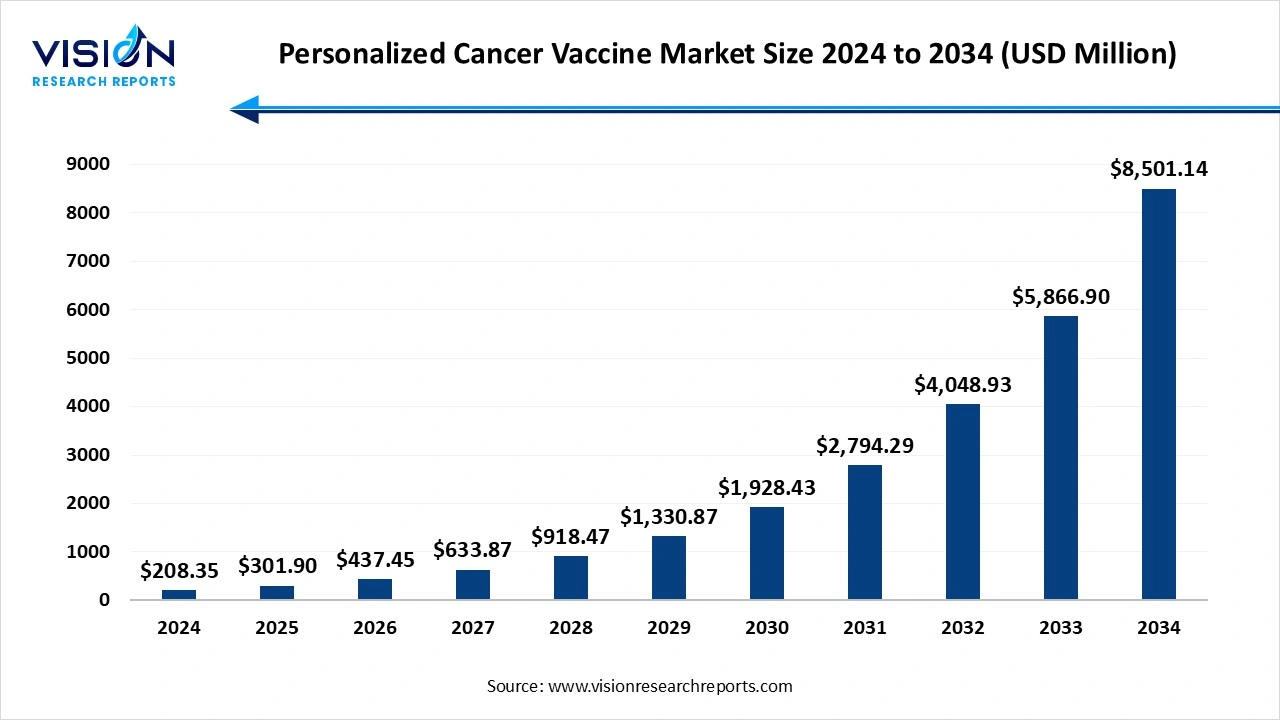
The personalized cancer vaccine market size stood at USD 208.35 million in 2024 and is estimated to reach USD 301.90 million in 2025. It is projected to hit USD 8,501.14 million by 2034, registering a robust CAGR of 44.9% from 2025 to 2034. The advancement in genomics and neoantigen identification, AI and bioinformatics for vaccine design, and innovations in vaccine delivery, such as using lipid nanoparticles and viral vectors, are enhancing the stability and effectiveness of personalized vaccines by ensuring they are delivered optimally to a patient's cells.
A personalized cancer vaccine is a type of immunotherapy that is custom-made for an individual patient to target the specific and unique mutations in their tumor. By focusing on these specific "neoantigens," the vaccine trains the patient's immune system to recognize and target their own cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. The global personalized vaccine market growth is driven by the advancement in genomics and neoantigen identification. Artificial intelligence and machine learning (ML) are being used to predict the most effective neoantigens and to design and optimize vaccine formulations. This streamlines the development process, making it faster and more accurate. The progress in mRNA technology drives the market growth.
NGS technology has significantly reduced the cost and time required to sequence a patient's tumor genome. This allows researchers to quickly identify unique tumor-specific mutations, known as neoantigens, that can be targeted by a personalized vaccine.
New and improved platforms, such as messenger RNA (mRNA), viral vectors, and dendritic cells, have renewed interest in therapeutic cancer vaccines. AI-driven algorithms analyze massive amounts of genomic data to predict the most effective neoantigens, streamlining development and reducing manufacturing costs over time.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 208.35 million |
| Revenue Forecast by 2034 | USD 8,501.14 million |
| Growth rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 44.9% |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Regions | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Companies Covered | Moderna, Inc., BioNTech SE, Gritstone Bio, Inc., GENCI (Genentech, a member of the Roche Group), Vaccibody AS (now Nykode Therapeutics), EpiVax, Inc., Immunovaccine Inc. (IMV Inc.), Ultimovacs ASA, CEL-SCI Corporation, and Advaxis, Inc. |
One of the key drivers propelling the personalized cancer vaccines market is the increasing prevalence of cancer on a global scale. These rising cases necessitate the development of targeted therapies. This stark reality pushes pharmaceutical companies and research institutions to invest heavily in the research and development of personalized vaccines that can offer more effective treatment options for patients. Furthermore, technological advancements in genomics and proteomics have enabled for more precise identification of tumor-specific antigens, thus enhancing the efficacy and potential of these vaccines.
Another key driver is the growing awareness and acceptance of immunotherapy as a viable treatment option. Patients and healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the benefits of utilizing the body’s immune system to combat cancer, which aligns with the whole idea of personalized cancer vaccines.
Despite its promising growth prospects, the personalized cancer vaccines market faces several challenges. One such challenge is the high costs that are associated with the development and manufacturing of these vaccines. The process of creating a personalized vaccine can be quite detailed and intricate, which leads to high expenses, making it difficult for widespread adoption, especially in emerging markets or under developed regions. Additionally, regulatory hurdles pose another barrier. The complex approval processes for new therapies often requires extensive clinical trials and substantial data. This can delay market entry and slow down growth.
The personalized cancer vaccines market has significant opportunities, particularly as research and development efforts intensify. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into the drug development process is one such opportunity. These technologies are able to streamline the identification of suitable targets for vaccines and also enhance patient stratification. As a result, companies that actively adopt these tools could potentially gain a competitive edge in today’s competitive market.
Collaborations between biotechnology firms and research institutions present additional opportunities for growth and development. Partnerships can facilitate knowledge sharing, resource pooling and accelerated development timelines. Governments and health organizations are also increasingly prioritizing initiatives that are aimed at tailoring treatments to individual patients, this creates a fertile environment for personalized cancer vaccines to flourish.
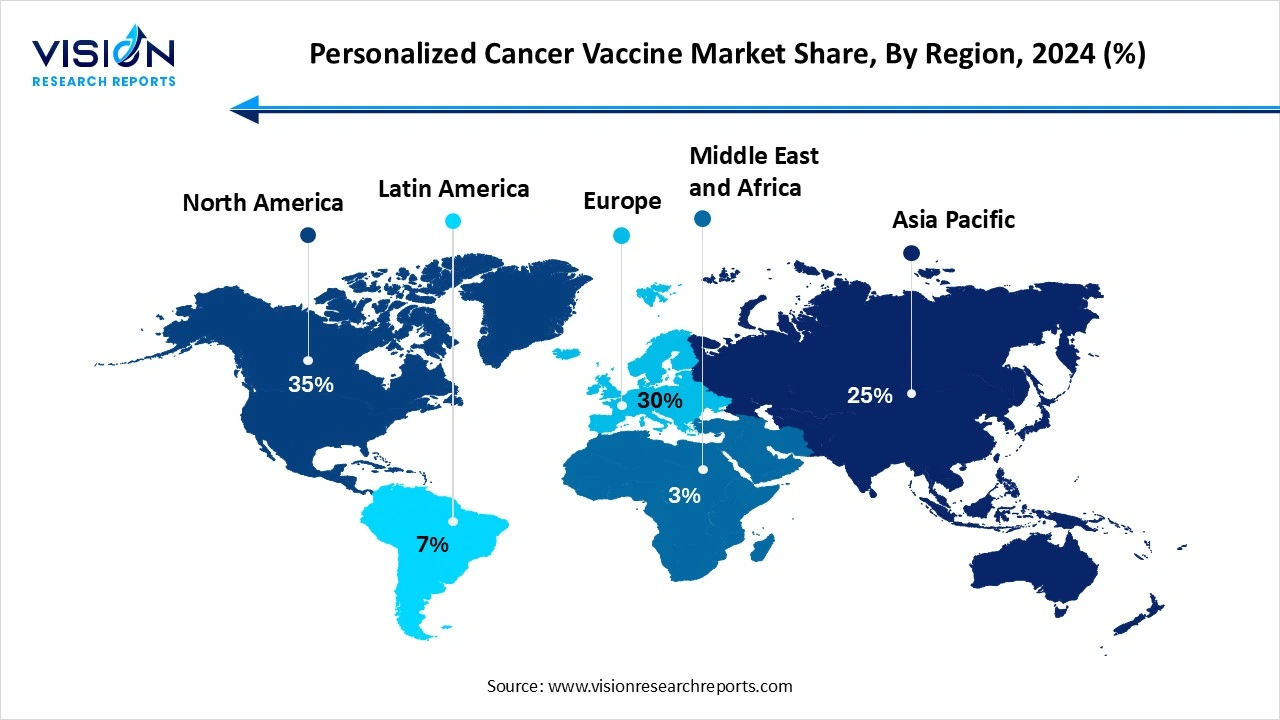
North America led the global personalized cancer vaccine market in 2024, capturing 35% of the market share. The North America region has a high prevalence of cancer cases and a strong demand for novel treatments like personalized cancer vaccines. Significant investment in research and development, advancement in personalized cancer vaccines, and new product launches. North America has a well-developed healthcare infrastructure, effective implementation, and adoption of new vaccine technologies. Their major role in cancer research worldwide fuels the market growth.
United States Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market Trends
The rising cases in the U.S. region drive the demand for more effective and targeted treatments. Advancements in immunotherapy and the successful applications of mRNA technology have led to significant investment in research and development in the region. The rising demand for personalized medicine, targeted therapies, and the growing availability of companion diagnostics drive the market growth.
Asia Pacific expects significant growth in the personalized cancer vaccine market during the forecast period. A large and aging population is facing a high cancer burden. This is combined with rising healthcare spending and rapid technological adoption in precision medicine across the region. Additionally, increased government initiatives and robust investments in R&D are driving development and market access for these advanced therapies.
Country Level Analysis
The U.S. personalized cancer vaccine industry growth has a robust ecosystem, driven by advancements in immunotherapy, increasing cancer prevalence and substantial investments in research and development. Additionally, institutions like the Center for Personal Cancer Vaccines (CPCV) in the country are pioneering patient-specific therapies, thus cementing their leadership in personalized oncology. The presence of major pharmaceutical companies, a supportive regulatory environment and increasing awareness of personalized medicine among healthcare professionals and patients contribute to the market's growth.
Why did the Dendritic Cell Segment Dominate the Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market?
The dendritic cell segment dominated the market in 2024. The rising demand for targeted and individualized immunotherapies, dendritic cell (DC)-based vaccines are engineered by isolating a patient’s own DCs, loading them with tumor-specific antigens, and reintroducing them to stimulate a precise immune attack on cancer cells. Leveraging DCs as powerful antigen-presenting cells to initiate T-cell activation has shown promising results in treating specific malignancies, including melanoma and prostate cancer. Advancing biotechnologies, increased clinical trials, and positive outcomes in patient survival and reduced relapse rates bolster the market for this highly personalized approach. Although promising, scalability and effectiveness challenges remain, highlighting the need for continued research into optimization and combination therapies.
The RNA-based (mRNA) segment is the fastest-growing in the personalized cancer vaccine market during the forecast period. They offer advantages in terms of speed and adaptability. Unlike traditional vaccines that require lengthy processes, mRNA sequences can be synthesized quickly once a cancer antigen is identified. This flexibility allows for rapid customization to individual patient tumor profiles. The success of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic further demonstrated the speed and scalability of this technology. The rising investment and funding, innovation in technology, and targeting neoantigens drive the market growth.
How the Cell-Based Segment hold the Largest Share in the Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market?
The cell-based segment held the largest revenue share in the personalized cancer vaccine market in 2024. The proven clinical success of dendritic cell therapies like Sipuleucel-T. This is supported by its significant history in antigen presentation and strong immune system activation. However, newer mRNA technologies are gaining ground rapidly due to faster and more flexible manufacturing. While cell-based vaccines face high production costs, the market is poised for future growth through innovations that will make personalized treatments more accessible.
The mRNA-based segment is experiencing the fastest growth in the market during the forecast period. The highly personalized, rapid, and flexible vaccine production targets a patient's specific tumor mutations. This technology has shown strong potential in clinical trials, notably improving recurrence-free survival in high-risk melanoma when combined with immunotherapy. The modular nature of mRNA, coupled with advances in delivery systems like LNPs and AI-driven neoantigen selection, facilitates a swift and tailored immune response. Finally, significant investment and regulatory support are accelerating research, pushing mRNA cancer vaccines toward broader clinical application.
How the Hospital Segment hold the Largest Share in the Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market?
The hospital segment held the largest revenue share in the personalized cancer vaccine market in 2024. Their central role in advanced cancer care. They possess the specialized infrastructure and expertise needed for complex vaccine handling and administration. Hospitals also serve as crucial hubs for clinical trials, driving the development and adoption of these novel therapies. Their ability to provide integrated care, from diagnosis to treatment, makes them the preferred setting for patients seeking personalized cancer solutions.
The clinics segment is experiencing the fastest growth in the market during the forecast period. The increasing shift towards outpatient care for managing cancer treatments like PCVs. Clinics offer greater convenience and are becoming more accessible as vaccine manufacturing becomes faster and more affordable, partly due to advances in genomics and mRNA technology. Increased patient and oncologist awareness of PCVs also supports the expansion of clinics in this market.
By Type
By Technology
By Distribution Channel
By Regional
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Research Objective
1.2. Scope of the Study
1.3. Definition
Chapter 2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Approach
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assumptions & Limitations
Chapter 3. Executive Summary
3.1. Market Snapshot
Chapter 4. Market Variables and Scope
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Market Classification and Scope
4.3. Industry Value Chain Analysis
4.3.1. Raw Material Procurement Analysis
4.3.2. Sales and Distribution Type Analysis
4.3.3. Downstream Buyer Analysis
Chapter 5. COVID 19 Impact on Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market
5.1. COVID-19 Landscape: Personalized Cancer Vaccine Industry Impact
5.2. COVID 19 - Impact Assessment for the Industry
5.3. COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
5.4. Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
Chapter 6. Market Dynamics Analysis and Trends
6.1. Market Dynamics
6.1.1. Market Drivers
6.1.2. Market Restraints
6.1.3. Market Opportunities
6.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.2.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
6.2.2. Bargaining power of buyers
6.2.3. Threat of substitute
6.2.4. Threat of new entrants
6.2.5. Degree of competition
Chapter 7. Competitive Landscape
7.1.1. Company Market Share/Positioning Analysis
7.1.2. Key Strategies Adopted by Players
7.1.3. Vendor Landscape
7.1.3.1. List of Suppliers
7.1.3.2. List of Buyers
Chapter 8. Global Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market, By Type
8.1. Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market, by Type
8.1.1 Dendritic Cell
8.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.2. RNA-Based (mRNA)
8.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.3. Neoantigen-Based
8.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
8.1.4. Tumor-Associated Antigen (TAA) Vaccines
8.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 9. Global Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market, By Technology
9.1. Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market, by Technology
9.1.1. Cell-based
9.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.2. mRNA PCV
9.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
9.1.3. Others
9.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 10. Global Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market, By Distribution Channel
10.1. Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market, by Distribution Channel
10.1.1. Hospitals
10.1.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.2. Clinics
10.1.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
10.1.3. Research & Academic Institutes
10.1.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast
Chapter 11. Global Personalized Cancer Vaccine Market, Regional Estimates and Trend Forecast
11.1. North America
11.1.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.1.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.1.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.1.4. U.S.
11.1.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.1.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.1.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.1.5. Rest of North America
11.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.1.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.1.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.2. Europe
11.2.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.2.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.2.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.2.4. UK
11.2.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.2.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.2.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.2.5. Germany
11.2.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.2.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.2.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.2.6. France
11.2.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.2.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.2.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.2.7. Rest of Europe
11.2.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.2.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.2.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.3. APAC
11.3.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.3.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.3.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.3.4. India
11.3.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.3.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.3.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.3.5. China
11.3.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.3.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.3.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.3.6. Japan
11.3.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.3.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.3.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.3.7. Rest of APAC
11.3.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.3.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.3.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.4. MEA
11.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.4.4. GCC
11.4.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.4.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.4.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.4.5. North Africa
11.4.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.4.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.4.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.4.6. South Africa
11.4.6.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.4.6.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.4.6.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.4.7. Rest of MEA
11.4.7.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.4.7.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.4.7.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.5. Latin America
11.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.5.4. Brazil
11.5.4.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.5.4.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.5.4.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
11.5.5. Rest of LATAM
11.5.5.1. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Type
11.5.5.2. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Technology
11.5.5.3. Market Revenue and Forecast, by Distribution Channel
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1. Moderna, Inc..
12.1.1. Company Overview
12.1.2. Product Offerings
12.1.3. Financial Performance
12.1.4. Recent Initiatives
12.2. BioNTech SE.
12.2.1. Company Overview
12.2.2. Product Offerings
12.2.3. Financial Performance
12.2.4. Recent Initiatives
12.3. Gritstone bio, Inc.
12.3.1. Company Overview
12.3.2. Product Offerings
12.3.3. Financial Performance
12.3.4. Recent Initiatives
12.4. GENCI (Genentech, a member of the Roche Group).
12.4.1. Company Overview
12.4.2. Product Offerings
12.4.3. Financial Performance
12.4.4. Recent Initiatives
12.5. Vaccibody AS (now Nykode Therapeutics).
12.5.1. Company Overview
12.5.2. Product Offerings
12.5.3. Financial Performance
12.5.4. Recent Initiatives
12.6. EpiVax, Inc.
12.6.1. Company Overview
12.6.2. Product Offerings
12.6.3. Financial Performance
12.6.4. Recent Initiatives
12.7. Immunovaccine Inc. (IMV Inc.).
12.7.1. Company Overview
12.7.2. Product Offerings
12.7.3. Financial Performance
12.7.4. Recent Initiatives
12.8. Ultimovacs ASA
12.8.1. Company Overview
12.8.2. Product Offerings
12.8.3. Financial Performance
12.8.4. Recent Initiatives
12.9. CEL-SCI Corporation.
12.9.1. Company Overview
12.9.2. Product Offerings
12.9.3. Financial Performance
12.9.4. Recent Initiatives
12.10. Advaxis, Inc.
12.10.1. Company Overview
12.10.2. Product Offerings
12.10.3. Financial Performance
12.10.4. Recent Initiatives
Chapter 13. Research Methodology
13.1. Primary Research
13.2. Secondary Research
13.3. Assumptions
Chapter 14. Appendix
14.1. About Us
14.2. Glossary of Terms
 Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
Cross-segment Market Size and Analysis for
Mentioned Segments
 Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
Additional Company Profiles (Upto 5 With No Cost)
 Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
Additional Countries (Apart From Mentioned Countries)
 Country/Region-specific Report
Country/Region-specific Report
 Go To Market Strategy
Go To Market Strategy
 Region Specific Market Dynamics
Region Specific Market Dynamics Region Level Market Share
Region Level Market Share Import Export Analysis
Import Export Analysis Production Analysis
Production Analysis Others
Others