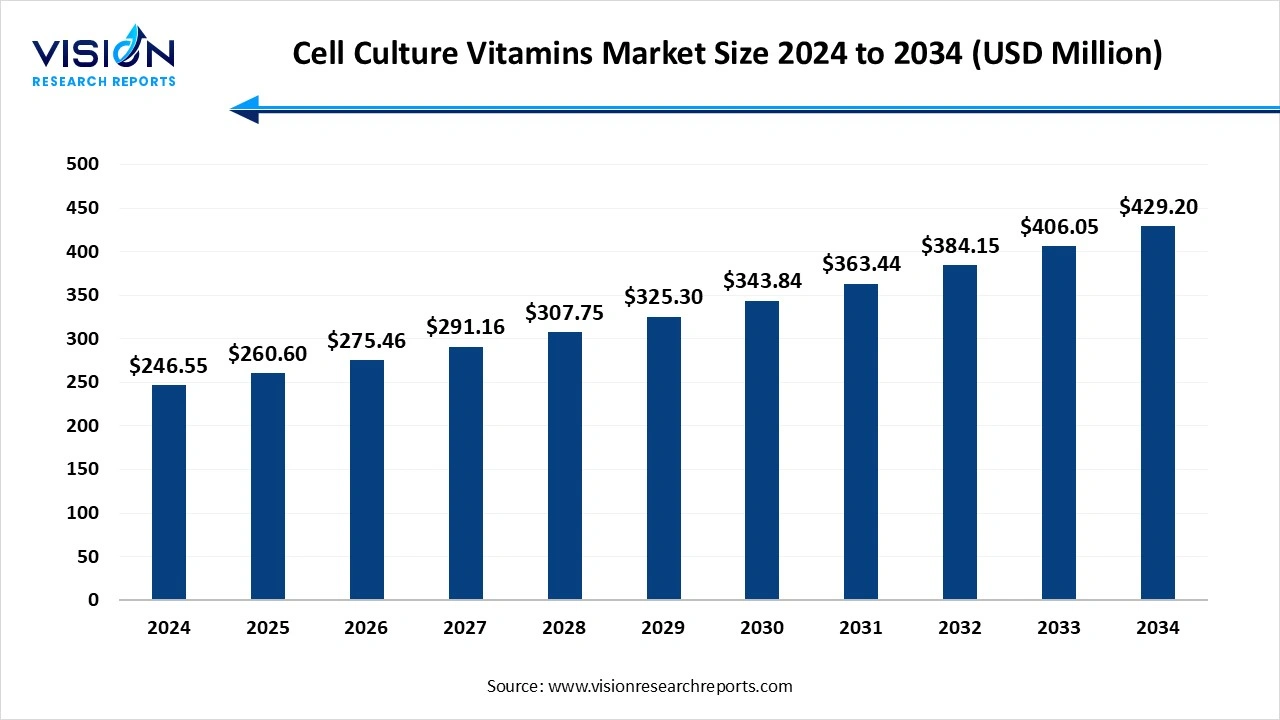
The global cell culture vitamins market size was estimated at USD 246.55 million in 2024 and is expected to grow to USD 260.60 million in 2025, ultimately reaching USD 429.20 million by 2034, reflecting a remarkable CAGR of 5.7%. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for biologics, vaccines, and cell-based therapies, coupled with advancements in cell culture technologies, the shift toward serum-free and chemically defined media, and rising investments in biopharmaceutical research and regenerative medicine.
The cell culture vitamins market is witnessing notable growth due to the rising demand for cell-based research and biopharmaceutical production. These vitamins are essential components in cell culture media, playing a vital role in cellular growth, metabolism and viability. As pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries continue to expand their focus on regenerative medicine, vaccine development and monoclonal antibody production, the need for optimized cell culture environments, including the right balance of vitamins, has surged. Advancements in cell culture technologies and an increasing number of biologics in development pipelines further propel the market.
One of the primary drivers of the cell culture vitamins market is the accelerating demand for biologics and cell-based therapies. As biopharmaceutical companies intensify their efforts in the development of monoclonal antibodies, vaccine, and gene therapies, the need for optimized cell culture systems becomes increasingly critical. Vitamins, as essential supplements in cell culture media, play a pivotal role in promoting cell growth, enhancing metabolic function, and improving the overall efficiency of production processes.
Another key factor contributing to market expansion is the shift toward serum-free and chemically defined media formulations. This transition has highlighted the importance of precise nutrient composition, where vitamins are integral to ensuring cell viability and consistency across batches. Advancements in cell culture techniques, increased funding for life sciences research, and the growth of contract manufacturing and research organizations (CMOs and CROs) also support market development.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 246.55 million |
| Revenue Forecast by 2034 | USD 429.20 million |
| Growth rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 5.7% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Regions | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Companies Covered | Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Merck KGaA (MilliporeSigma in the U.S. and Canada), Cytiva (a Danaher company), Lonza Group Ltd., Corning Incorporated, FUJIFILM Irvine Scientific, HiMedia Laboratories, PromoCell GmbH, Sartorius AG, and Bio-Techne Corporation. |
Increase of Cell Therapy Adoption
One of the key drivers propelling the cell culture vitamins market forward is the increase of cell therapy adoption and the growing recognition of culture media optimization. Standardization efforts and quality assurance programs continue to influence product development and market adoption patterns.
The growing development of chemically defined supplement formulations enables for more consistent and reproducible cell culture conditions while simultaneously reducing batch-to-batch variability in therapeutic manufacturing processes. Defined media formulations provide precise nutrient compositions and eliminate animal-derived components that may potentially create contamination risks or regulatory concerns. These supplements are particularly valuable for cell therapy applications that require stringent quality control and regulatory compliance throughout the manufacturing process.
High Production Costs and Regulatory Standards
Despite promising growth prospects, the market does have its fair share of restraints. One such restraint is the high cost of production. The development of high-quality, cell-specific vitamin formulations requires a significant amount of investment in research, quality control as well as production technologies. These high costs can limit market accessibility, especially for small scale and medium scale biotechnology firms.
Strict regulatory standards for biologics and cell-based products also mandate thorough validation and documentation of every component, including vitamins. Meeting these compliance requirements can be time-consuming and costly for manufacturers. This in turn, slows down market growth and development.
Technological Advancements
Modern supplement manufacturers are increasingly incorporating advanced monitoring systems and quality control technologies that improve supplement consistency and reduce manufacturing variability. The integration of real-time analytical methods and automated quality testing enables for a more precise supplement formulation and comprehensive batch documentation. Advancements in manufacturing also support the development of customized supplement formulations for specific cell lines and therapeutic applications, thus opening up new avenues of opportunity.
A new area of medicine called “regenerative medicine” is also gaining traction as it claims to have treatments for replacing organ and tissue system in patients. Regenerative medicine uses cells, biomaterials and chemicals to repair body tissue that have been harmed by disease or injury.
North America dominated the cell culture vitamins market, accounting for the largest share at 38% in 2024. This dominance is due to the presence of leading biopharmaceutical companies, advanced research infrastructure and strong government funding for life sciences research. The region has seen a surge in biologics and personalized medicine development, where cell culture media enriched with essential vitamins plays a crucial role in ensuring the viability and productivity of cultured cells.
Asia-Pacific is experiencing the fastest growth rate as of this year, fueled by rising investments in biotechnology, an expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing base and growing government initiatives to support biomedical research. Countries such as China, India, Japan and South Korea are witnessing increased outsourcing of research and production activities to local contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) and research institutions. The region also benefits from cost advantages as well as improvements in infrastructure and regulatory systems.
Which product segment dominated the market in 2024?
The Vitamin B complex segment dominated the market in 2024 due to its vital role in supporting cellular metabolism and growth. This group of water-soluble vitamins is essential for maintaining optimal enzymatic activity within cultured cells. These vitamins serve as coenzymes in various biochemical pathways, including DNA synthesis, energy production and amino acid metabolism. As the demand for high-yield and high-quality cell cultures continues to grow, the inclusion of Vitamin B complex in culture media has become more critical.
The Vitamin A segment is projected to experience the fastest growth throughout the forecast period. This segment plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression, influencing cell differentiation and maintaining cellular integrity. The use of Vitamin A is especially prominent in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering, where precise control is required. As research in advanced cell-based therapies continues to expand, the demand for stable, biologically active Vitamin A derivatives is also equally expected to rise.
Which end user held the largest market share as of this year?
The cell culture media manufacturers segment held the largest market share, accounting for 46% in 2024. These companies are responsible for formulating and supplying customized and standardized media solutions that support a wide range of cell-based applications. With the increasing demand for serum-free and chemically defined media, manufacturers are focusing more on the inclusion of precise concentrations of essential vitamins to ensure reproducibility and scalability in both research as well as commercial production.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology company segment is seen to grow the fastest throughout the forecast period. These organizations depend on reliable and high-quality cell culture systems for drug discovery, preclinical testing, and large-scale production of therapeutic proteins and monoclonal antibodies. With increased regulatory scrutiny and the need for GMP-compliant production environments, pharmaceutical firms are actively seeking media components, including vitamins that offer traceability, safety and functional efficacy.
By Product
By End Use
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Channel Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Cell Culture Vitamins Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Cell Culture Vitamins Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Cell Culture Vitamins Market, By Product
8.1. Cell Culture Vitamins Market, by Product
8.1.1. Vitamin B Complex
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. Vitamin A
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Vitamin C
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.4. Other Vitamins
8.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Cell Culture Vitamins Market, By End Use
9.1. Cell Culture Vitamins Market, by End Use
9.1.1. Cell Culture Media Manufacturers
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. CDMOs/ CMOs & CROs
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Cell Culture Vitamins Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
10.1. U.S.
10.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Product
10.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by End Use
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1. Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
11.1.1. Company Overview
11.1.2. Product Offerings
11.1.3. Financial Performance
11.1.4. Recent Initiatives
11.2. Merck KGaA (MilliporeSigma in the U.S. and Canada)
11.2.1. Company Overview
11.2.2. Product Offerings
11.2.3. Financial Performance
11.2.4. Recent Initiatives
11.3. Cytiva (a Danaher company)
11.3.1. Company Overview
11.3.2. Product Offerings
11.3.3. Financial Performance
11.3.4. Recent Initiatives
11.4. Lonza Group Ltd.
11.4.1. Company Overview
11.4.2. Product Offerings
11.4.3. Financial Performance
11.4.4. LTE Scientific
11.5. Corning Incorporated
11.5.1. Company Overview
11.5.2. Product Offerings
11.5.3. Financial Performance
11.5.4. Recent Initiatives
11.6. FUJIFILM Irvine Scientific
11.6.1. Company Overview
11.6.2. Product Offerings
11.6.3. Financial Performance
11.6.4. Recent Initiatives
11.7. HiMedia Laboratories
11.7.1. Company Overview
11.7.2. Product Offerings
11.7.3. Financial Performance
11.7.4. Recent Initiatives
11.8. PromoCell GmbH
11.8.1. Company Overview
11.8.2. Product Offerings
11.8.3. Financial Performance
11.8.4. Recent Initiatives
11.9. Sartorius AG
11.9.1. Company Overview
11.9.2. Product Offerings
11.9.3. Financial Performance
11.9.4. Recent Initiatives
11.10. Bio-Techne Corporation
11.10.1. Company Overview
11.10.2. Product Offerings
11.10.3. Financial Performance
11.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 12. Research Methodology
12.1. Primary Research
12.2. Secondary Research
12.3. Assumptions
Chapter 13. Appendix
13.1. About Us
13.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others