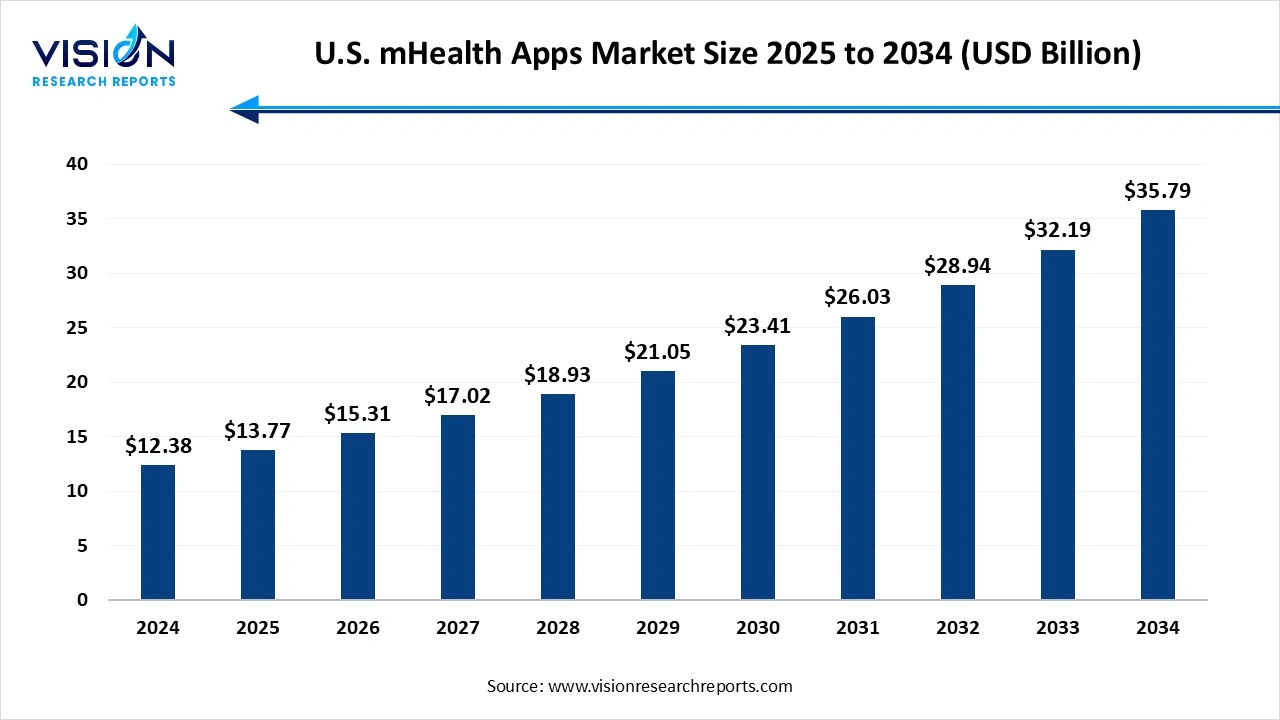
The U.S. mhealth apps market size was valued at around USD 12.38Â billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 35.79Â billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 11.20%Â from 2025 to 2034. The market growth is driven by the increasing adoption of smartphones and wearable devices, the U.S. mHealth apps market is experiencing robust growth.Â
The U.S. mHealth (mobile health) apps market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by rising smartphone penetration, increasing health consciousness among consumers, and a growing demand for remote healthcare solutions. These apps, which range from fitness trackers and diet planners to chronic disease management tools and telemedicine platforms, have become integral to modern healthcare delivery. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated adoption by highlighting the need for accessible, contactless medical services. Regulatory support, rising investment in digital health technologies, and the expanding presence of tech giants and startups in the healthcare space continue to shape the market’s landscape.Â
The growth of the U.S. mHealth apps market is largely fueled by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disorders, which has led to a greater demand for continuous health monitoring and management tools. Mobile health apps offer users the ability to track vital signs, medication schedules, and lifestyle habits from their smartphones, improving adherence to treatment plans and encouraging proactive health behaviors.
Another key factor contributing to market expansion is the advancement in mobile technology and increasing internet penetration. The integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics into mHealth apps has enhanced their functionality and accuracy, enabling more personalized health recommendations and predictive diagnostics.
One of the primary challenges facing the U.S. mHealth apps market is data privacy and security concerns. As these apps collect and store sensitive health information, ensuring compliance with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is critical. Many consumers remain skeptical about sharing personal health data due to fears of data breaches, unauthorized access, or misuse by third parties. This lack of trust can hinder adoption, particularly among older or less tech-savvy users who may be more cautious about digital healthcare solutions.
Another significant hurdle is the lack of standardized clinical validation and interoperability. Many mHealth apps are developed without rigorous scientific backing or integration with electronic health records (EHRs), limiting their usefulness to healthcare professionals and creating fragmentation within digital health systems.
The medical apps segment led the market, accounting for a dominant revenue share of 72% in 2024. These apps cater to a wide range of medical needs, including remote consultations, chronic disease management, medication reminders, and diagnostic support. With the increasing adoption of telemedicine, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, medical apps have become essential tools for both healthcare providers and patients. They offer real-time communication between doctors and patients, streamline workflows, and enable faster decision-making, all of which contribute to improved patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing has significantly enhanced the functionality of medical apps. These features allow for personalized treatment plans, predictive analytics, and seamless data sharing, which are crucial for modern healthcare delivery. Regulatory support, along with rising investment in digital health startups, continues to fuel innovation in this segment.
The iOS segment emerged as the leading platform in the market, capturing a revenue share of 53% in 2024. Apple’s strong emphasis on privacy, security, and seamless integration with its ecosystem has made iOS a preferred choice for many mHealth app developers. The platform’s compatibility with advanced features such as HealthKit and Apple Watch enables users to monitor various health parameters like heart rate, activity levels, and sleep patterns in real time.
The Android segment is projected to witness substantial growth at a notable CAGR during the forecast period. The open-source nature of the Android operating system encourages innovation and allows developers greater flexibility in customizing app functionalities. This has resulted in a vast and diverse library of mHealth apps tailored to different medical conditions and user needs. Android’s extensive reach makes it especially effective for public health initiatives and telemedicine services targeting underserved populations.
By TypeÂ
By PlatformÂ
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others