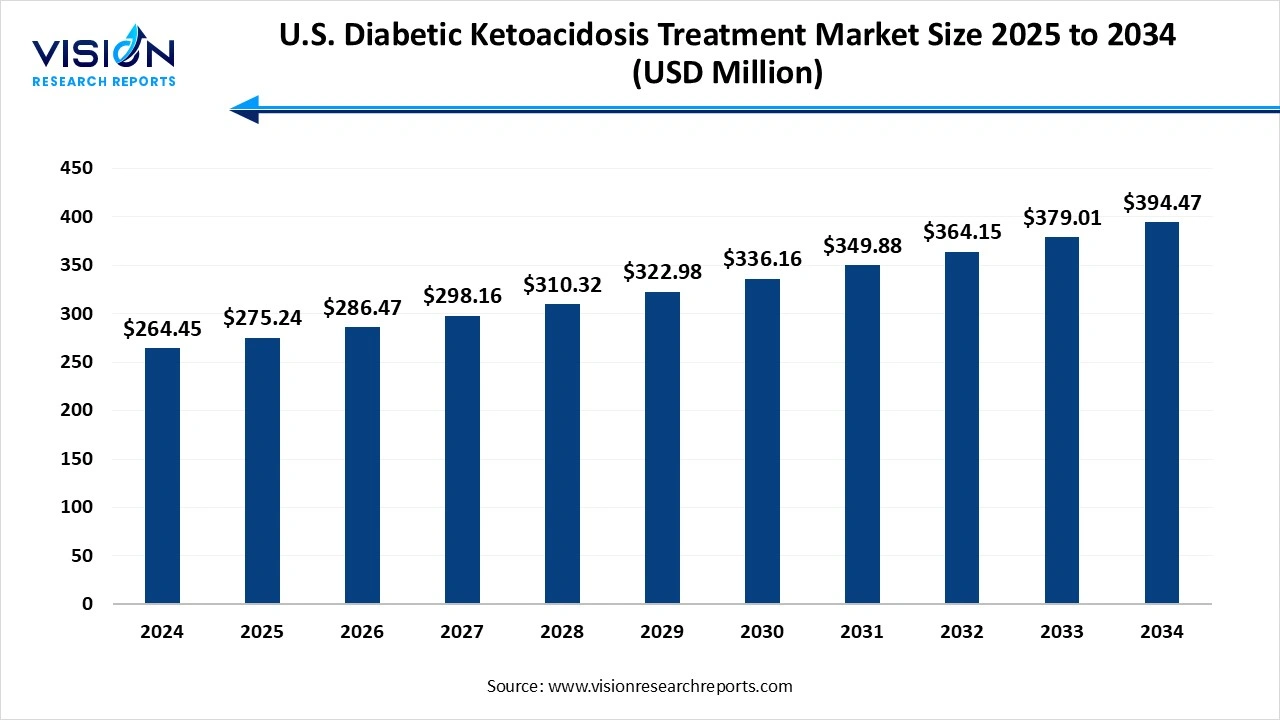
The U.S. diabetic ketoacidosis treatment market size was valued at around USD 264.45 million in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 394.47 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4.08% from 2025 to 2034. The market growth is driven by the rising prevalence of diabetes, increasing hospital admissions for diabetic emergencies, and growing awareness about early intervention, the U.S. diabetic ketoacidosis treatment market is witnessing steady growth.
| Report Coverage     | Details |
| Market Size in 2024     | USD 264.45 million |
| Revenue Forecast by 2034    USD 1,833.29 million | USD 394.47 million |
| Growth rate from 2025 to 2034     | CAGR of 4.08% |
| Base Year     | 2024 |
| Forecast Period     | 2025 to 2034 |
| Companies Covered | Novo Nordisk A/S, Eli Lilly and Company, Sanofi S.A., Pfizer Inc, B. Braun Melsungen AG, Baxter International Inc., Abbott Laboratories, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Medtronic plc, Dexcom, Inc. |
The U.S. diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) treatment market plays a critical role in the broader diabetes care landscape, driven by the increasing prevalence of type 1 and insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes. DKA is a serious and potentially life-threatening complication caused by a severe lack of insulin, leading to the accumulation of ketones in the blood. Rising hospitalization rates associated with diabetes emergencies, increased awareness among patients and healthcare providers, and advancements in diagnostic and treatment protocols are contributing to the market’s growth. The market benefits from a well-established healthcare infrastructure and the widespread availability of emergency care services, which facilitate early diagnosis and prompt treatment of DKA.
One of the primary growth factors driving the U.S. diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) treatment market is the rising prevalence of diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes, which is closely linked to DKA incidents. As more individuals are diagnosed with diabetes at a younger age, the risk of developing DKA increases, especially in cases of insulin mismanagement or missed doses. This trend is further supported by a growing awareness of the symptoms and risks associated with DKA, leading to earlier diagnosis and intervention. 
Another key growth driver is the advancement in treatment protocols and healthcare infrastructure. The availability of rapid-acting insulin analogs, improved intravenous fluid therapies, and enhanced monitoring systems have elevated the standard of care for DKA patients. Hospitals and emergency departments across the U.S. are better equipped with trained personnel and technologies to manage acute diabetic complications efficiently.
One of the major challenges faced by the U.S. diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) treatment market is the high cost of care, particularly for uninsured or underinsured patients. DKA treatment often requires hospitalization, intensive monitoring, and emergency interventions, which can lead to substantial medical bills.
Another significant challenge is the lack of early diagnosis and awareness, especially among newly diagnosed diabetic patients or those in underserved communities. Many individuals fail to recognize the early warning signs of DKA, such as nausea, abdominal pain, and excessive thirst, resulting in late-stage hospital admissions. Moreover, disparities in healthcare access, language barriers, and limited availability of endocrinologists in certain regions contribute to gaps in effective diabetes education and follow-up care.
The insulin therapy segment accounted for a notable revenue share of 28% in 2024, DKA occurs due to a significant deficiency or absence of insulin, which causes the body to break down fat for energy, resulting in the production of ketones that acidify the blood. The primary objective of insulin therapy in DKA management is to reverse this metabolic state by lowering blood glucose levels and suppressing ketone production. Typically administered through intravenous infusion in a hospital setting, rapid-acting insulin helps restore glucose utilization and halt further fat breakdown.
The electrolyte replacement therapy segment is expected to register a notable CAGR of 3.22% throughout the forecast period. during a DKA episode, excessive urination, vomiting, and fluid loss result in dehydration and depletion of critical electrolytes necessary for normal cellular function. Potassium levels, in particular, require careful management, as insulin therapy can drive potassium into cells and exacerbate existing hypokalemia, potentially leading to cardiac arrhythmias. Replenishing fluids and electrolytes through intravenous solutions helps restore circulatory volume, correct acid-base imbalances, and support organ function.
The hospital segment led the market with the highest revenue share of 76% in 2024, primarily due to the high prevalence of DKA cases that necessitate inpatient treatment and constant monitoring. Most DKA cases require immediate medical intervention, which involves continuous monitoring, intravenous insulin administration, fluid replacement, and electrolyte management. Hospitals are equipped with intensive care units (ICUs) and emergency departments that provide the necessary infrastructure and trained personnel to handle the complexity of DKA treatment. The need for rapid diagnosis, frequent lab testing, and around-the-clock observation makes hospital settings indispensable for managing moderate to severe cases.
The homecare settings segment is anticipated to experience the fastest growth, with a projected CAGR of 5.21% during the forecast period. Advances in digital health technologies such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), smart insulin pumps, and remote patient monitoring systems have made it possible to manage diabetes more effectively at home. With proper guidance from healthcare professionals and access to telehealth services, patients can detect early warning signs of DKA and take timely corrective actions.
By Treatment 
By End Use 
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on U.S. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatment Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: U.S. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatment Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. U.S. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatment Market, By Treatment
8.1. U.S. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatment Market, by Treatment, 2024-2033
8.1.1. Fluid Replacement Therapy
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
8.1.2. Electrolyte Replacement Therapy
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
8.1.3. Insulin Therapy
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
8.1.4. Others
8.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 9. U.S. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatment Market, By End Use
9.1. U.S. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatment Market, by End Use, 2024-2033
9.1.1. Hospital
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.2. Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs)
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
9.1.3. Homecare Settings
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2021-2033)
Chapter 10. U.S. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatment Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
10.1. U.S.
10.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Treatment (2021-2033)
10.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use (2021-2033)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1. Novo Nordisk A/S
11.1.1. Company Overview
11.1.2. Product Offerings
11.1.3. Financial Performance
11.1.4. Eli Lilly and Company
11.2. Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc
11.2.1. Company Overview
11.2.2. Product Offerings
11.2.3. Financial Performance
11.2.4. Sanofi S.A.
11.3. Cytiva (Danaher)
11.3.1. Company Overview
11.3.2. Product Offerings
11.3.3. Financial Performance
11.3.4. Recent Initiatives
11.4. Pfizer, Inc.
11.4.1. Company Overview
11.4.2. Product Offerings
11.4.3. Financial Performance
11.4.4. B. Braun Melsungen AG
11.5. Intermountain Life Sciences
11.5.1. Company Overview
11.5.2. Product Offerings
11.5.3. Financial Performance
11.5.4. Recent Initiatives
11.6. Baxter International Inc.
11.6.1. Company Overview
11.6.2. Product Offerings
11.6.3. Financial Performance
11.6.4. Recent Initiatives
11.7. General Electric
11.7.1. Company Overview
11.7.2. Product Offerings
11.7.3. Financial Performance
11.7.4. Abbott Laboratories
11.8. Aqua Solutions
11.8.1. Company Overview
11.8.2. Product Offerings
11.8.3. Financial Performance
11.8.4. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
11.9. Evoqua Water Technologies
11.9.1. Company Overview
11.9.2. Product Offerings
11.9.3. Financial Performance
11.9.4. Medtronic plc
11.10. Nexus Pharmaceuticals
11.10.1. Company Overview
11.10.2. Product Offerings
11.10.3. Financial Performance
11.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 12. Research Methodology
12.1. Primary Research
12.2. Secondary Research
12.3. Assumptions
Chapter 13. Appendix
13.1. About Us
13.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others