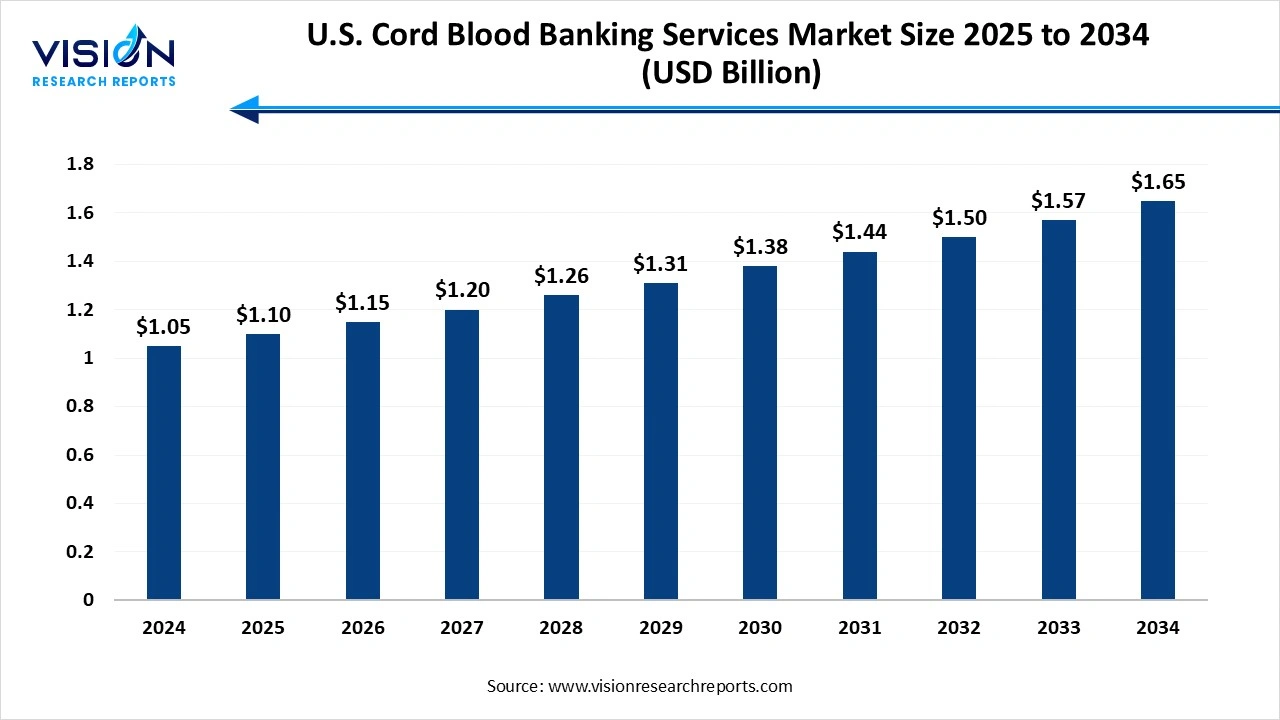
The U.S. Cord blood banking services market size was estimated at USD 1.05 billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 1.65 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4.6% from 2025 to 2034.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.05 billion |
| Revenue Forecast by 2034 | USD 1.65 billion |
| Growth rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 4.6% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Companies Covered | California Cryobank, StemCyte Inc., Cryo-Cell International Inc., Lifeforce Cryobank Sciences Inc., Stem Cell Cryobank Inc., Norton Healthcare Viacord, MiracleCord Inc., New Jersey Cord Blood Bank, Carter BloodCare. |
The U.S. cord blood banking services market has seen steady growth in recent years, driven by rising awareness about the long-term therapeutic potential of stem cells derived from umbilical cord blood. These services involve the collection, processing, and storage of cord blood for future medical use, particularly in the treatment of various blood disorders, genetic diseases, and immune deficiencies. The increasing prevalence of chronic and rare diseases, advancements in stem cell research, and growing acceptance of regenerative medicine have significantly contributed to the market’s expansion.
The growth of the U.S. cord blood banking services market is primarily fueled by the increasing recognition of cord blood as a valuable source of hematopoietic stem cells, which are used in the treatment of over 80 medical conditions, including leukemia, lymphoma, and sickle cell anemia. Rising awareness among expecting parents, driven by educational campaigns and healthcare provider recommendations, has significantly boosted the adoption of both private and public cord blood banking.
Another key driver is the growing investment in regenerative medicine and stem cell research, which continues to broaden the therapeutic potential of cord blood beyond traditional hematologic disorders. The increasing incidence of chronic and genetic diseases, along with a rising birth rate among health-conscious parents, has created a favorable environment for market expansion.
One of the major challenges confronting the U.S. cord blood banking services market is the high cost associated with private banking. The initial collection, processing, and long-term storage fees can be financially burdensome for many families, making it less accessible to the broader population. Additionally, insurance coverage for cord blood storage is limited, and the relatively low probability of actually using the stored cord blood for treatment contributes to hesitancy among potential customers. This cost-benefit uncertainty often steers families toward public banking or away from banking entirely, impacting the growth of private service providers.
Another significant obstacle is the limited utilization of stored cord blood units. Despite the growing number of samples banked annually, only a small fraction is ever used for transplantation or therapy, raising concerns about the practical value of storage. Moreover, public awareness of the full potential and limitations of cord blood applications remains uneven, leading to misconceptions and underutilization.
The private bank type segment held the dominant share, accounting for over 98% of the market in 2024. Private banks operate by storing the cord blood exclusively for the donor family, offering a sense of assurance in case of medical needs related to stem cell therapy. The rising awareness of stem cell treatments, coupled with the growing prevalence of genetic and blood-related disorders, has encouraged more families to opt for private banking. Moreover, advancements in processing technologies and improved service offerings, such as flexible payment plans and enhanced storage safety, have made private banks a more attractive option.
The hybrid bank segment is projected to witness the highest CAGR of 12.04% between 2024 and 2034. These banks allow families to store a portion of the cord blood for personal use while contributing the remaining portion to a public registry, enabling potential use by others in need. This dual-purpose approach appeals to families who value both personal security and social contribution. The hybrid model offers a cost-effective solution and increases the likelihood of stored units being used, which addresses one of the major challenges in the industry underutilization.
The cord blood (CB) led the industry, contributing over 51% of the total revenue in 2024. The U.S. cord blood banking services market, the cord blood (CB) component continues to be the cornerstone of storage services due to its rich source of hematopoietic stem cells. These stem cells are widely used in the treatment of various blood-related disorders, including leukemia, lymphoma, and certain immune and metabolic diseases. The clinical success of cord blood transplants has significantly boosted demand for its preservation, particularly among families with a history of such conditions.
The cord tissue component segment is projected to experience the highest growth rate over the forecast period. Cord tissue contains mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which are known for their regenerative capabilities and potential to treat a wider range of conditions such as orthopedic injuries, neurological disorders, and autoimmune diseases. Although cord tissue applications are still largely in the research and clinical trial stages, increasing interest in its therapeutic promise has led many private banks to offer dual storage options. This has not only expanded the scope of services but also allowed families to invest in the future of personalized medicine.
The california led the overall market, contributing over 18.4% of the total revenue in 2024. California represents one of the most prominent and rapidly growing markets in the U.S. cord blood banking services sector, driven by its large population, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and high level of public awareness. The state benefits from a strong network of hospitals, birthing centers, and healthcare professionals who actively promote the importance of cord blood and tissue banking.
The increasing prevalence of chronic and genetic disorders in the state has also contributed to a growing demand for both private and hybrid cord blood banking services. Parents in California, particularly in urban and affluent areas, are more inclined to invest in future health preparedness through personalized stem cell storage. Moreover, the state has supportive policies and a progressive regulatory environment that encourage innovation and participation in biomedical advancements.
By Bank Type
By Component Scope
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on U.S. Cord Blood Banking Services Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: U.S. Cord Blood Banking Services Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. U.S. Cord Blood Banking Services Market, By Bank Type
8.1. U.S. Cord Blood Banking Services Market, by Bank Type, 2023-2034
8.1.1. Private
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2025-2034)
8.1.2. Public
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2025-2034)
8.1.3. Hybrid
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2025-2034)
Chapter 9. U.S. Cord Blood Banking Services Market, By Component
9.1. U.S. Cord Blood Banking Services Market, by Component, 2023-2034
9.1.1. Cord Blood
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2025-2034)
9.1.2. Cord Tissue
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2025-2034)
9.1.3. Placenta
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast (2025-2034)
Chapter 10. U.S. Cord Blood Banking Services Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
10.1. U.S.
10.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Bank Type (2025-2034)
10.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Component (2025-2034)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1. California Cryobank
11.1.1. Company Overview
11.1.2. Product Offerings
11.1.3. Financial Performance
11.1.4. Recent Initiatives
11.2. StemCyte Inc.
11.2.1. Company Overview
11.2.2. Product Offerings
11.2.3. Financial Performance
11.2.4. Recent Initiatives
11.3. Cryo-Cell International Inc.
11.3.1. Company Overview
11.3.2. Product Offerings
11.3.3. Financial Performance
11.3.4. Recent Initiatives
11.4. Lifeforce Cryobank Sciences Inc.
11.4.1. Company Overview
11.4.2. Product Offerings
11.4.3. Financial Performance
11.4.4. LTE Scientific
11.5. Stem Cell Cryobank Inc.
11.5.1. Company Overview
11.5.2. Product Offerings
11.5.3. Financial Performance
11.5.4. Recent Initiatives
11.6. Norton Healthcare Viacord
11.6.1. Company Overview
11.6.2. Product Offerings
11.6.3. Financial Performance
11.6.4. Recent Initiatives
11.7. MiracleCord Inc.
11.7.1. Company Overview
11.7.2. Product Offerings
11.7.3. Financial Performance
11.7.4. Recent Initiatives
11.8. New Jersey Cord Blood Bank
11.8.1. Company Overview
11.8.2. Product Offerings
11.8.3. Financial Performance
11.8.4. Recent Initiatives
11.9. Carter BloodCare.
11.9.1. Company Overview
11.9.2. Product Offerings
11.9.3. Financial Performance
11.9.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 12. Research Methodology
12.1. Primary Research
12.2. Secondary Research
12.3. Assumptions
Chapter 13. Appendix
13.1. About Us
13.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others