initiatives
11.2. Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd.
11.2.1. Company Overview
11.2.2. Product Offerings
11.2.3. Financial Performance
11.2.4. Recent Initiatives
11.3. SMA Solar Technology AG
11.3.1. Company Overview
11.3.2. Product Offerings
11.3.3. Financial Performance
11.3.4. Recent Initiatives
11.4. Schneider Electric SE
11.4.1. Company Overview
11.4.2. Product Offerings
11.4.3. Financial Performance
11.4.4. LTE Scientific
11.5. Delta Electronics, Inc.
11.5.1. Company Overview
11.5.2. Product Offerings
11.5.3. Financial Performance
11.5.4. Recent Initiatives
11.6. ABB Ltd.
11.6.1. Company Overview
11.6.2. Product Offerings
11.6.3. Financial Performance
11.6.4. Recent Initiatives
11.7. Growatt New Energy Technology Co., Ltd.
11.7.1. Company Overview
11.7.2. Product Offerings
11.7.3. Financial Performance
11.7.4. Recent Initiatives
11.8. Ginlong Technologies (Solis)
11.8.1. Company Overview
11.8.2. Product Offerings
11.8.3. Financial Performance
11.8.4. Recent Initiatives
11.9. Fronius International GmbH
11.9.1. Company Overview
11.9.2. Product Offerings
11.9.3. Financial Performance
11.9.4. Recent Initiatives
11.10. KACO new energy GmbH
11.10.1. Company Overview
11.10.2. Product Offerings
11.10.3. Financial Performance
11.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 12. Research Methodology
12.1. Primary Research
12.2. Secondary Research
12.3. Assumptions
Chapter 13. Appendix
13.1. About Us
13.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others