The global switchgear market size was surpassed at around USD 107.36 billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 217.19 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 7.30% from 2025 to 2034.
.webp)
The global switchgear market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for reliable and efficient power distribution systems across industrial, commercial, and residential sectors. Switchgear, which includes components such as circuit breakers, disconnectors, and fuses, plays a critical role in protecting electrical networks by isolating faults and ensuring safe power flow. With increasing investments in renewable energy projects, smart grid infrastructure, and the expansion of transmission and distribution networks, the demand for advanced switchgear solutions is accelerating. Moreover, the growing need for energy efficiency and grid modernization in emerging economies is further contributing to market expansion.
The growth of the switchgear market is primarily fueled by the rising demand for electricity and the expansion of power generation and distribution infrastructure worldwide. Rapid urbanization, industrial development, and population growth are increasing the need for reliable electrical networks, particularly in emerging economies. Governments and utility providers are heavily investing in upgrading aging grid infrastructure and expanding renewable energy installations, which require advanced switchgear systems to ensure efficient and safe power distribution.
Another significant growth factor is the increasing emphasis on energy efficiency and smart grid technologies. The adoption of digital switchgear equipped with real-time monitoring, automation, and predictive maintenance capabilities is transforming traditional power systems into intelligent, data-driven networks. These advancements help reduce operational costs, enhance safety, and improve overall system reliability.
One of the prominent trends in the switchgear market is the rapid adoption of digital and smart switchgear systems. These advanced systems incorporate sensors, IoT connectivity, and data analytics, enabling real-time monitoring, remote control, and predictive maintenance of electrical networks. Utilities and industries are increasingly shifting from traditional switchgear to intelligent solutions to improve operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance safety.
Another emerging trend is the growing preference for eco-efficient and sustainable switchgear technologies. Environmental concerns and stricter regulations on greenhouse gas emissions are prompting manufacturers to develop alternatives to sulfur hexafluoride (SF₆)-based switchgear, which is a potent greenhouse gas. As a result, vacuum-based and air-insulated switchgear solutions are gaining traction, especially in regions with strong environmental policies.
One of the key challenges faced by the switchgear market is the high initial cost of advanced and eco-efficient systems. While digital and smart switchgear solutions offer long-term benefits in terms of efficiency, safety, and reliability, their upfront installation costs can be prohibitive, especially for small-scale utilities and businesses in developing regions. Additionally, the transition from conventional to smart switchgear often requires significant infrastructure upgrades and skilled labor, which can slow down adoption.
Another challenge is the growing complexity of regulatory compliance and environmental standards. The industry is under increasing pressure to phase out SF₆ gas due to its high global warming potential, but finding cost-effective and scalable alternatives remains difficult. Manufacturers must invest heavily in research and development to create new materials and technologies that meet performance standards while aligning with environmental regulations.
North America led the switchgear market, accounting for a revenue share of 38% in 2024. The United States and Canada are investing heavily in smart grid infrastructure, which includes the deployment of intelligent switchgear for enhanced control and real-time monitoring. Moreover, increasing integration of distributed energy resources such as solar and wind power, along with rising demand for electric vehicle charging infrastructure, is further boosting the need for robust and adaptable switchgear systems.
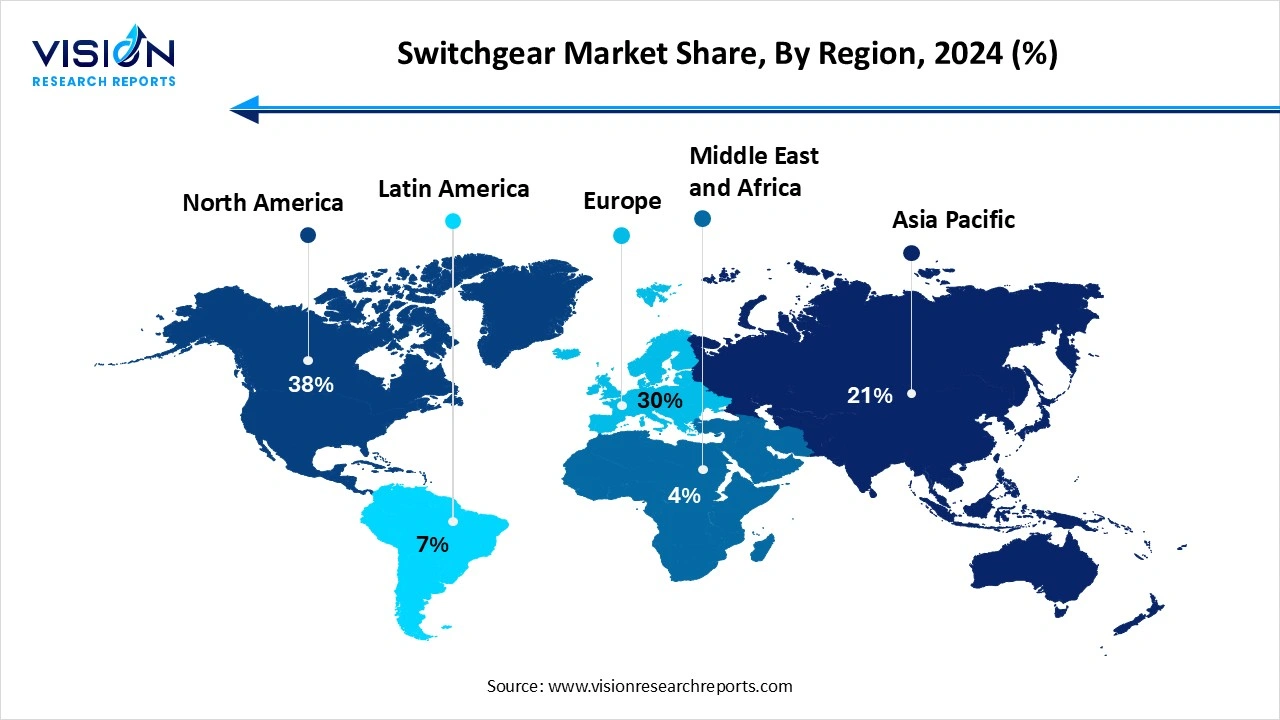 The switchgear industry in Asia Pacific is projected to expand at the fastest CAGR of 8.8% over the forecast period. Government initiatives aimed at expanding power generation capacities, upgrading aging electrical infrastructure, and improving rural electrification are major contributors to market growth. Additionally, large-scale investments in renewable energy projects and smart grid development are fueling demand for advanced switchgear solutions across the region. With a growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainable technologies, Asia Pacific is expected to maintain its leadership position in the global market over the coming years.
The switchgear industry in Asia Pacific is projected to expand at the fastest CAGR of 8.8% over the forecast period. Government initiatives aimed at expanding power generation capacities, upgrading aging electrical infrastructure, and improving rural electrification are major contributors to market growth. Additionally, large-scale investments in renewable energy projects and smart grid development are fueling demand for advanced switchgear solutions across the region. With a growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainable technologies, Asia Pacific is expected to maintain its leadership position in the global market over the coming years.
The low voltage segment led the market, capturing the highest revenue share of 70% in 2024. Low voltage switchgear is typically used for systems that operate at voltages up to 1 kV and plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient distribution of electricity. These systems protect electrical circuits and equipment from overloads, short circuits, and other faults, helping maintain uninterrupted power supply in low-voltage networks. The rising demand for energy-efficient infrastructure, along with the expansion of smart buildings and residential projects, is contributing to the sustained growth of this segment.
The medium voltage segment is projected to experience the highest CAGR during the forecast period. Operating within the range of 1 kV to 36 kV, medium voltage switchgear is critical for managing and protecting power distribution networks in high-load environments. The increasing focus on grid reliability, coupled with the integration of renewable energy sources, is leading to higher demand for medium voltage systems. These switchgear units are essential in substations, power distribution centers, and infrastructure projects where efficient load management and system stability are vital.
The others segment accounted for the largest share of the switchgear market in 2024. These alternatives are increasingly being adopted in response to the environmental limitations of SF₆-based systems. Air-insulated switchgear (AIS), for example, is commonly used in open and less space-constrained environments due to its simplicity and lower cost. Solid and vacuum-insulated systems are gaining popularity for their eco-friendliness, enhanced safety, and lower lifecycle emissions. These insulation methods are being integrated into modern switchgear designs to meet the growing demand for sustainable and efficient power solutions, especially in sectors focused on renewable energy integration and grid modernization.
The gas segment is anticipated to grow at a moderate CAGR of 7.2% over the forecast period. GIS is widely used in environments where space is limited, such as urban infrastructure, underground substations, and offshore installations. These systems are filled with insulating gas, commonly sulfur hexafluoride (SF₆), which provides excellent arc-quenching and dielectric properties. Although concerns over the environmental impact of SF₆ have prompted regulatory scrutiny, GIS remains in demand for its ability to operate efficiently in harsh conditions, withstand high voltages, and require minimal maintenance.
The outdoor segment led the market with the largest share in 2024. Outdoor switchgear is designed to withstand various environmental conditions such as extreme temperatures, humidity, and pollution, making it ideal for use in substations, transmission networks, and industrial plants. These systems are typically housed in weatherproof enclosures and are often used in rural or remote locations where space is not a limiting factor. The increasing investment in grid expansion and renewable energy projects, especially wind and solar farms, is boosting the demand for outdoor switchgear.
The indoor segment is expected to witness the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. These systems are compact and installed within buildings or specially designed enclosures, offering protection from external environmental factors. Indoor switchgear is commonly used in data centers, manufacturing facilities, high-rise buildings, and institutional infrastructure. The rise in smart building developments and the growing emphasis on energy efficiency have contributed to the increased adoption of indoor switchgear.
The commercial and residential segment held the largest share of the market in 2024. In residential applications, switchgear ensures the safe and efficient distribution of electricity throughout homes and apartment complexes, protecting appliances and systems from electrical faults. Similarly, commercial facilities such as shopping centers, office buildings, and hospitals rely heavily on reliable switchgear to maintain uninterrupted power supply and prevent costly downtimes.
The transmission & distribution utilities (T&D utility) segment is expected to register a notable CAGR over the forecast period. Switchgear is used extensively across substations and distribution networks to isolate faults, reroute power, and protect equipment from damage. With the global shift toward cleaner energy sources and the integration of renewable power into existing grids, utilities are increasingly upgrading to modern switchgear technologies that offer better control, real-time monitoring, and higher efficiency. Furthermore, initiatives aimed at grid modernization, especially in developed regions, are driving investment in medium- and high-voltage switchgear solutions.
By Voltage Type
By Insulation
By Installation
By End Use
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Switchgear Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Switchgear Market Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Switchgear Market, By Voltage Type
8.1. Switchgear Market, by Voltage Type
8.1.1. Low Voltage
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Medium Voltage
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. High Voltage
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global Switchgear Market, By Insulation
9.1. Switchgear Market, by Insulation
9.1.1. Air
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Gas
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Others
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Global Switchgear Market, By Installation
10.1. Switchgear Market, by Installation
10.1.1. Indoor
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.2. Outdoor
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 11. Global Switchgear Market, By End Use
11.1. Switchgear Market, by End Use
11.1.1. T & D Utilities
11.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.2. Commercial & Residential
11.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
11.1.3. Industrial
11.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 12. Global Switchgear Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
12.1. North America
12.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.1.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.1.5. U.S.
12.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.1.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.1.6. Rest of North America
12.1.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.1.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.1.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.1.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.2. Europe
12.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.2.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.2.5. UK
12.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.2.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.2.6. Germany
12.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.2.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.2.7. France
12.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.2.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.2.8. Rest of Europe
12.2.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.2.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.2.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.2.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.3. APAC
12.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.3.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.3.5. India
12.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.3.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.3.6. China
12.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.3.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.3.7. Japan
12.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.3.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.3.8. Rest of APAC
12.3.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.3.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.3.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.3.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.4. MEA
12.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.4.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.4.5. GCC
12.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.4.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.4.6. North Africa
12.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.4.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.4.7. South Africa
12.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.4.7.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.4.8. Rest of MEA
12.4.8.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.4.8.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.4.8.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.4.8.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.5. Latin America
12.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.5.5. Brazil
12.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.5.5.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
12.5.6. Rest of LATAM
12.5.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Voltage Type
12.5.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Insulation
12.5.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Installation
12.5.6.4. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
Chapter 13. Company Profiles
13.1. ABB Ltd.
13.1.1. Company Overview
13.1.2. Product Offerings
13.1.3. Financial Performance
13.1.4. Recent Initiatives
13.2. Schneider Electric SE
13.2.1. Company Overview
13.2.2. Product Offerings
13.2.3. Financial Performance
13.2.4. Recent Initiatives
13.3. Siemens AG
13.3.1. Company Overview
13.3.2. Product Offerings
13.3.3. Financial Performance
13.3.4. Recent Initiatives
13.4. Eaton Corporation plc
13.4.1. Company Overview
13.4.2. Product Offerings
13.4.3. Financial Performance
13.4.4. Recent Initiatives
13.5. General Electric Company
13.5.1. Company Overview
13.5.2. Product Offerings
13.5.3. Financial Performance
13.5.4. Recent Initiatives
13.6. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
13.6.1. Company Overview
13.6.2. Product Offerings
13.6.3. Financial Performance
13.6.4. Recent Initiatives
13.7. Toshiba Corporation
13.7.1. Company Overview
13.7.2. Product Offerings
13.7.3. Financial Performance
13.7.4. Recent Initiatives
13.8. Hitachi, Ltd.
13.8.1. Company Overview
13.8.2. Product Offerings
13.8.3. Financial Performance
13.8.4. Recent Initiatives
13.9. Larsen & Toubro Limited (L&T)
13.9.1. Company Overview
13.9.2. Product Offerings
13.9.3. Financial Performance
13.9.4. Recent Initiatives
13.10. Hyundai Electric & Energy Systems Co., Ltd.
13.10.1. Company Overview
13.10.2. Product Offerings
13.10.3. Financial Performance
13.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 14. Research Methodology
14.1. Primary Research
14.2. Secondary Research
14.3. Assumptions
Chapter 15. Appendix
15.1. About Us
15.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others